
Glycinato ligand is:
A.
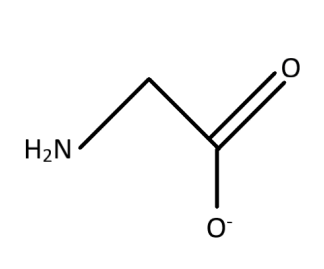
B. Bidentate ligand
C. Two donor sites
D. All of the above

Answer
547.5k+ views
Hint: The ligand which forms a bonded structure or interacts with a metal ion depends on the presence of a lone pair of electrons in the ligand structure. The lone pair fills the vacant orbitals of the metal ion which is responsible for the formation of the complex.
Complete step by step solution:
The structure of the glycinato ligand is considered as the ligand form of glycinate. The structure of glycinate is formed with a central carbon associated with amino $ \left( { - N{H_2}} \right) $ group and there is $ \left( { - CO{O^ - }} \right) $ as the other association of the central carbon. The two other bonds are associated with hydrogen residues. Therefore, the given structure of glycinato as given in the option is true.
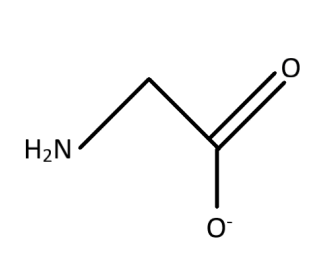
The ligand is bidentate as there are two sites from which the electron pairs can be shared with the metal ions for the association. The oxygen residue in the $ \left( { - CO{O^ - }} \right) $ and the nitrogen residue in $ \left( { - N{H_2}} \right) $ group are the two residues with the free lone pair of electrons which makes the ligand bidentate. The bidentate character means that there are two regions which act as the donor site for the donation of electrons. The electronic character is formed from the interaction between the ligand and the metal ion. This means that among the interaction of the ligands with the metal ions two of the bond formation or interaction takes place with the two donor sites.
Note:
The ligand has the specific property of getting associated with the metal ion based on the nature of the electron sharing. The differences in the type of ligand cause changes in the geometry of the complex that is formed with the metal ion.
Complete step by step solution:
The structure of the glycinato ligand is considered as the ligand form of glycinate. The structure of glycinate is formed with a central carbon associated with amino $ \left( { - N{H_2}} \right) $ group and there is $ \left( { - CO{O^ - }} \right) $ as the other association of the central carbon. The two other bonds are associated with hydrogen residues. Therefore, the given structure of glycinato as given in the option is true.

The ligand is bidentate as there are two sites from which the electron pairs can be shared with the metal ions for the association. The oxygen residue in the $ \left( { - CO{O^ - }} \right) $ and the nitrogen residue in $ \left( { - N{H_2}} \right) $ group are the two residues with the free lone pair of electrons which makes the ligand bidentate. The bidentate character means that there are two regions which act as the donor site for the donation of electrons. The electronic character is formed from the interaction between the ligand and the metal ion. This means that among the interaction of the ligands with the metal ions two of the bond formation or interaction takes place with the two donor sites.
Note:
The ligand has the specific property of getting associated with the metal ion based on the nature of the electron sharing. The differences in the type of ligand cause changes in the geometry of the complex that is formed with the metal ion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




