
Glucose on prolonged heating with HI gives:
A) hexanoic acid
B) iodohexanal
C) n-hexane
D) 1-hexene
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: Hydroiodic acid is a reducing agent. It reduces primary alcohol, secondary alcohol and aldehyde group.
Complete step by step answer:
Glucose is a polyhydroxy aldehyde. It is a carbohydrate containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. The structure of glucose is as given below:
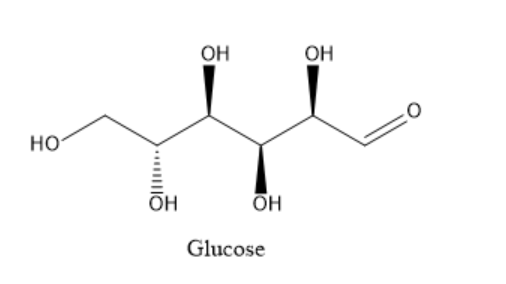
It contains one aldehyde group, one primary alcoholic group and four secondary alcoholic groups. To determine the open chain structure of glucose, several reactions with different reagents can be carried out. The product of each reaction can then be analysed and the structure of product can be correlated with the structure of the reactant. From this, the open chain structure of glucose can then be determined.
HI can reduce the aldehyde group to methyl group. HI can also reduce the primary alcoholic group to methyl group. HI reduces secondary alcohol to methylene group.
The structure of the product of prolonged heating of glucose with HI is given below:
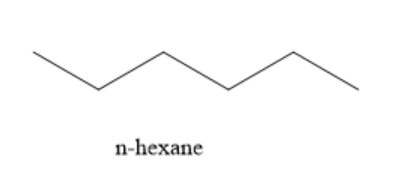
Since glucose on reduction with HI gives a straight chain hydrocarbon containing 6 carbon atoms, this confirms the straight chain structure of glucose containing 6 carbon atoms. During the reaction, carbon-carbon bonds are not broken. Hence, the straight chain structure of glucose remains intact.
The reaction is as shown below:
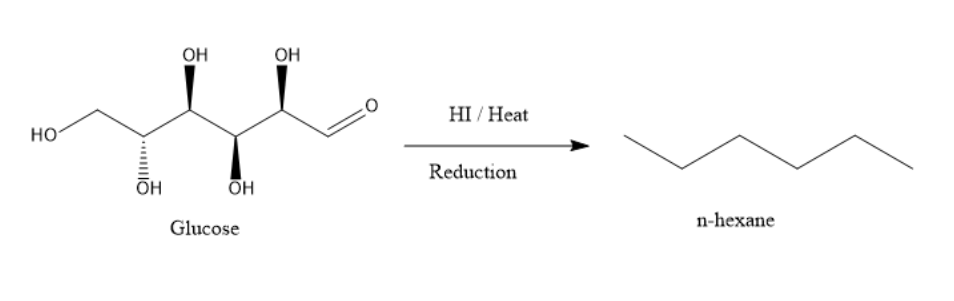
Thus, the option C is the correct option.
Note:
Do not write the oxidation product such as hexanoic acid because HI acts as a reducing agent. Also during the reaction, the aldehyde group will also be reduced.
Complete step by step answer:
Glucose is a polyhydroxy aldehyde. It is a carbohydrate containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. The structure of glucose is as given below:

It contains one aldehyde group, one primary alcoholic group and four secondary alcoholic groups. To determine the open chain structure of glucose, several reactions with different reagents can be carried out. The product of each reaction can then be analysed and the structure of product can be correlated with the structure of the reactant. From this, the open chain structure of glucose can then be determined.
HI can reduce the aldehyde group to methyl group. HI can also reduce the primary alcoholic group to methyl group. HI reduces secondary alcohol to methylene group.
The structure of the product of prolonged heating of glucose with HI is given below:

Since glucose on reduction with HI gives a straight chain hydrocarbon containing 6 carbon atoms, this confirms the straight chain structure of glucose containing 6 carbon atoms. During the reaction, carbon-carbon bonds are not broken. Hence, the straight chain structure of glucose remains intact.
The reaction is as shown below:

Thus, the option C is the correct option.
Note:
Do not write the oxidation product such as hexanoic acid because HI acts as a reducing agent. Also during the reaction, the aldehyde group will also be reduced.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




