
Given is the representation of the life cycle of members of classes Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes. Select the correct option for processes A, B, and C.
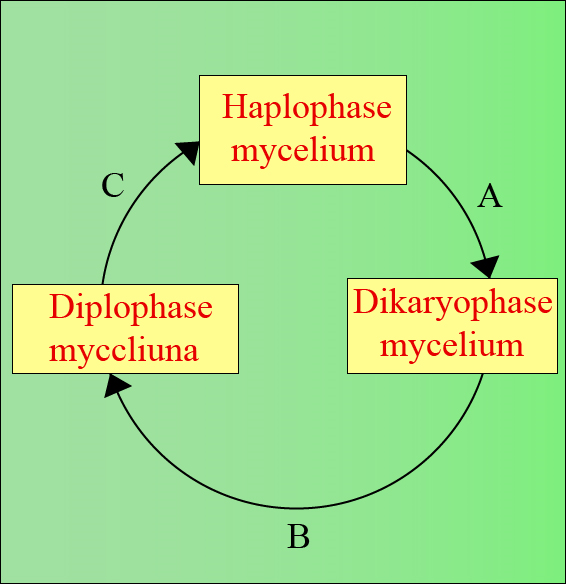
(a)A.Karyogamy B.Plasmogamy C.Meiosis
(b)A.Plasmogamy B.Karyogamy C.Meiosis
(c)A.Plasmogamy B.Meiosis C.Karyogamy
(d)A.Karyogamy B.Meiosis C.Plasmogamy

Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: Sexual reproduction brings genetic variability, which allows the fungus to adapt to new environments. The cell formed by karyogamy is called the zygoteOnce karyogamy has occurred, meiosis generally follows and restores the haploid phase.
Complete answer:
In fungi, the second step in sexual reproduction karyogamy is delayed and occurs just before meiosis. In the stage intervening between plasmogamy and karyogamy, the cells often contain two nuclei or dikaryon. So, the process will occur as ‘Plasmogamy, karyogamy, and meiosis'.
Additional Information: -Rhizopus belongs to the phylum Zygomycota is a filamentous fungus found in soil, decaying fruit and vegetables, animal feces, and old bread. They are common contaminants, also occasional causes of serious infections in humans. The best grows at 45-degree Celsius. The sporangium is spherical in shape and sporangiophore is mostly brown and unbranched. The columella is spherical or elongated. The apophysis is not prominent.
-Mucor also belongs to the phylum Zygomycota is also a filamentous fungus found in soil, plants, decaying fruits, and vegetables. The best growth is below 37degree Celcius. The sporangium is spherical and sporangiophore is branched or unbranched and hyaline. The columella was found in varying shapes.
-Penicillium belongs to the phylum Ascomycota. The mycelium consists of highly branched networks of multinucleated and colorless hyphae, with each pair of cells separated by a septum. Conidiophores are present at the end of each branch accompanied by green spherical conidia. These propagules play a significant role in reproduction as conidia are the main dispersal strategy of these fungi.
So, the correct answer is, ‘ A - Plasmogamy, B - Karyogamy, C - Meiosis.’
Note: -Fungi can reproduce sexually and asexually. It produces by budding, or by fragmentation or it produces spores during asexual reproduction and sexually they produce homothallic or heterothallic mycelia.
-New colonies of fungi are able to grow from the fragmentation of hyphae.
-During budding, a bulge forms on the side of the cell-like that of a hydra; the bud ultimately detaches after the nucleus and it divides mitotically.
-Asexual spores are genetically just like the parent and may release either outside or within a special reproductive sac called a sporangium.
-Adverse environmental conditions are responsible for sexual reproduction in fungi.
-Mycelium can be homothallic or heterothallic when they are reproducing sexually.
-Fungal sexual reproduction includes the subsequent three stages: plasmogamy, karyogamy, and meiosis.
Complete answer:
In fungi, the second step in sexual reproduction karyogamy is delayed and occurs just before meiosis. In the stage intervening between plasmogamy and karyogamy, the cells often contain two nuclei or dikaryon. So, the process will occur as ‘Plasmogamy, karyogamy, and meiosis'.
Additional Information: -Rhizopus belongs to the phylum Zygomycota is a filamentous fungus found in soil, decaying fruit and vegetables, animal feces, and old bread. They are common contaminants, also occasional causes of serious infections in humans. The best grows at 45-degree Celsius. The sporangium is spherical in shape and sporangiophore is mostly brown and unbranched. The columella is spherical or elongated. The apophysis is not prominent.
-Mucor also belongs to the phylum Zygomycota is also a filamentous fungus found in soil, plants, decaying fruits, and vegetables. The best growth is below 37degree Celcius. The sporangium is spherical and sporangiophore is branched or unbranched and hyaline. The columella was found in varying shapes.
-Penicillium belongs to the phylum Ascomycota. The mycelium consists of highly branched networks of multinucleated and colorless hyphae, with each pair of cells separated by a septum. Conidiophores are present at the end of each branch accompanied by green spherical conidia. These propagules play a significant role in reproduction as conidia are the main dispersal strategy of these fungi.
So, the correct answer is, ‘ A - Plasmogamy, B - Karyogamy, C - Meiosis.’
Note: -Fungi can reproduce sexually and asexually. It produces by budding, or by fragmentation or it produces spores during asexual reproduction and sexually they produce homothallic or heterothallic mycelia.
-New colonies of fungi are able to grow from the fragmentation of hyphae.
-During budding, a bulge forms on the side of the cell-like that of a hydra; the bud ultimately detaches after the nucleus and it divides mitotically.
-Asexual spores are genetically just like the parent and may release either outside or within a special reproductive sac called a sporangium.
-Adverse environmental conditions are responsible for sexual reproduction in fungi.
-Mycelium can be homothallic or heterothallic when they are reproducing sexually.
-Fungal sexual reproduction includes the subsequent three stages: plasmogamy, karyogamy, and meiosis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




