
Glycogen is stored in?
A. Liver and muscles
B. Liver only
C. Muscles only
D. Pancreas
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: Glycogen is a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria, similar to that of starch in the case of plants. Glycogen is a polysaccharide of glucose present in organs that help in energy metabolism. It is a readily mobilized storage form of glucose that is converted into energy based on body needs.
Complete answer:
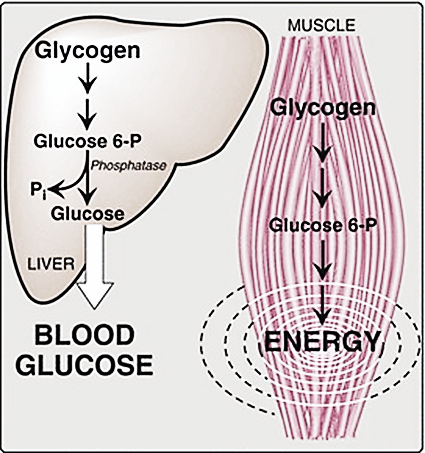
-Glycogen is stored in the cells of the liver and muscles, where it is converted into energy for metabolism and physical activities of the body.
-The liver performs a variety of functions such as synthesis, storage, and secretion of various substances like bile juices that help during digestion. It plays a key role in carbohydrates metabolism (glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, and lipogenesis). Glycogen stored in the liver also maintains the blood glucose concentration during fasting.
-Glycogen is also stored in muscles especially the skeletal muscles and in fat cells. Where it serves as an energy fuel for the synthesis of ATP during muscle contraction.
Figure 1: Glycogen storage and its use
Additional information:
> In muscle, there is only a 1% weight of muscle as glycogen. Whereas, 10% of the liver weight is due to glycogen storage.
> Most of the glycogen from muscles are used up during physical activities, the glycogen storage of the liver is used up for different metabolisms like digestion and brain activity.
Note:
Most of the carbohydrates from the food we eat are converted into glucose (a type of sugar). This glucose is the main source of fuel for the cells throughout the body. When the body does not need the glucose for energy it is stored in the form of glycogen mostly in the liver and some amount in muscles too. During energy requirement, this stored glycogen is broken down into glucose and released into the bloodstream to reach the cells that require the energy.
Complete answer:
-Glycogen is stored in the cells of the liver and muscles, where it is converted into energy for metabolism and physical activities of the body.
-The liver performs a variety of functions such as synthesis, storage, and secretion of various substances like bile juices that help during digestion. It plays a key role in carbohydrates metabolism (glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, and lipogenesis). Glycogen stored in the liver also maintains the blood glucose concentration during fasting.
-Glycogen is also stored in muscles especially the skeletal muscles and in fat cells. Where it serves as an energy fuel for the synthesis of ATP during muscle contraction.
Figure 1: Glycogen storage and its use

Additional information:
> In muscle, there is only a 1% weight of muscle as glycogen. Whereas, 10% of the liver weight is due to glycogen storage.
> Most of the glycogen from muscles are used up during physical activities, the glycogen storage of the liver is used up for different metabolisms like digestion and brain activity.
Note:
Most of the carbohydrates from the food we eat are converted into glucose (a type of sugar). This glucose is the main source of fuel for the cells throughout the body. When the body does not need the glucose for energy it is stored in the form of glycogen mostly in the liver and some amount in muscles too. During energy requirement, this stored glycogen is broken down into glucose and released into the bloodstream to reach the cells that require the energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




