
Give structure of diethyl ether.
Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint: As the name suggest, diethyl means two ethyl groups bonded to form an ether, \[R - O - R\] Using the general formula of ether, two ethyl groups as R groups will result in the formation of diethyl ether, which is a common name given to the ether.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Diethyl Ether, \[{({C_2}{H_5})_2}O\] is a volatile, flammable, colourless liquid with a distinctive odour. It belongs to the large functional group of organic compounds called ethers. It is also known as ethyl ether and its IUPAC name is Ethoxyethane. Ether is synthesized by the dehydration (removal of water molecule) of ethanol using sulphuric acid.
\[2C{H_3}C{H_2}OH + 2{H_2}S{O_4} \to {(C{H_3}C{H_2})_2}O + {H_2}S{O_4} + {H_2}O\]
Its molecular structure consists of two ethyl groups bonded to an oxygen central atom either side following the general formula trend, \[R - O - R\] .
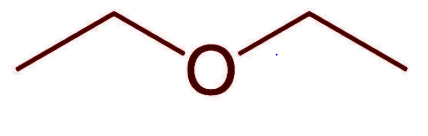
Additional information: Ether undergoes combustion reaction, reacts with oxygen and forms carbon dioxide and water. It is highly flammable and reacts with halogens like chlorine or bromine to form halogen substituted ether that undergoes substitution reaction in the absence of sunlight.
It is used as a solvent in laboratories and an excellent solvent for dyes, alkaloids, oils, fats, etc. as it can readily dissolve polar as well as non-polar organic compounds. It is also used as an anaesthetic due to its high therapeutic index.
Note: From the structure, we get that ethers do not have a hydrogen bonding network that needs to be broken up to dissolve the solute. It is a nonpolar molecule similar in structure to alcohols, and both ethers and alcohols are similar in structure to water.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Diethyl Ether, \[{({C_2}{H_5})_2}O\] is a volatile, flammable, colourless liquid with a distinctive odour. It belongs to the large functional group of organic compounds called ethers. It is also known as ethyl ether and its IUPAC name is Ethoxyethane. Ether is synthesized by the dehydration (removal of water molecule) of ethanol using sulphuric acid.
\[2C{H_3}C{H_2}OH + 2{H_2}S{O_4} \to {(C{H_3}C{H_2})_2}O + {H_2}S{O_4} + {H_2}O\]
Its molecular structure consists of two ethyl groups bonded to an oxygen central atom either side following the general formula trend, \[R - O - R\] .

Additional information: Ether undergoes combustion reaction, reacts with oxygen and forms carbon dioxide and water. It is highly flammable and reacts with halogens like chlorine or bromine to form halogen substituted ether that undergoes substitution reaction in the absence of sunlight.
It is used as a solvent in laboratories and an excellent solvent for dyes, alkaloids, oils, fats, etc. as it can readily dissolve polar as well as non-polar organic compounds. It is also used as an anaesthetic due to its high therapeutic index.
Note: From the structure, we get that ethers do not have a hydrogen bonding network that needs to be broken up to dissolve the solute. It is a nonpolar molecule similar in structure to alcohols, and both ethers and alcohols are similar in structure to water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




