
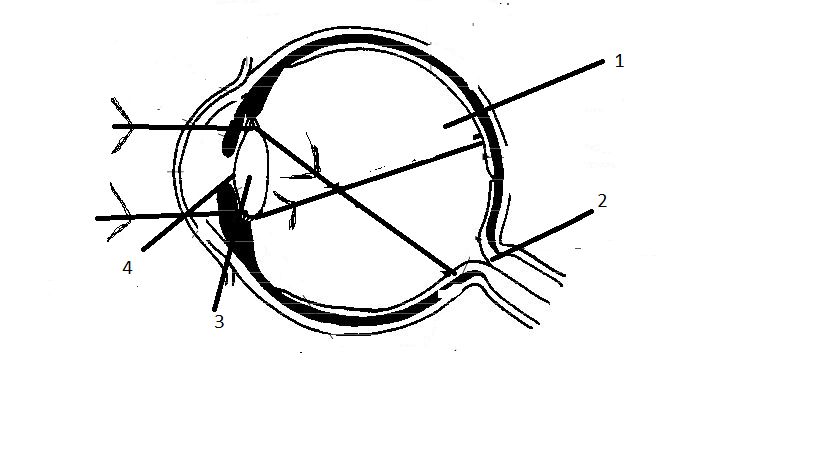
Given is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye. Study the same and answer the questions that follows:
A) Name the defect shown in the diagram
B) Give two reasons for this defect
C) Name the paws labelled 1 to 4
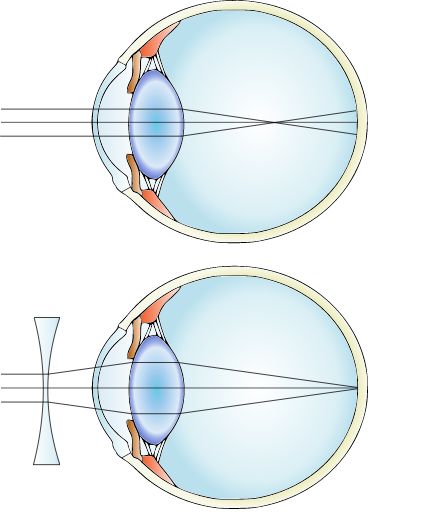
D) Name the type of lens used to correct this eye defect
E) Draw a labelled diagram to show how the above mentioned defect is rectified using the lens named above

Answer
556.8k+ views
Hint: Sensory organs are the specialized organs that are composed of sensory neurons that help to perceive and respond to our surroundings. These organs involve eyes, ears, nose, tongue and skin.
Complete answer:
Eyes are part of the sensory nervous system that reacts to light and allows vision. There are pairs of eyes located in sockets of the skull called orbits. The movement of eyes is assisted by six extra ocular muscles. The main function of human eyes is to read the external stimulus of light and form meaningful information and colour identification, differentiation, depth and distance analysis.
A. The defect shown is Myopia or near-sightedness. Myopia is a common type of refractive error in which the person suffers from a condition where the objects closer to the individual appear clearly but the distant objects appear to be blurry. This defect is commonly seen in children.
B. The two reasons for the Myopia are:
(i) The variation occurs in the distance from the middle to the eye lens and the retina as it becomes big when the eyeball gets extended in its axis.
(ii) If the curvature of the cornea is big, then it may lead to the refraction of light into the eye and results in making the focal length of the eyeball tiny.
C. The parts labelled in the diagram are:
(i) Vitreous humour: is a transparent, uncoloured liquid that engages the space in the middle of the lens and retina of the eyes. It performs a crucial role in protecting the eye, maintaining the shape of the eye and it causes refraction of light inside the eye.
(ii) Blind Spot: is present to the right of the bottom of vision and there is a problem in the ability for vision. They are insensitive to light as there are no rods and cons. The photoreceptors cells are absent in this region.
(iii) Lens: The transparent portion situated behind the pupil is called a lens. It alters the shape to focus light on the retina with the help of ciliary muscles.
Pupils: It is the small opening in the iris. The iris controls the size of the pupil. The function of the pupil is to adjust the amount of light entering the eye.
D. The lens used to correct myopia is a concave lens. It is a curved lens which is curved inwards, and is placed in front of the myopic eye. The concave lens helps in moving the image back to the retina and thus helping the person to get a clearer vision.
E. The above mentioned defect is rectified by the concave lens
Note: Regular complaining of headaches or tired eyes or water coming from the eyes and regularly rubbing eyes are the signs of myopia. For the children to avoid this problem they should not sit close to television sets.
Complete answer:
Eyes are part of the sensory nervous system that reacts to light and allows vision. There are pairs of eyes located in sockets of the skull called orbits. The movement of eyes is assisted by six extra ocular muscles. The main function of human eyes is to read the external stimulus of light and form meaningful information and colour identification, differentiation, depth and distance analysis.
A. The defect shown is Myopia or near-sightedness. Myopia is a common type of refractive error in which the person suffers from a condition where the objects closer to the individual appear clearly but the distant objects appear to be blurry. This defect is commonly seen in children.
B. The two reasons for the Myopia are:
(i) The variation occurs in the distance from the middle to the eye lens and the retina as it becomes big when the eyeball gets extended in its axis.
(ii) If the curvature of the cornea is big, then it may lead to the refraction of light into the eye and results in making the focal length of the eyeball tiny.
C. The parts labelled in the diagram are:
(i) Vitreous humour: is a transparent, uncoloured liquid that engages the space in the middle of the lens and retina of the eyes. It performs a crucial role in protecting the eye, maintaining the shape of the eye and it causes refraction of light inside the eye.
(ii) Blind Spot: is present to the right of the bottom of vision and there is a problem in the ability for vision. They are insensitive to light as there are no rods and cons. The photoreceptors cells are absent in this region.
(iii) Lens: The transparent portion situated behind the pupil is called a lens. It alters the shape to focus light on the retina with the help of ciliary muscles.
Pupils: It is the small opening in the iris. The iris controls the size of the pupil. The function of the pupil is to adjust the amount of light entering the eye.
D. The lens used to correct myopia is a concave lens. It is a curved lens which is curved inwards, and is placed in front of the myopic eye. The concave lens helps in moving the image back to the retina and thus helping the person to get a clearer vision.
E. The above mentioned defect is rectified by the concave lens

Note: Regular complaining of headaches or tired eyes or water coming from the eyes and regularly rubbing eyes are the signs of myopia. For the children to avoid this problem they should not sit close to television sets.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




