
What happens to cells if they lose too much water?
Answer
491.4k+ views
Hint: Mammalian cells are composed of various organelles. Cellular division has functions like- they can generate cellular reproduction from only one cell, entire unicellular organisms. Cell division is the splitting of a parent cell into the formation of two daughter cells. Different stages of cell division involve- meiosis and mitosis in an animal life cycle where the mother cell divides into genetically identical two daughter cells.
Complete answer-
As cells have water inside them and cells are protected by a covering known as plasma membrane which acts as a barrier and it contains channels which only allow certain ions for the cell's benefit. Also, cells contain water as a mode of nutrition so that cells do not dry off and organelles can continue to function in a regular manner.
Cells have cytoplasm which also act as a shock absorber and protect the cells from unfavorable anaphylactic conditions. If cells lose water, then, it becomes hard because of the osmosis. The cell becomes stiff and tends to shrink from the cell wall.
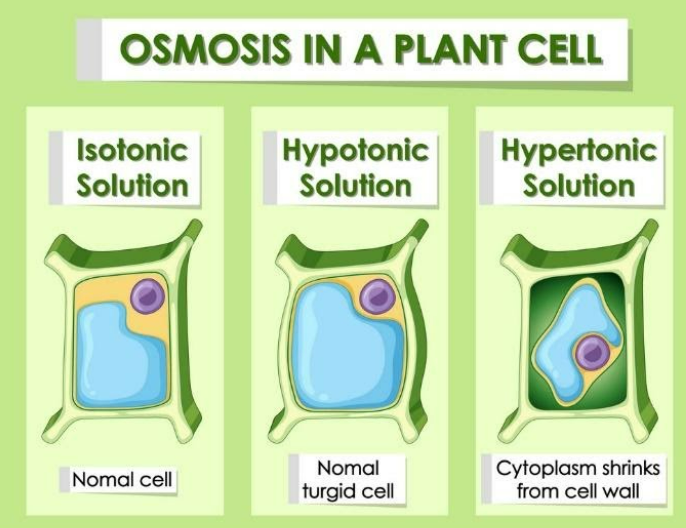
The cell contents start to move out from the cell through the cell wall and push the membrane away from the cell. This condition of the cell is called plasmolysis. The plasmolyzed cell does not survive and die. There are two solutions – hypertonic solution and hypotonic solution. Cells react to both the conditions.
In hypertonic solution cells possess water inside and swells, when the outer membrane cannot cross outside and the water remain swells, the solutes are salt and water hence it is called as hypertonic solution and in hypotonic solution occurs due to endosmosis.
Note:
Isotonic solution is a solution which has osmolarity or solute concentration. Hypotonic as we discussed is when a cell swells and hypertonic is when a cell shrinks. A cell contains gated channels so that it controls the outflow and inflow of nutrients across a semipermeable membrane. In Endosmosis the water cannot go inside from the plasma membrane into the cell membrane where the cell swells.
Complete answer-
As cells have water inside them and cells are protected by a covering known as plasma membrane which acts as a barrier and it contains channels which only allow certain ions for the cell's benefit. Also, cells contain water as a mode of nutrition so that cells do not dry off and organelles can continue to function in a regular manner.
Cells have cytoplasm which also act as a shock absorber and protect the cells from unfavorable anaphylactic conditions. If cells lose water, then, it becomes hard because of the osmosis. The cell becomes stiff and tends to shrink from the cell wall.
The cell contents start to move out from the cell through the cell wall and push the membrane away from the cell. This condition of the cell is called plasmolysis. The plasmolyzed cell does not survive and die. There are two solutions – hypertonic solution and hypotonic solution. Cells react to both the conditions.
In hypertonic solution cells possess water inside and swells, when the outer membrane cannot cross outside and the water remain swells, the solutes are salt and water hence it is called as hypertonic solution and in hypotonic solution occurs due to endosmosis.

Note:
Isotonic solution is a solution which has osmolarity or solute concentration. Hypotonic as we discussed is when a cell swells and hypertonic is when a cell shrinks. A cell contains gated channels so that it controls the outflow and inflow of nutrients across a semipermeable membrane. In Endosmosis the water cannot go inside from the plasma membrane into the cell membrane where the cell swells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




