
What happens during the prophase of meiosis?
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: The prophase is the first stage of the meiosis in which the chromosomes are formed from the chromatids through the process of their thickening. The chromosomes move outwards resulting in the disappearance of the nuclear envelope.
Complete answer:
Prophase marks the onset of the mitotic cycle. It involves both nuclear bad cytoplasmic events. In the prophase stage, the chromosomes condense and are arranged to move towards the nuclear envelope from the nucleus resulting in the entanglement of the chromosomes causing them to break. During this process, the chromosomes condense and shorten themselves and obtain their specific structure. The nucleolus and the nuclear membrane completely disappear and the chromosomes become districts which can be easily differentiated from others. Centrioles and asters are present at the opposite chromosomal ends while each centromere of the chromosomes are attached to the protein spindles. The chromosomes are arranged through the mitotic spindle during this phase and the chromosomes start to arrange themselves. The nuclear envelope starts to disappear completely resulting in the release of the chromosomes. The mitotic spindle grows more along with some of the microtubules and then starts to form the chromosomes.
In this stage, the nuclear membrane begins to disintegrate resulting in the cell organelles like ER, Golgi complex, cytoplasm, etc beginning to disappear. During this phase, the cell and the nucleus change their shape into a spheroid. The cytoplasm will have increased refractivity and viscosity. The DNA molecules along with the proteins began to condense resulting in the shortening of the chromosomes making them condensed.
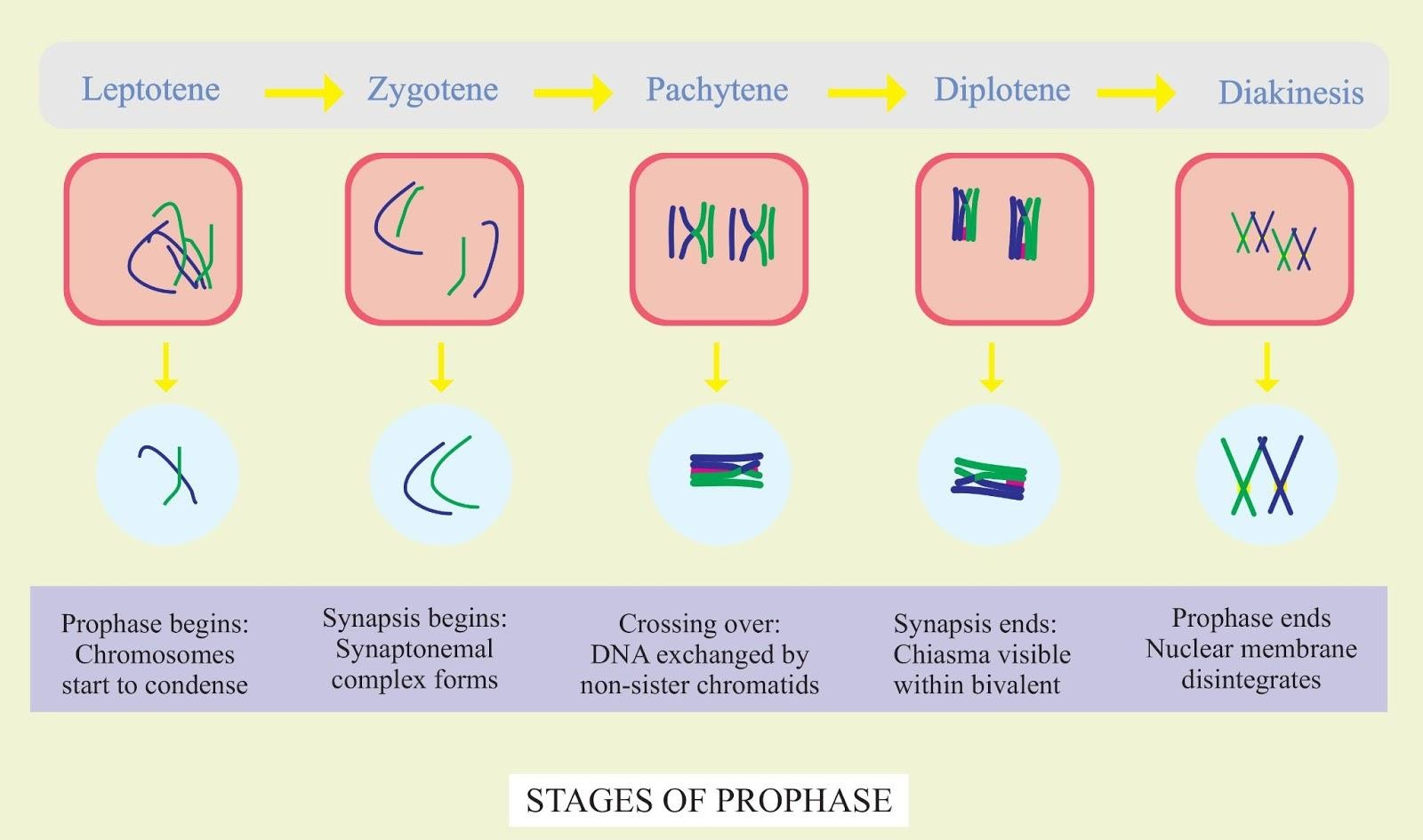
Note:
Meiosis is a reduction in cell division. The gametes produced from meiosis contain half the number of chromosomes of the original somatic cells. It is mainly responsible for the production of gametes in sexually reproducing organisms that result in the variation.
Complete answer:
Prophase marks the onset of the mitotic cycle. It involves both nuclear bad cytoplasmic events. In the prophase stage, the chromosomes condense and are arranged to move towards the nuclear envelope from the nucleus resulting in the entanglement of the chromosomes causing them to break. During this process, the chromosomes condense and shorten themselves and obtain their specific structure. The nucleolus and the nuclear membrane completely disappear and the chromosomes become districts which can be easily differentiated from others. Centrioles and asters are present at the opposite chromosomal ends while each centromere of the chromosomes are attached to the protein spindles. The chromosomes are arranged through the mitotic spindle during this phase and the chromosomes start to arrange themselves. The nuclear envelope starts to disappear completely resulting in the release of the chromosomes. The mitotic spindle grows more along with some of the microtubules and then starts to form the chromosomes.
In this stage, the nuclear membrane begins to disintegrate resulting in the cell organelles like ER, Golgi complex, cytoplasm, etc beginning to disappear. During this phase, the cell and the nucleus change their shape into a spheroid. The cytoplasm will have increased refractivity and viscosity. The DNA molecules along with the proteins began to condense resulting in the shortening of the chromosomes making them condensed.

Note:
Meiosis is a reduction in cell division. The gametes produced from meiosis contain half the number of chromosomes of the original somatic cells. It is mainly responsible for the production of gametes in sexually reproducing organisms that result in the variation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




