
Giving examples of homologous and analogous organs explain what they tell us about the process of evolution.
Answer
603.3k+ views
Hint: Homologous organs have the same origin but perform different functions while analogous organs have different origins but perform the same functions.
Complete answer:
Homologous structures are a result of divergent evolution which explains that the same structures are developed along with different directions due to adaptations to different needs. It indicates that the homologous organs evolved from the common ancestor.
Examples: The example includes the pattern of bones of forelimbs of frogs, lizards, birds, and humans that share similarities in their structures but performs different functions according to their needs in these animals. The forelimbs structure of these organisms indicates that organisms bearing them are evolutionary related.
The analogous structures are not anatomically similar but perform similar functions. These analogous organs result in convergent evolution and hence they are evolving for the same functions.
Examples: Examples of analogy include the structure of wings of a butterfly and of birds that are not looking anatomically similar but they perform similar functions. Another example of analogy includes the eye of the octopus and of mammals that may appear similar features in diverse groups of organisms but their origin is different that performs the same function.
Note:
> Anthropogenic action involves the excessive use of herbicides and pesticides that has resulted in the selection of resistant varieties of pests in very less time not in centuries.
> This evolutionary action also states that evolution is not a direct process in the sense of determinism but a stochastic process based on chance events in nature and chance mutation in the organisms.
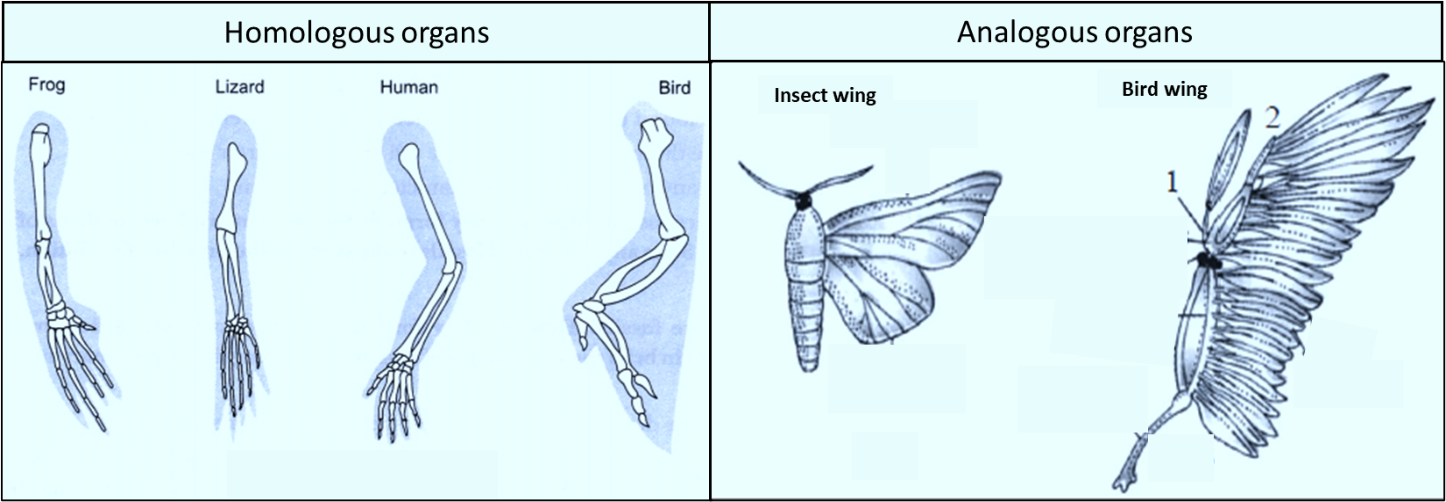
Figure: Difference between the homologous organs and analogous organ
Complete answer:
Homologous structures are a result of divergent evolution which explains that the same structures are developed along with different directions due to adaptations to different needs. It indicates that the homologous organs evolved from the common ancestor.
Examples: The example includes the pattern of bones of forelimbs of frogs, lizards, birds, and humans that share similarities in their structures but performs different functions according to their needs in these animals. The forelimbs structure of these organisms indicates that organisms bearing them are evolutionary related.
The analogous structures are not anatomically similar but perform similar functions. These analogous organs result in convergent evolution and hence they are evolving for the same functions.
Examples: Examples of analogy include the structure of wings of a butterfly and of birds that are not looking anatomically similar but they perform similar functions. Another example of analogy includes the eye of the octopus and of mammals that may appear similar features in diverse groups of organisms but their origin is different that performs the same function.
Note:
> Anthropogenic action involves the excessive use of herbicides and pesticides that has resulted in the selection of resistant varieties of pests in very less time not in centuries.
> This evolutionary action also states that evolution is not a direct process in the sense of determinism but a stochastic process based on chance events in nature and chance mutation in the organisms.

Figure: Difference between the homologous organs and analogous organ
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




