
Give two examples of chromosomal disorder showing trisomy.
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: A condition where an individual has three copies of X-chromosomes instead of two copies leading to a severe genetic disorder that results in the development of the new abnormal characters in an individual. One of the disorders was discovered by Langdon and the other by John Hilton.
Complete answer:
Trisomy is a genetic disorder as the chromosomal composition of the parents may have an extra X-chromosome. This may occur due to the nondisjunction of the chromosomes at the time of cell division. The trisomic cell is represented as 2n+1 (if one trisomy is present), and 2n+1+1 (if two trisomies are present).
The two Chromosomal disorder showing trisomy
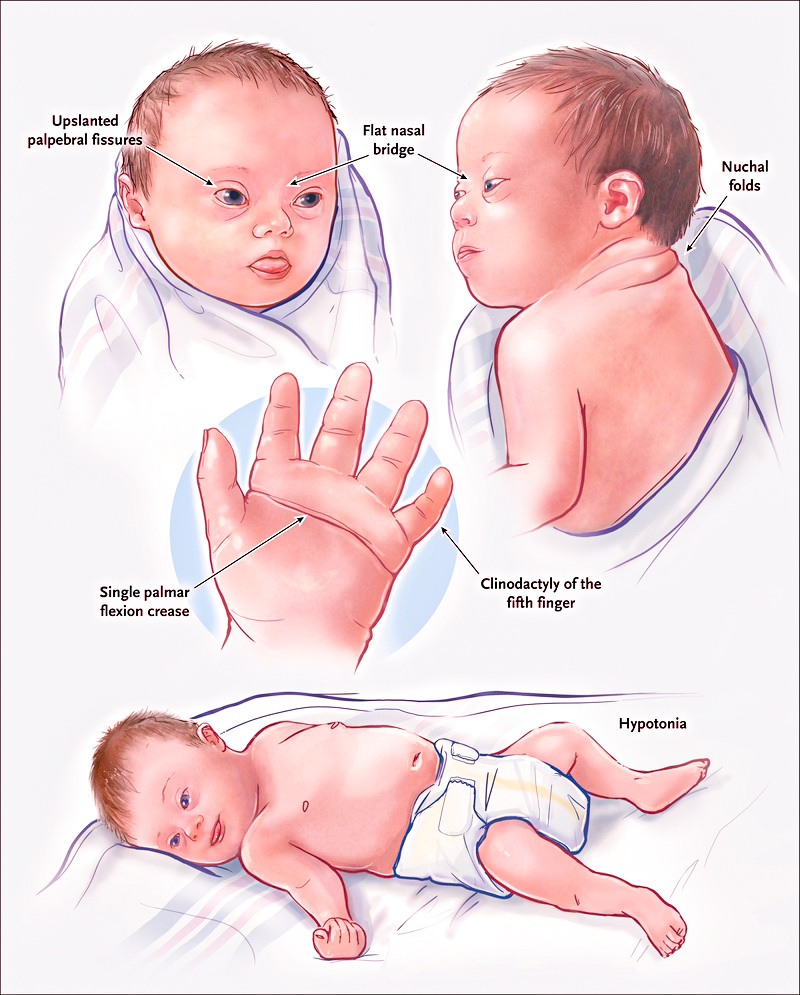
Down’s Syndrome
-It is a genetic disorder where the trisomy is present on chromosome 21. The extra copy of the complete chromosome or the part of the chromosome is present which is responsible for the physical growth of the body. This disorder may result in mental disability and various characteristic facial features.
-The person has a very low IQ level around 50, which is that of the 8 or 9 years old child. The parents of the individual are normal, the nondisjunction of a chromosome has occurred by chance.
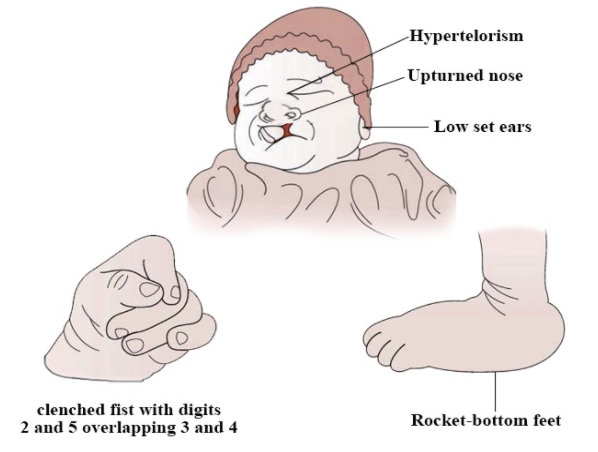
Edward’s Syndrome
-It is a genetic disorder where the trisomy is present on chromosome 18. The extra copy of the complete chromosome 18 or the part of the chromosome that is present affects various organs of the boys most importantly the heart. The child may have a mental disability, small head, and jaws with overlapping fingers and clenched fists. It is not generally inherited from the parents instead it occurs at the time of the formation of the reproductive cells.
-The rate of the disorder is 1 in around 5000 children. It was first discovered in 1960 by an English geneticist John Hilton Edwards.
-If the trisomy is present in autosomes, it is called autosomal trisomies and if it is present on the sex chromosome it is known as sex chromosomal trisomies.
Note: Trisomy is differentiated into four types: Full trisomy (it is also called as primary trisomy, where an extra chromosome is present), Partial trisomy (only a part of a chromosome is copied extra), Secondary trisomy (duplicated arms are present on the chromosomes), and tertiary trisomy (copies of arms are present).
Complete answer:
Trisomy is a genetic disorder as the chromosomal composition of the parents may have an extra X-chromosome. This may occur due to the nondisjunction of the chromosomes at the time of cell division. The trisomic cell is represented as 2n+1 (if one trisomy is present), and 2n+1+1 (if two trisomies are present).
The two Chromosomal disorder showing trisomy
Down’s Syndrome
-It is a genetic disorder where the trisomy is present on chromosome 21. The extra copy of the complete chromosome or the part of the chromosome is present which is responsible for the physical growth of the body. This disorder may result in mental disability and various characteristic facial features.
-The person has a very low IQ level around 50, which is that of the 8 or 9 years old child. The parents of the individual are normal, the nondisjunction of a chromosome has occurred by chance.
Edward’s Syndrome
-It is a genetic disorder where the trisomy is present on chromosome 18. The extra copy of the complete chromosome 18 or the part of the chromosome that is present affects various organs of the boys most importantly the heart. The child may have a mental disability, small head, and jaws with overlapping fingers and clenched fists. It is not generally inherited from the parents instead it occurs at the time of the formation of the reproductive cells.
-The rate of the disorder is 1 in around 5000 children. It was first discovered in 1960 by an English geneticist John Hilton Edwards.
-If the trisomy is present in autosomes, it is called autosomal trisomies and if it is present on the sex chromosome it is known as sex chromosomal trisomies.


Note: Trisomy is differentiated into four types: Full trisomy (it is also called as primary trisomy, where an extra chromosome is present), Partial trisomy (only a part of a chromosome is copied extra), Secondary trisomy (duplicated arms are present on the chromosomes), and tertiary trisomy (copies of arms are present).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




