
What is the ground state configuration of chlorine?
Answer
528.9k+ views
Hint: The electronic configuration of any neutral atomic species is used to describe and understand the structure of an atom. It can be written by assigning the number of electrons to specified orbitals and a set of rules known as the Aufbau principle, Hund’s rule, and Pauli exclusion principle are followed in doing so. The atomic number of chlorine is 17.
Complete answer:
The atoms consist of many subatomic particles including electron, proton, neutron, etc. Each kind of atom has its own arrangement of these subatomic particles. But every arrangement follows certain rules. The arrangement of electrons in the atomic orbitals is known as the electronic configuration.
Also, every system in the universe prefers to attain the lowest energy. Similarly, the lowest energy and most stable state of electronic configuration is called ground state configuration.
Let us write the electronic configuration of chlorine.
Step 1- Find the number of electrons:
It is a group 17 element and its atomic number is 17. It means that it possesses 17 protons and 17 electrons.
Step 2 – Fill the atomic orbitals using Aufbau’s principle. It states that electrons must fill the lowest energy orbital first according to the scheme given below.
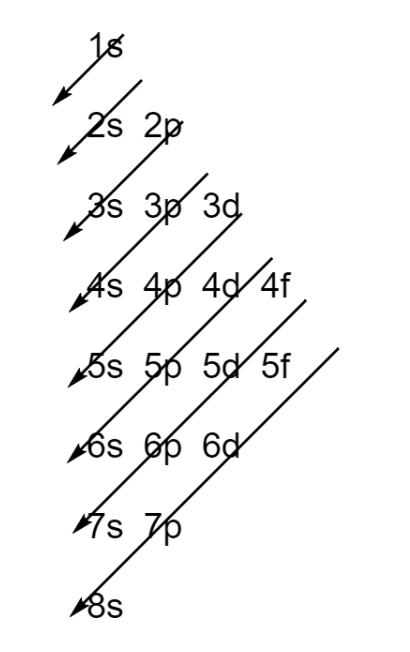
Hence, the ground state configuration of chlorine is $\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{6}}}\text{3}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{3}{{\text{p}}^{\text{5}}}$.
Note:
The other two rules followed in writing electronic configuration are Hund’s rule and the Pauli exclusion principle. Hund’s rule states that electrons must not be paired in the orbitals until each orbital contains one electron, and no orbital can have two electrons with the same spin.
And, Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no two electrons can have the same quantum numbers $\left( \text{n, l, }{{\text{m}}_{\text{l}}},\text{ }{{\text{m}}_{\text{s}}} \right)$.
Complete answer:
The atoms consist of many subatomic particles including electron, proton, neutron, etc. Each kind of atom has its own arrangement of these subatomic particles. But every arrangement follows certain rules. The arrangement of electrons in the atomic orbitals is known as the electronic configuration.
Also, every system in the universe prefers to attain the lowest energy. Similarly, the lowest energy and most stable state of electronic configuration is called ground state configuration.
Let us write the electronic configuration of chlorine.
Step 1- Find the number of electrons:
It is a group 17 element and its atomic number is 17. It means that it possesses 17 protons and 17 electrons.
Step 2 – Fill the atomic orbitals using Aufbau’s principle. It states that electrons must fill the lowest energy orbital first according to the scheme given below.

Hence, the ground state configuration of chlorine is $\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{6}}}\text{3}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{3}{{\text{p}}^{\text{5}}}$.
Note:
The other two rules followed in writing electronic configuration are Hund’s rule and the Pauli exclusion principle. Hund’s rule states that electrons must not be paired in the orbitals until each orbital contains one electron, and no orbital can have two electrons with the same spin.
And, Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no two electrons can have the same quantum numbers $\left( \text{n, l, }{{\text{m}}_{\text{l}}},\text{ }{{\text{m}}_{\text{s}}} \right)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




