
What is gynoecium? List the parts of gynoecium.
Answer
471.6k+ views
Hint: Flowers are a plant's reproductive organ. They are not only involved in reproduction, but also serve as a food supply for other living things. They produce a lot of nectar.
Flowers come in a variety of forms-
Complete- The sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils all make up a whole flower.
Incomplete- An incomplete flower is one that lacks one or more of these structures.
A whole flower is made up of two distinct parts: Reproductive Part and Vegetative Part.
Complete answer:
1. Gynoecium is a term that refers to all of the components of a flower that produce ovules and eventually mature into fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the flower's innermost whorl, made up of pistils and surrounded by the pollen-producing reproductive organs, the stamens, which are collectively known as the androecium. The gynoecium is sometimes referred to as the "female" part of the flower, despite the fact that it produces megaspores, each of which develops into a female gametophyte, which then creates egg cells, rather than directly creating female gametes.
2. Pistillate or carpellate flowers are those that have a gynoecium but no stamens. Staminate flowers are those that lack a gynoecium.
3. Because it produces female gametophytes, the gynoecium is sometimes referred to as female; however, sporophytes do not have a sex, only gametophytes do.
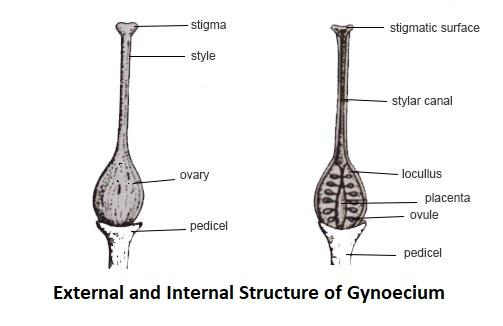
4. The pistil is a plant's feminine component. It is fashioned like a bowling pin and is found in the middle of the flower. There are three elements to it: a stigma, a style, and an ovary. The stigma is at the apex of the ovary, and the style connects it to it. The ovary is home to eggs, which are housed in ovules. The ovule develops into a seed when an egg is fertilised.
Note:
Functions of a flower-
1. In the blooms, gametophytes grow.
2. Without fertilisation, the blooms might develop diaspores.
3. The flower's ovary develops into a fruit with a seed after fertilisation.
4. Flowers' most crucial function is reproduction. They help the male and female gametes to unite.
5. Flowers supply nectar to a variety of birds and insects, which aid in pollen transport from one flower to the next.
6. Selfing, or the union of sperms and eggs from the same flower, or cross-fertilization, or the union of sperms and eggs from separate flowers, may be encouraged by flowers.
7. The meal is digested and the nutrients are absorbed in the small intestine.
8. The large intestine absorbs water, electrolytes, and vitamins, while waste is excreted.
Flowers come in a variety of forms-
Complete- The sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils all make up a whole flower.
Incomplete- An incomplete flower is one that lacks one or more of these structures.
A whole flower is made up of two distinct parts: Reproductive Part and Vegetative Part.
Complete answer:
1. Gynoecium is a term that refers to all of the components of a flower that produce ovules and eventually mature into fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the flower's innermost whorl, made up of pistils and surrounded by the pollen-producing reproductive organs, the stamens, which are collectively known as the androecium. The gynoecium is sometimes referred to as the "female" part of the flower, despite the fact that it produces megaspores, each of which develops into a female gametophyte, which then creates egg cells, rather than directly creating female gametes.
2. Pistillate or carpellate flowers are those that have a gynoecium but no stamens. Staminate flowers are those that lack a gynoecium.
3. Because it produces female gametophytes, the gynoecium is sometimes referred to as female; however, sporophytes do not have a sex, only gametophytes do.
4. The pistil is a plant's feminine component. It is fashioned like a bowling pin and is found in the middle of the flower. There are three elements to it: a stigma, a style, and an ovary. The stigma is at the apex of the ovary, and the style connects it to it. The ovary is home to eggs, which are housed in ovules. The ovule develops into a seed when an egg is fertilised.

Note:
Functions of a flower-
1. In the blooms, gametophytes grow.
2. Without fertilisation, the blooms might develop diaspores.
3. The flower's ovary develops into a fruit with a seed after fertilisation.
4. Flowers' most crucial function is reproduction. They help the male and female gametes to unite.
5. Flowers supply nectar to a variety of birds and insects, which aid in pollen transport from one flower to the next.
6. Selfing, or the union of sperms and eggs from the same flower, or cross-fertilization, or the union of sperms and eggs from separate flowers, may be encouraged by flowers.
7. The meal is digested and the nutrients are absorbed in the small intestine.
8. The large intestine absorbs water, electrolytes, and vitamins, while waste is excreted.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




