
What happens when
(a) Sodium phenoxide is treated with\[C{H_3}Cl\]?
(b) \[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - OH\] is oxidized by PCC
(c) Phenol is treated with \[C{H_3}COCl\]/anhydrous \[AlC{l_3}\]
Write the chemical equations to support your answer.
Answer
468.9k+ views
Hint: All the above reactions are the direct reactions taking place and all of them are one-step reactions. The first reaction is an example of Williamsons synthesis reaction, the second one is the basic oxidation reaction and the third one is the friedel-craft reaction. By the names of the reactions you can guess what might be the products of these reactions.
Complete step by step answer:
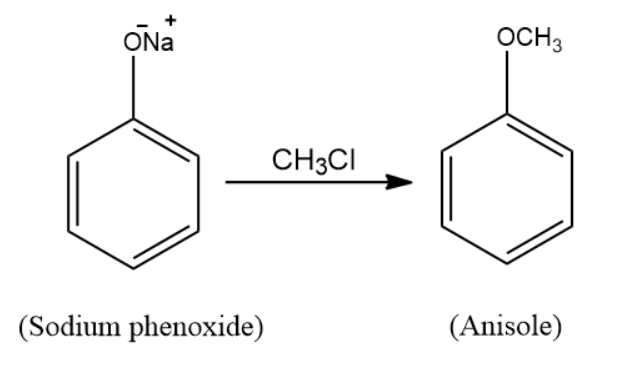
(a) When sodium phenoxide is treated with methyl chloride \[\left( {C{H_3}Cl} \right)\], the product formed is anisole. The reaction taking place here is a nucleophilic substitution reaction. Sodium phenoxide is an alkoxide and methyl chloride is a halide. When the two react, Williamson’s ether synthesis process occurs and the resulting product is ether, which is anisole. The reaction for the following takes place in the following manner:
(b) \[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - OH\] is a primary alcohol. When a primary alcohol is treated with PCC, it undergoes oxidation and gets oxidized to an aldehyde. PCC is Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC), a complex of chromium trioxide with pyridine and HCl. It is a better reagent for the oxidation of primary alcohols to an aldehyde. The reaction of \[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - OH\] with PCC takes place in the following manner:
$C{H_2} = CH - CH - OH\xrightarrow{{PCC}}C{H_2} = CH - CHO$
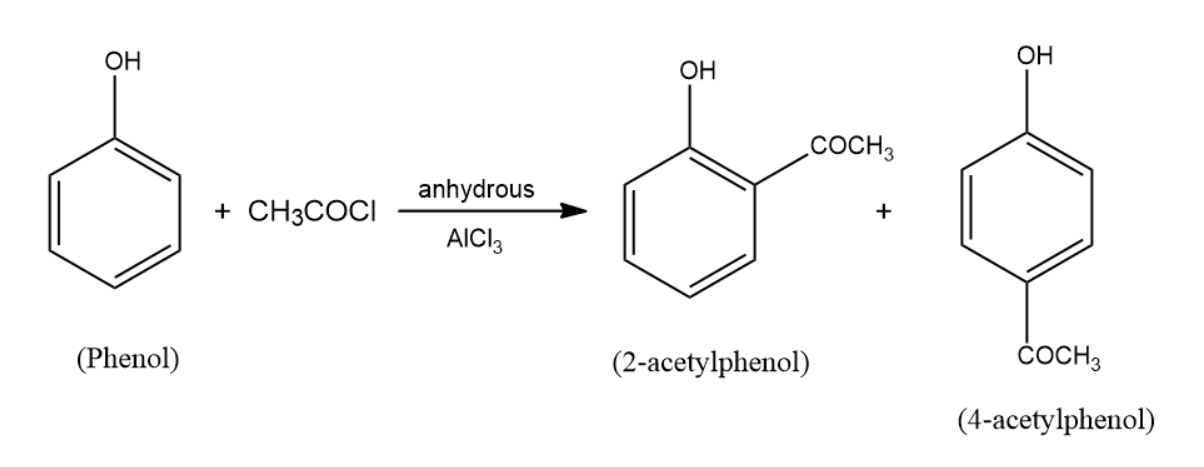
(c) When phenol is treated with \[C{H_3}COCl\]/anhydrous \[AlC{l_3}\] two products are formed among which one of them is major and the other one is minor. The reaction that occurs here is the friedel-craft acylation reaction. The products formed as a result are the two acetylphenol products. These products are $2 - $acetylphenol and $4 - $acetylphenol, among them $4 - $acetylphenol is the major product. The reaction takes place in the following manner:
Note:
Williamson’s synthesis reaction occurs between an organohalide and a deprotonated alcohol to yield ether as the product. This deprotonated alcohol is also called alkoxide. And the reaction occurs via the $Sn2$ mechanism. PCC are very good reagents for converting a primary alcohol to an aldehyde or a secondary alcohol to a ketone. However, PCC cannot oxidize aldehydes to carboxylic acids. Friedel-crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. There is also friedel-craft alkylation in which instead of $C{H_3}COCl$, $C{H_3}Cl$ is used.
Complete step by step answer:
(a) When sodium phenoxide is treated with methyl chloride \[\left( {C{H_3}Cl} \right)\], the product formed is anisole. The reaction taking place here is a nucleophilic substitution reaction. Sodium phenoxide is an alkoxide and methyl chloride is a halide. When the two react, Williamson’s ether synthesis process occurs and the resulting product is ether, which is anisole. The reaction for the following takes place in the following manner:

(b) \[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - OH\] is a primary alcohol. When a primary alcohol is treated with PCC, it undergoes oxidation and gets oxidized to an aldehyde. PCC is Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC), a complex of chromium trioxide with pyridine and HCl. It is a better reagent for the oxidation of primary alcohols to an aldehyde. The reaction of \[C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2} - OH\] with PCC takes place in the following manner:
$C{H_2} = CH - CH - OH\xrightarrow{{PCC}}C{H_2} = CH - CHO$
(c) When phenol is treated with \[C{H_3}COCl\]/anhydrous \[AlC{l_3}\] two products are formed among which one of them is major and the other one is minor. The reaction that occurs here is the friedel-craft acylation reaction. The products formed as a result are the two acetylphenol products. These products are $2 - $acetylphenol and $4 - $acetylphenol, among them $4 - $acetylphenol is the major product. The reaction takes place in the following manner:

Note:
Williamson’s synthesis reaction occurs between an organohalide and a deprotonated alcohol to yield ether as the product. This deprotonated alcohol is also called alkoxide. And the reaction occurs via the $Sn2$ mechanism. PCC are very good reagents for converting a primary alcohol to an aldehyde or a secondary alcohol to a ketone. However, PCC cannot oxidize aldehydes to carboxylic acids. Friedel-crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. There is also friedel-craft alkylation in which instead of $C{H_3}COCl$, $C{H_3}Cl$ is used.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




