
Give ozonolysis of but-2-ene?
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: But-2-ene is an alkene and its structural formula is-
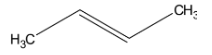
Alkenes on ozonolysis gives aldehyde, ketone or mixture of both depending on the substitution pattern on alkene.
Complete step by step solution:
Ozonolysis can be defined as the process of formation of ozonides and its decomposition to give carbonyl compounds. Ozonides are formed by addition of the ozone molecule to double bond at alkene. It is practically obtained by passing a stream of ozone or ozonized oxygen on a solution of alkene which is in an inert solvent such as ether or carbon tetrachloride and adds ozone at double bond to give ozonides. Ozonides are unstable and highly reactive. Further it is either reduced with hydrogen in presence of catalysts such as palladium or on boiling in water with zinc dust to give carbonyl compounds as a product.
Ozonolysis of but-2-ene:
Step 1: Formation of ozonides: Reaction of But-2-ene with ozone to give butene ozonide

Step 2: Formation of carbonyl compound from butene ozonide that obtained in step 1 by two different methods but the product formed is the same.
(1) Reducing with hydrogen in presence of catalyst such as palladium or platinum to give 2 molecules of ethanal
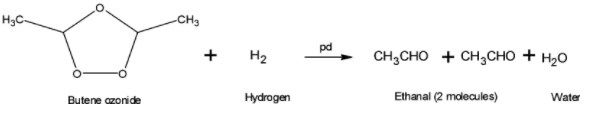
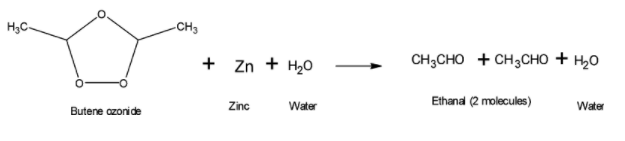
(2) By boiling butene with zinc dust in water to give 2 molecules of ethanal.
Mechanism involved in ozonolysis of but-2-ene
Step 1: Electrophilic addition of an ozone to carbon-carbon double bond in but-2-ene gives molozonide reverts to its corresponding carbonyl oxide.
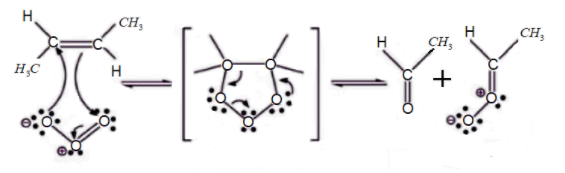
Step 2: The carbonyl molecules and the carbonyl oxide molecule formed in Step 1 and aldehyde formed in step 2 rearranges and forms a stable intermediate known as ozonide intermediate.
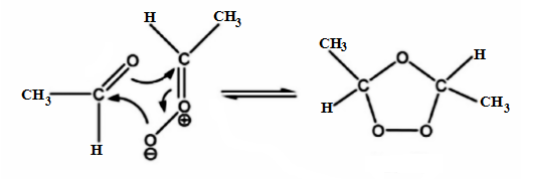
Step 3: Once ozonides are formed certain reagents are added in order to get desired carbonyl compounds. There are two types of techniques for conversion of ozonides to carbonyl compounds, they are reductive workup and oxidative workup.
Reductive workup are used to yield either alcohols or carbonyl compounds whereas oxidative workup are used to yield either carboxylic acid or ketone. Reductive workup is widely used over oxidative workup. Zinc dust in water is a condition of reductive workup as it is a mild reducing agent.
Thus this step follows reductive workup:

On ozonolysis of But-2-ene two molecules of ethanol that is the carbonyl compound obtained is ethanal.
Note: If the alkene taken is symmetrical the carbonyl compounds obtained will be purely aldehyde. If the alkene taken is unsymmetrical the carbonyl compounds obtained will be a mixture of ketone and aldehyde.

Alkenes on ozonolysis gives aldehyde, ketone or mixture of both depending on the substitution pattern on alkene.
Complete step by step solution:
Ozonolysis can be defined as the process of formation of ozonides and its decomposition to give carbonyl compounds. Ozonides are formed by addition of the ozone molecule to double bond at alkene. It is practically obtained by passing a stream of ozone or ozonized oxygen on a solution of alkene which is in an inert solvent such as ether or carbon tetrachloride and adds ozone at double bond to give ozonides. Ozonides are unstable and highly reactive. Further it is either reduced with hydrogen in presence of catalysts such as palladium or on boiling in water with zinc dust to give carbonyl compounds as a product.
Ozonolysis of but-2-ene:
Step 1: Formation of ozonides: Reaction of But-2-ene with ozone to give butene ozonide

Step 2: Formation of carbonyl compound from butene ozonide that obtained in step 1 by two different methods but the product formed is the same.
(1) Reducing with hydrogen in presence of catalyst such as palladium or platinum to give 2 molecules of ethanal

(2) By boiling butene with zinc dust in water to give 2 molecules of ethanal.

Mechanism involved in ozonolysis of but-2-ene
Step 1: Electrophilic addition of an ozone to carbon-carbon double bond in but-2-ene gives molozonide reverts to its corresponding carbonyl oxide.

Step 2: The carbonyl molecules and the carbonyl oxide molecule formed in Step 1 and aldehyde formed in step 2 rearranges and forms a stable intermediate known as ozonide intermediate.

Step 3: Once ozonides are formed certain reagents are added in order to get desired carbonyl compounds. There are two types of techniques for conversion of ozonides to carbonyl compounds, they are reductive workup and oxidative workup.
Reductive workup are used to yield either alcohols or carbonyl compounds whereas oxidative workup are used to yield either carboxylic acid or ketone. Reductive workup is widely used over oxidative workup. Zinc dust in water is a condition of reductive workup as it is a mild reducing agent.
Thus this step follows reductive workup:

On ozonolysis of But-2-ene two molecules of ethanol that is the carbonyl compound obtained is ethanal.
Note: If the alkene taken is symmetrical the carbonyl compounds obtained will be purely aldehyde. If the alkene taken is unsymmetrical the carbonyl compounds obtained will be a mixture of ketone and aldehyde.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




