
Graph of specific heat at constant volume for a monatomic gas is
A.)
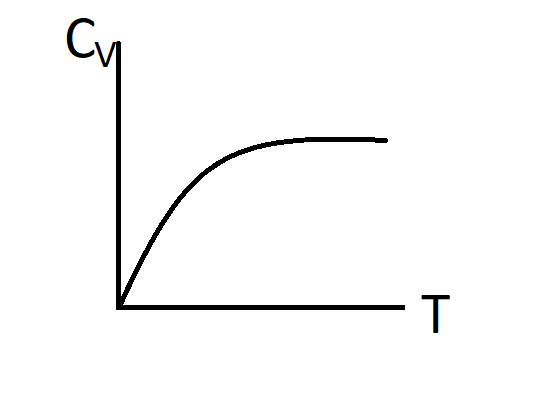
B.)
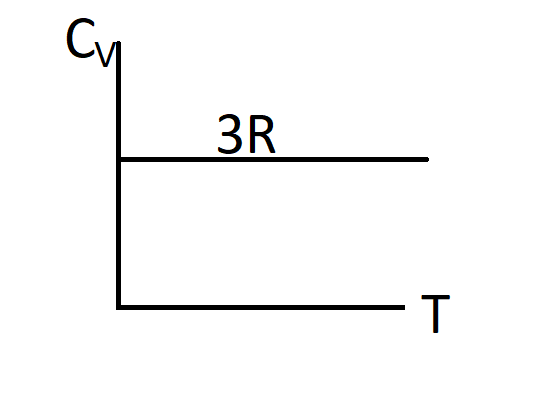
C.)
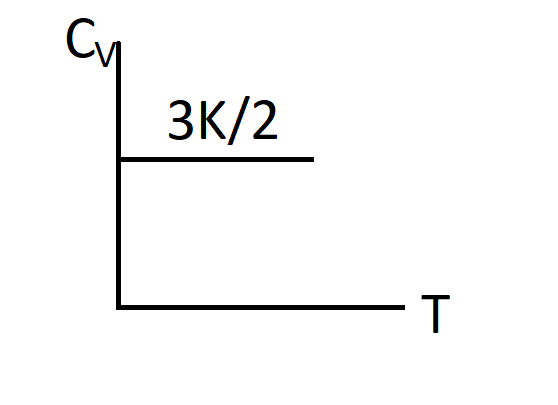
D.)
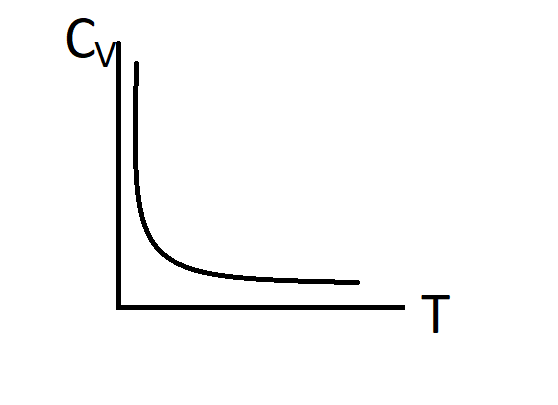



Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: The basic thermal ability of the substance is the thermal ability of the sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample. Informally, it is the amount of energy that must be applied, in the form of heat, to one unit of mass of the material in order to induce a temperature rise of one unit. Monatomic gas is one of which atoms are not bound together. Examples of normal conditions include noble gases argon, krypton, and xenon, but all chemical elements would be monatomic in the gas phase at sufficiently high temperatures.
Complete answer:
Specific heat is a physical volume
It is essentially known as the great quantity needed to increase the temperature by ${{1}^{o}}$ .
They are degraded by c.
Relevant heat is provided by Cv at constant volume.
The system involving constant volume is referred to as the Isochoric mechanism.
Ice has a specific heat smaller than that of water. Monatomic means a single atomic atom that does not bind gases to each other.
For an ideal gas,
$Cv=\dfrac{f}{2}K$
Where f is the total number of degrees of freedom.
For an ideal monatomic gas, three translational degrees of freedom exist in the three directions. No rotational degree of freedom exists.
Thus, $Cv=\dfrac{3}{2}K$
Which is an independent temperature.
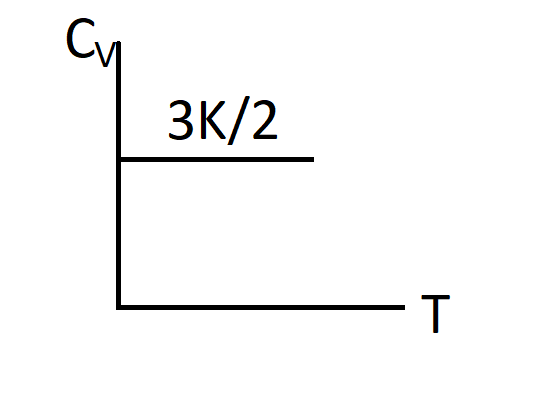
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The Scottish scientist Joseph Black, in the 18th century, found that equal masses of different substances required different quantities of heat to be increased through the same temperature interval, and, on this discovery, he based the principle of particular heat.
Complete answer:
Specific heat is a physical volume
It is essentially known as the great quantity needed to increase the temperature by ${{1}^{o}}$ .
They are degraded by c.
Relevant heat is provided by Cv at constant volume.
The system involving constant volume is referred to as the Isochoric mechanism.
Ice has a specific heat smaller than that of water. Monatomic means a single atomic atom that does not bind gases to each other.
For an ideal gas,
$Cv=\dfrac{f}{2}K$
Where f is the total number of degrees of freedom.
For an ideal monatomic gas, three translational degrees of freedom exist in the three directions. No rotational degree of freedom exists.
Thus, $Cv=\dfrac{3}{2}K$
Which is an independent temperature.

So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The Scottish scientist Joseph Black, in the 18th century, found that equal masses of different substances required different quantities of heat to be increased through the same temperature interval, and, on this discovery, he based the principle of particular heat.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




