
Give the location of the centre of mass of a (i) sphere, (ii) cylinder, (iii) ring, and (iv) cube, each of uniform mass density. Does the centre of mass of a body necessarily lie inside the body ?
Answer
522.6k+ views
Hint: For each and every uniform figure, which has uniform mass density, the center of mass will lie on the point where the symmetrical axis intersects with another symmetrical axis.
Complete step-by-step answer:
For sphere,
We know that center of mass lies on the symmetrical axis,
A sphere is a uniform figure hence center of mass will lie where the symmetrical axis intersects with another symmetrical axis.
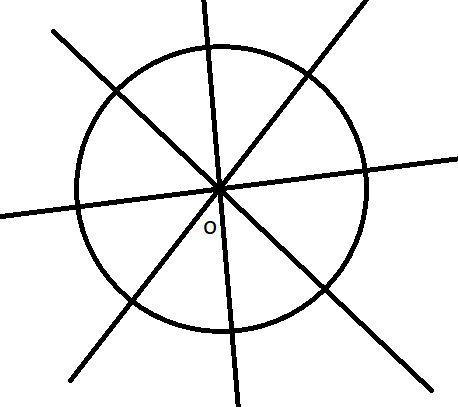
Here the lines drawn are the symmetrical lines, or random diameter for the sphere
O is the point where the center of mass lies.
For Cylinder,
We know that center of mass lies on the symmetrical axis,
A cylinder is a uniform figure hence center of mass will lie where the symmetrical axis intersects with another symmetrical axis.
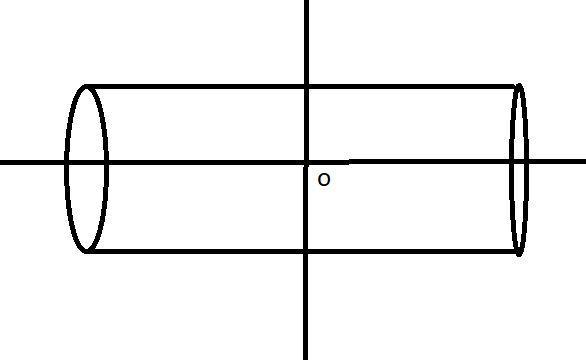
Here the lines drawn are the symmetrical lines, O is the point where the center of mass lies.
For the ring,
We know that center of mass lies on the symmetrical axis,
A ring is a uniform figure hence center of mass will lie where the symmetrical axis intersects with another symmetrical axis.
Symmetrical axes are lies drawn on an object through which when we cut the object we get two parts of the object exactly symmetrical.

Hence in the above figure we see that the center of mass lies outside the body of the ring.
O is the point where the center of mass lies.
For a cube, we can say from the above observations that the center of mass will lie on the geometrical center of the body.
The center of mass for the body is not necessary that it will be on the body just in case of the ring the center of mass is outside the body in the middle of the ring where it is hollow.
Note: Symmetrical axis are lines drawn on an object through which when we cut the object we get two parts of the object exactly symmetrical to each other. It is not necessary that the center of mass of the body will lie on the body; it can lie outside the body also.
Complete step-by-step answer:
For sphere,
We know that center of mass lies on the symmetrical axis,
A sphere is a uniform figure hence center of mass will lie where the symmetrical axis intersects with another symmetrical axis.

Here the lines drawn are the symmetrical lines, or random diameter for the sphere
O is the point where the center of mass lies.
For Cylinder,
We know that center of mass lies on the symmetrical axis,
A cylinder is a uniform figure hence center of mass will lie where the symmetrical axis intersects with another symmetrical axis.

Here the lines drawn are the symmetrical lines, O is the point where the center of mass lies.
For the ring,
We know that center of mass lies on the symmetrical axis,
A ring is a uniform figure hence center of mass will lie where the symmetrical axis intersects with another symmetrical axis.
Symmetrical axes are lies drawn on an object through which when we cut the object we get two parts of the object exactly symmetrical.

Hence in the above figure we see that the center of mass lies outside the body of the ring.
O is the point where the center of mass lies.
For a cube, we can say from the above observations that the center of mass will lie on the geometrical center of the body.
The center of mass for the body is not necessary that it will be on the body just in case of the ring the center of mass is outside the body in the middle of the ring where it is hollow.
Note: Symmetrical axis are lines drawn on an object through which when we cut the object we get two parts of the object exactly symmetrical to each other. It is not necessary that the center of mass of the body will lie on the body; it can lie outside the body also.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




