
Grafting is the art of joining parts of plants such that they grow as one plant. What is the name given to the part of the graft which gives rise to the upper position?
(a) Bud
(b) Stock
(c) Scion
(d) Meristem
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: In grafting, the part that is selected to grow leaves, fruits, and flowers are called scion, and the part that is used for roots is called stock.
Complete answer:
Grafting is one of the artificial techniques used to grow plants vegetatively. It also used to produce plants of desired characters. It is a horticultural technique where two parts of the plants are attracted together and allow them to grow. The upper part of the plant used to grow leaves, flowers, fruits is called scion and the lower part which is used as a root portion is called stock or rootstock. Vascular tissue growth is important for the success of growth in the attached parts.
Additional Information: - Cutting, layering, grafting, and tissue culture are artificial techniques to develop new plants.
- In cutting the vegetative part of the plant is cut and it is planted in the moist soil, it develops adventitious roots and develops as a new individual plant. Example: acacia, rose
- Layering is the same as cutting but the vegetative part of the plant is cut after developing adventitious roots. Examples: jasmine
- In grafting, two desired plants are selected and the upper portion of one plant is cut and is attached to the lower part of the other plant containing roots. The part that contains roots is called stock and the portion that is used to grow leaves and other parts of the plant is called the scion.
So, the correct answer is ‘scion’
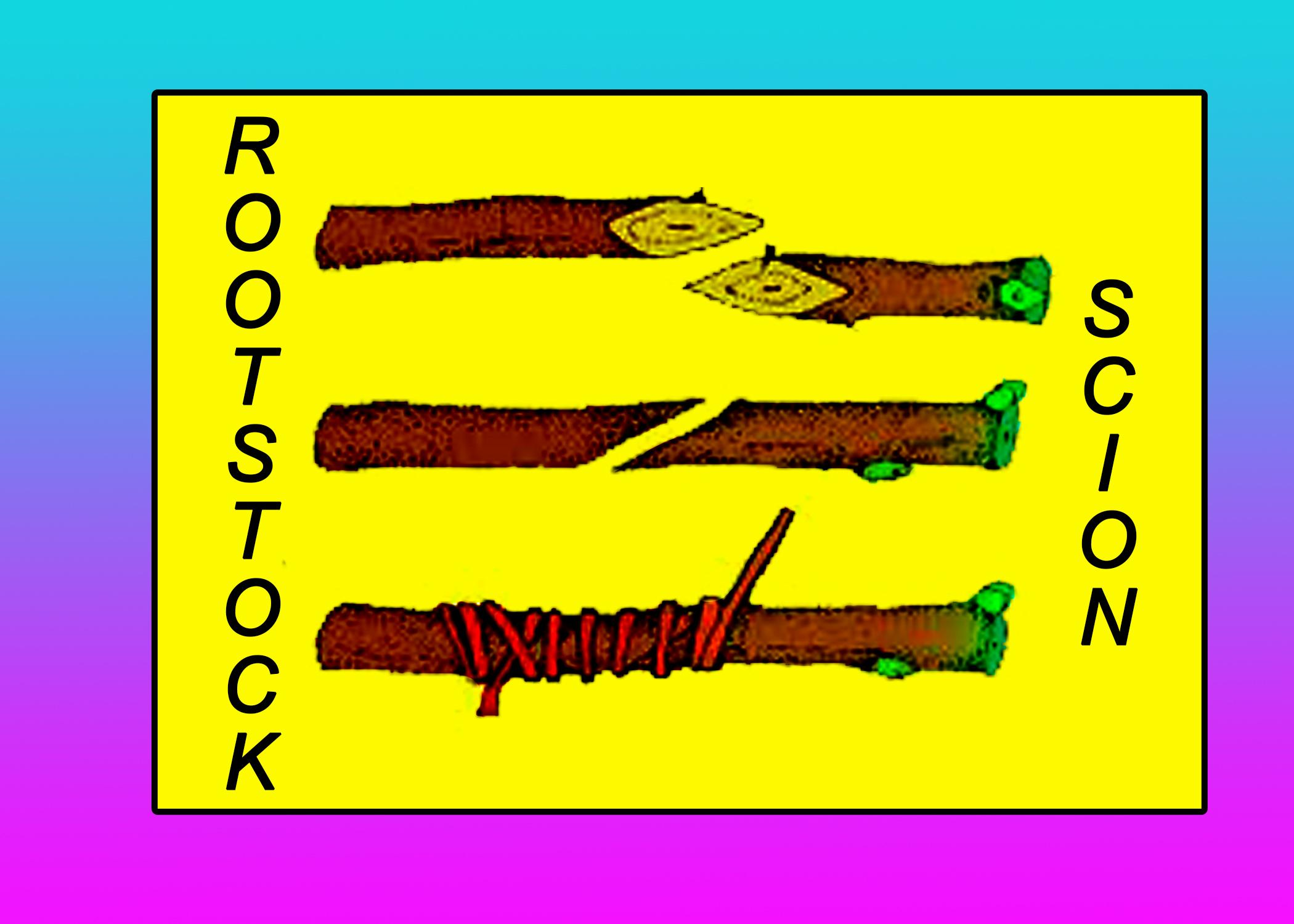
Note: Different techniques used in grafting are bud grafting, approach grafting, cleft grafting, whip grafting, Awl grafting, stub grafting, veneer grafting, four-flap grafting, and rind grafting.
Grafting is used in various scientific studies like plant virus transmission, genetic engineering studies, etc.
Complete answer:
Grafting is one of the artificial techniques used to grow plants vegetatively. It also used to produce plants of desired characters. It is a horticultural technique where two parts of the plants are attracted together and allow them to grow. The upper part of the plant used to grow leaves, flowers, fruits is called scion and the lower part which is used as a root portion is called stock or rootstock. Vascular tissue growth is important for the success of growth in the attached parts.
Additional Information: - Cutting, layering, grafting, and tissue culture are artificial techniques to develop new plants.
- In cutting the vegetative part of the plant is cut and it is planted in the moist soil, it develops adventitious roots and develops as a new individual plant. Example: acacia, rose
- Layering is the same as cutting but the vegetative part of the plant is cut after developing adventitious roots. Examples: jasmine
- In grafting, two desired plants are selected and the upper portion of one plant is cut and is attached to the lower part of the other plant containing roots. The part that contains roots is called stock and the portion that is used to grow leaves and other parts of the plant is called the scion.
So, the correct answer is ‘scion’

Note: Different techniques used in grafting are bud grafting, approach grafting, cleft grafting, whip grafting, Awl grafting, stub grafting, veneer grafting, four-flap grafting, and rind grafting.
Grafting is used in various scientific studies like plant virus transmission, genetic engineering studies, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




