
Give the role of Plasmids in bacterial cells.
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: Double-stranded DNA molecule which provides bacteria with genetic advantages, such as antibiotic resistance. A small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule found within a cell and is physically separated from that of Chromosomal DNA.
Complete answer:
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; however, plasmids are sometimes found in archaea and eukaryotic organisms.
Additional Information:
In nature, plasmids often carry genes that benefit the survival of the organism and confer selective advantage like antibiotic resistance. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids could also be introduced into a cell via transformation.
Functions of the plasmid:
Plasmids have many different functions.
-Some plasmids facilitate the process of replication in the bacterial cell.
Artificial plasmids:
Based on the origin or source of plasmids, they have been divided into two major classes namely natural and artificial.
Natural plasmids: They occur naturally in prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Example: ColE1.
Artificial plasmids: they're constructed in -vitro by re-combining selected segments of two or more other plasmids (natural or artificial). Example: pBR322.
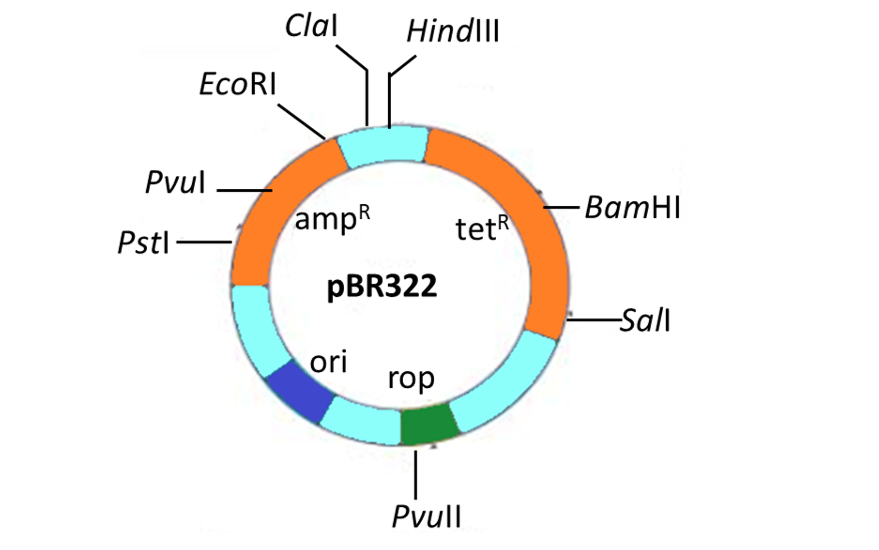
Naturally occurring plasmids have several limitations like for example, some are stringent and not relaxed, some have poor marker genes (ColE1), and some are too large. So to overcome the limitations of natural vectors, the artificial plasmid is designed by combining different elements from diverse sources.
Note: Plasmids carry only a couple of genes and exist independently of chromosomes, the first structures that contain DNA in cells. They can self-replicate, plasmids can be picked up from the environment and transferred between bacteria. Plasmids are used by their host organism to overcome stress-related conditions.
Complete answer:
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; however, plasmids are sometimes found in archaea and eukaryotic organisms.
Additional Information:
In nature, plasmids often carry genes that benefit the survival of the organism and confer selective advantage like antibiotic resistance. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids could also be introduced into a cell via transformation.
Functions of the plasmid:
Plasmids have many different functions.
-Some plasmids facilitate the process of replication in the bacterial cell.
Artificial plasmids:
Based on the origin or source of plasmids, they have been divided into two major classes namely natural and artificial.
Natural plasmids: They occur naturally in prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Example: ColE1.
Artificial plasmids: they're constructed in -vitro by re-combining selected segments of two or more other plasmids (natural or artificial). Example: pBR322.

Naturally occurring plasmids have several limitations like for example, some are stringent and not relaxed, some have poor marker genes (ColE1), and some are too large. So to overcome the limitations of natural vectors, the artificial plasmid is designed by combining different elements from diverse sources.
Note: Plasmids carry only a couple of genes and exist independently of chromosomes, the first structures that contain DNA in cells. They can self-replicate, plasmids can be picked up from the environment and transferred between bacteria. Plasmids are used by their host organism to overcome stress-related conditions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




