
Graphite is a:
A. molecular solid
B. covalent solid
C. ionic solid
D. metallic solid
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: A molecular solid is the one in which the molecules of the solids are held together by intermolecular forces of attraction. Although they have covalent bonds in some of them, their solid structure is rather maintained by the intermolecular forces of attraction.
Complete answer:
Graphite is a crystalline solid and is made up of a regular arrangement of hexagonal framework of carbon atoms. It is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions of temperature and pressure. When the graphite is subjected to a very high pressure and high temperature, it gets converted into diamond. It is a good conductor of heat and electricity. The high conductivity of graphite makes it usable in batteries, electrodes, etc.
In graphite, the hybridization is $s{p^2}$ and the structure is planar with the angles between the carbon atoms being at ${120^o}$. The structure of graphite is as follows:
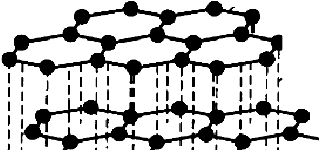
The dash lines shown in the diagram represent the covalent bonds that exist in between the carbon atoms whereas the dotted lines represent the intermolecular cohesive forces that keep the solid structure of graphite intact. The cohesive forces in a graphite structure involve Van der Waals forces, London dispersion forces, etc and are responsible to hold the layer structure of graphite in solid form.
Thus, we can say that graphite is a molecular solid.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note:
It is quite confusing between choosing graphite as a molecular solid or covalent solid. But, the type of solid is determined by the type of bonds that help the molecules to maintain the solid structure of a solid. Thus, graphite is a molecular solid.
Complete answer:
Graphite is a crystalline solid and is made up of a regular arrangement of hexagonal framework of carbon atoms. It is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions of temperature and pressure. When the graphite is subjected to a very high pressure and high temperature, it gets converted into diamond. It is a good conductor of heat and electricity. The high conductivity of graphite makes it usable in batteries, electrodes, etc.
In graphite, the hybridization is $s{p^2}$ and the structure is planar with the angles between the carbon atoms being at ${120^o}$. The structure of graphite is as follows:

The dash lines shown in the diagram represent the covalent bonds that exist in between the carbon atoms whereas the dotted lines represent the intermolecular cohesive forces that keep the solid structure of graphite intact. The cohesive forces in a graphite structure involve Van der Waals forces, London dispersion forces, etc and are responsible to hold the layer structure of graphite in solid form.
Thus, we can say that graphite is a molecular solid.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note:
It is quite confusing between choosing graphite as a molecular solid or covalent solid. But, the type of solid is determined by the type of bonds that help the molecules to maintain the solid structure of a solid. Thus, graphite is a molecular solid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




