
How do you graph \[3x - 2y = 6\] by finding the x and y intercepts?
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: Using the equation of line, we find the intercepts of the line by substituting x as 0 and calculating the value of y and similarly substituting y as 0 and calculating the value of x. Since it is a straight line, two points are enough to plot the graph, so we join the two points on the graph.
* Intercept means the point where the line crosses the respective axis.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have equation of line \[3x - 2y = 6\] … (1)
We know that x-intercept means the point on x-axis where the line cuts the axis and y-intercept means the point on y-axis where the line cuts the y-axis.
First we calculate x-intercept:
Since, x-intercept means that line \[3x - 2y = 6\] cuts the x-axis and we know any point on the x-axis has y-coordinate or ordinate as 0, we put the value of y as 0.
Substitute the value of \[y = 0\] in equation (1)
\[ \Rightarrow 3x - 2 \times 0 = 6\]
Calculate the product on left hand side of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow 3x - 0 = 6\]
\[ \Rightarrow 3x = 6\]
Divide both sides of the equation by 3
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{3x}}{3} = \dfrac{6}{3}\]
Cancel same factors from numerator denominator on both sides of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow x = 2\]
So, when y is 0, x is 2
\[ \Rightarrow \] x-intercept becomes \[(2,0)\]
Now we calculate y-intercept:
Since, y-intercept means that line \[3x - 2y = 6\] cuts the y-axis and we know any point on the y-axis has x-coordinate or abscissa as 0, we put the value of x as 0.
Substitute the value of \[x = 0\] in equation (1)
\[ \Rightarrow 3 \times 0 - 2y = 6\]
Calculate the product on left hand side of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow 0 - 2y = 6\]
\[ \Rightarrow - 2y = 6\]
Divide both sides of the equation by -2,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - 2y}}{{ - 2}} = \dfrac{6}{{ - 2}}\]
Cancel same factors from numerator and denominator on both sides of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow y = - 3\]
So, when x is 0, y is -3,
\[ \Rightarrow \] y-intercept becomes \[(0, - 3)\]
Now we plot the intercepts on the graph and join the intercepts for the graph of the line \[3x - 2y = 6\]
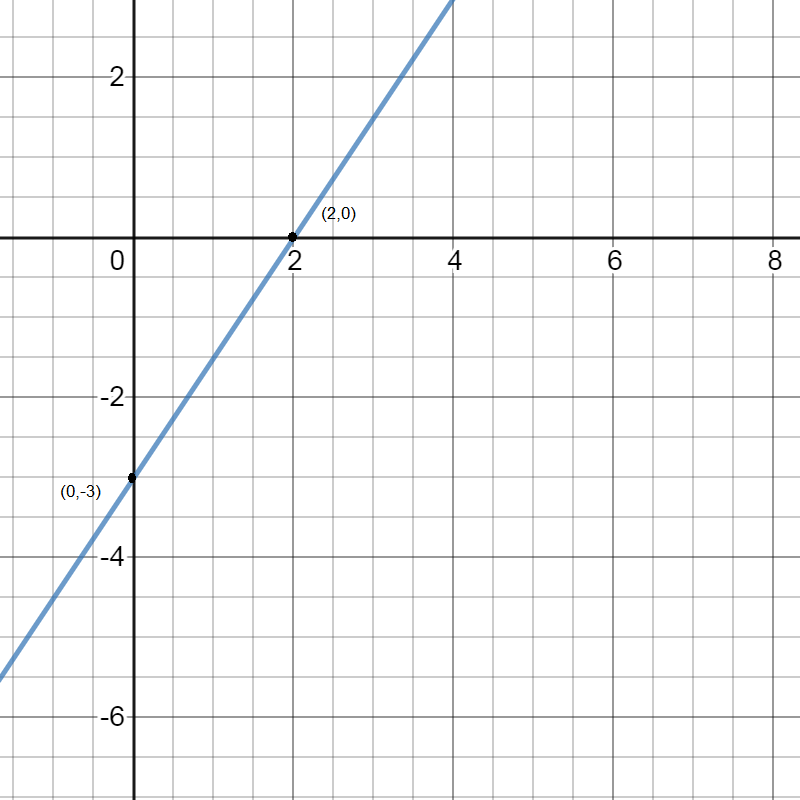
Note:
Students are likely to make mistakes while shifting the values from one side of the equation to another side of the equation as they forget to change the sign of the value shifted. Keep in mind we always change the sign of the value from positive to negative and vice versa when shifting values from one side of the equation to another side of the equation.
Also, many students attempt a method of converting the equation into point slope form first and then calculating the intercept from there. Keep in mind we don’t need the slope here so we directly put in x and y simultaneously.
* Intercept means the point where the line crosses the respective axis.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have equation of line \[3x - 2y = 6\] … (1)
We know that x-intercept means the point on x-axis where the line cuts the axis and y-intercept means the point on y-axis where the line cuts the y-axis.
First we calculate x-intercept:
Since, x-intercept means that line \[3x - 2y = 6\] cuts the x-axis and we know any point on the x-axis has y-coordinate or ordinate as 0, we put the value of y as 0.
Substitute the value of \[y = 0\] in equation (1)
\[ \Rightarrow 3x - 2 \times 0 = 6\]
Calculate the product on left hand side of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow 3x - 0 = 6\]
\[ \Rightarrow 3x = 6\]
Divide both sides of the equation by 3
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{3x}}{3} = \dfrac{6}{3}\]
Cancel same factors from numerator denominator on both sides of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow x = 2\]
So, when y is 0, x is 2
\[ \Rightarrow \] x-intercept becomes \[(2,0)\]
Now we calculate y-intercept:
Since, y-intercept means that line \[3x - 2y = 6\] cuts the y-axis and we know any point on the y-axis has x-coordinate or abscissa as 0, we put the value of x as 0.
Substitute the value of \[x = 0\] in equation (1)
\[ \Rightarrow 3 \times 0 - 2y = 6\]
Calculate the product on left hand side of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow 0 - 2y = 6\]
\[ \Rightarrow - 2y = 6\]
Divide both sides of the equation by -2,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - 2y}}{{ - 2}} = \dfrac{6}{{ - 2}}\]
Cancel same factors from numerator and denominator on both sides of the equation
\[ \Rightarrow y = - 3\]
So, when x is 0, y is -3,
\[ \Rightarrow \] y-intercept becomes \[(0, - 3)\]
Now we plot the intercepts on the graph and join the intercepts for the graph of the line \[3x - 2y = 6\]

Note:
Students are likely to make mistakes while shifting the values from one side of the equation to another side of the equation as they forget to change the sign of the value shifted. Keep in mind we always change the sign of the value from positive to negative and vice versa when shifting values from one side of the equation to another side of the equation.
Also, many students attempt a method of converting the equation into point slope form first and then calculating the intercept from there. Keep in mind we don’t need the slope here so we directly put in x and y simultaneously.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




