
Give the structural formula for 2 -methyl propane.
Answer
517.5k+ views
Hint: A chemical compound's structural formula is a graphic depiction of the molecular structure (determined by structural chemistry methods) that shows how the atoms could be organised in actual three-dimensional space. The molecule's chemical bonding is often depicted, either directly or indirectly.
Complete answer:
Unlike chemical formulas, which have a limited number of symbols and can only describe a limited number of molecular structures, structural formulas have a more complete geometric description of the molecular structure. Many chemical compounds, for example, occur in various isomeric configurations, each with a different enantiomeric structure but the same chemical formula.
Lewis structures (also known as "Lewis dot structures") are two-dimensional graphical formulas that depict atom connectivity and lone pair or unpaired electrons. This is the most popular notation for small molecules. Each line reflects a single bond's two electrons. Double and triple bonds are represented by two or three parallel lines between pairs of atoms, respectively. Pairs of dots may also be used to reflect bonding pairs. Both non-bonded electrons (paired or unpaired) as well as any formal charges on atoms are also seen.
2 methylpropane
Molecular formula =
Longest chain – Propane
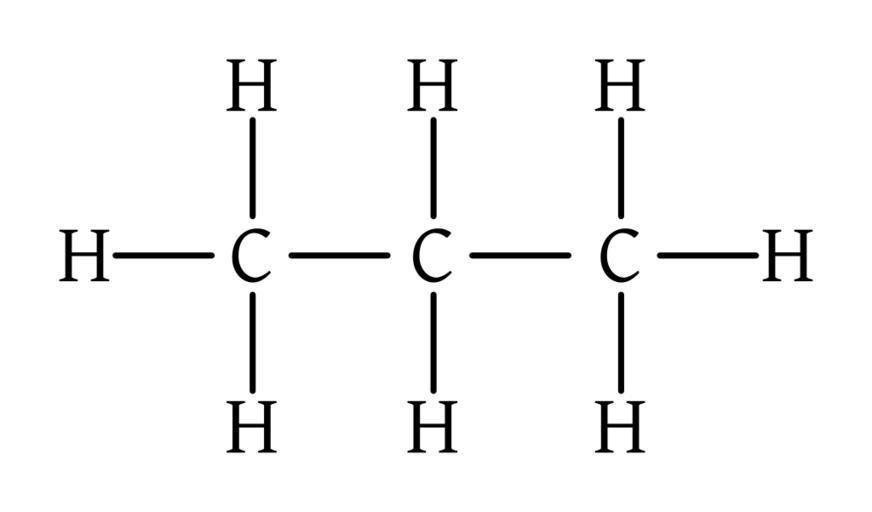
methyl is assigned in the second position
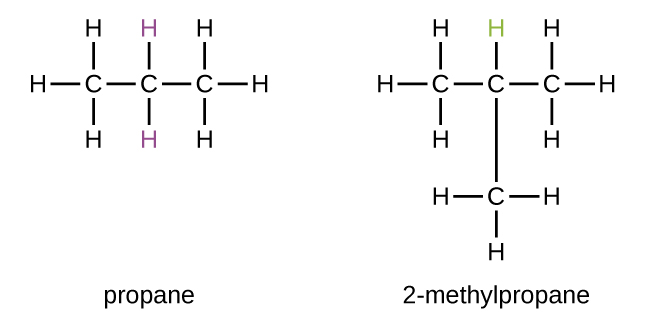
Isobutane is a chemical compound with the molecular formula HC(CH₃)₃. It is also known as i-butane, 2-methylpropane, or methylpropane. It's a kind of butane isomer. Isobutane is a gas that is colourless and odourless. That is the most basic tertiary carbon alkane. In the petrochemical industry, isobutane is used as a precursor molecule, for example, in the synthesis of isooctane.
Note:
Isobutane is the primary feedstock for refinery alkylation units. Gasoline-grade "blendstocks" with high branching for good combustion properties are created using isobutane. 2,4-dimethylpentane and, in particular, 2,2,4-trimethylpentane are typical isobutane drugs.
Complete answer:
Unlike chemical formulas, which have a limited number of symbols and can only describe a limited number of molecular structures, structural formulas have a more complete geometric description of the molecular structure. Many chemical compounds, for example, occur in various isomeric configurations, each with a different enantiomeric structure but the same chemical formula.
Lewis structures (also known as "Lewis dot structures") are two-dimensional graphical formulas that depict atom connectivity and lone pair or unpaired electrons. This is the most popular notation for small molecules. Each line reflects a single bond's two electrons. Double and triple bonds are represented by two or three parallel lines between pairs of atoms, respectively. Pairs of dots may also be used to reflect bonding pairs. Both non-bonded electrons (paired or unpaired) as well as any formal charges on atoms are also seen.
2 methylpropane
Molecular formula =
Longest chain – Propane

methyl is assigned in the second position

Isobutane is a chemical compound with the molecular formula HC(CH₃)₃. It is also known as i-butane, 2-methylpropane, or methylpropane. It's a kind of butane isomer. Isobutane is a gas that is colourless and odourless. That is the most basic tertiary carbon alkane. In the petrochemical industry, isobutane is used as a precursor molecule, for example, in the synthesis of isooctane.
Note:
Isobutane is the primary feedstock for refinery alkylation units. Gasoline-grade "blendstocks" with high branching for good combustion properties are created using isobutane. 2,4-dimethylpentane and, in particular, 2,2,4-trimethylpentane are typical isobutane drugs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




