
What happens when benzene undergoes Friedel-Crafts acylation with succinic anhydride in presence of $ AlC{l_3} $ ?
Answer
544.5k+ views
Hint : In order to answer this question, you must recall the Friedel-Crafts Reaction in which you have studied about reaction of benzene with Succinic Anhydride in presence of $ AlC{l_3} $ , and what was the mechanism and products. Use the correct mechanism to find the correct required answer.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Step 1: In this step we will understand the concept of Friedel-Crafts Reaction:
Friedel-Crafts Reaction: A Friedel-Crafts reaction is an organic coupling reaction involving an electrophilic aromatic substitution that is used for the attachment of substituents to aromatic rings. The two primary types of Friedel-Crafts reactions are the alkylation and acylation reactions.
Step 2: In this step we will Friedel-Crafts acylation and its mechanism:
Friedel-Crafts Acylation: The Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction involves the addition of an acyl group to an aromatic ring. Typically, this is done by employing an acid chloride and a Lewis acid catalyst such as $ AlC{l_3} $ . In a Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction, the aromatic ring is transformed into a ketone.
Mechanism:
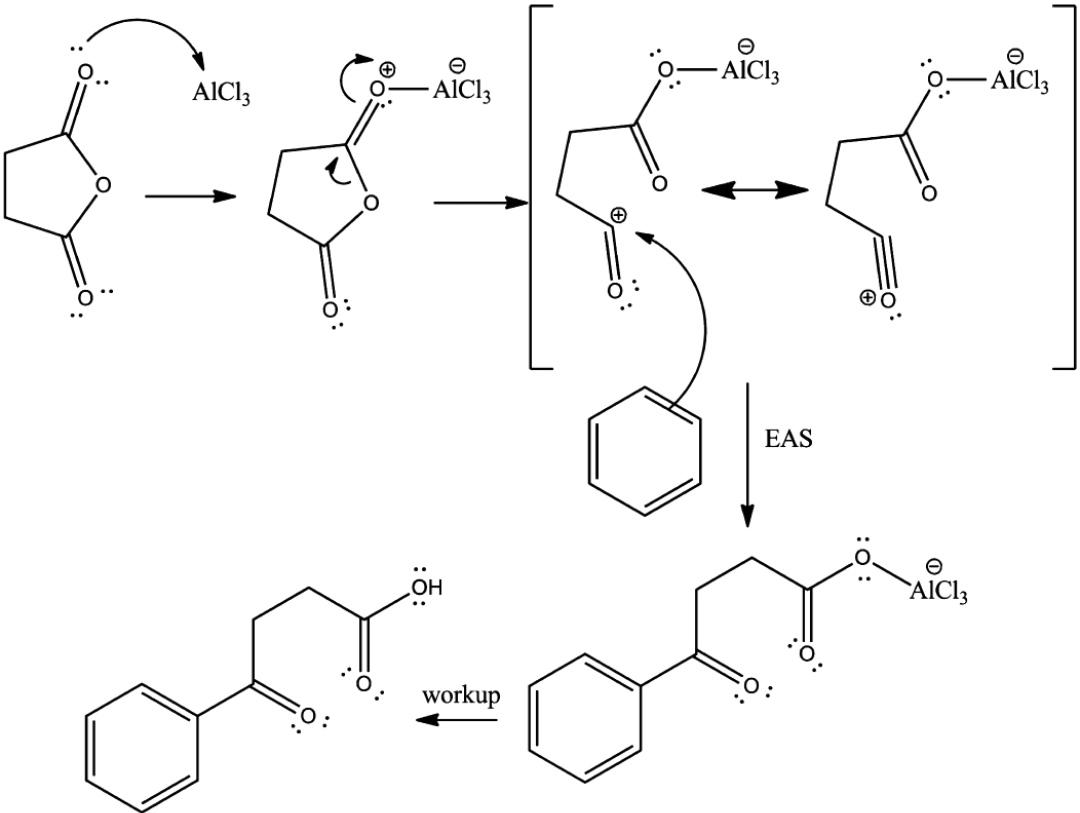
A reaction occurs between the Lewis acid catalyst $ (AlC{l_3}) $ and the acyl halide. A complex is formed and the acyl halide loses a halide ion, forming an acylium ion which is stabilized by resonance.
The acylium ion goes on to execute an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring. The aromaticity of the ring is temporarily lost as a complex is formed.
The intermediate complex is now deprotonated, restoring the aromaticity to the ring. This proton attaches itself to a chloride ion (from the complexed Lewis acid), forming $ HCl $ . The $ AlC{l_3} $ catalyst is now regenerated.
The regenerated catalyst can now attack the carbonyl oxygen. Therefore, the ketone product must be liberated by adding water to the products formed in the previous step.
Step 3: In this step we will Follow the above listed mechanism to solve the question:
When Benzene is treated with ethanoyl chloride in the presence of an Aluminium Chloride catalyst then as a product which we obtain a ketonic group get attached to the benzene ring which is named as Phenylethanone and $ HCl $ gas is evolved out.
Hence, the final product which we get from the reaction is Phenylethanone.
Note :
Friedel–Crafts alkylation has been hypothesized to be reversible. In a retro-Friedel–Crafts reaction of Friedel–Crafts dealkylation, alkyl groups are removed in the presence of protons or other Lewis acid.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Step 1: In this step we will understand the concept of Friedel-Crafts Reaction:
Friedel-Crafts Reaction: A Friedel-Crafts reaction is an organic coupling reaction involving an electrophilic aromatic substitution that is used for the attachment of substituents to aromatic rings. The two primary types of Friedel-Crafts reactions are the alkylation and acylation reactions.
Step 2: In this step we will Friedel-Crafts acylation and its mechanism:
Friedel-Crafts Acylation: The Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction involves the addition of an acyl group to an aromatic ring. Typically, this is done by employing an acid chloride and a Lewis acid catalyst such as $ AlC{l_3} $ . In a Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction, the aromatic ring is transformed into a ketone.
Mechanism:

A reaction occurs between the Lewis acid catalyst $ (AlC{l_3}) $ and the acyl halide. A complex is formed and the acyl halide loses a halide ion, forming an acylium ion which is stabilized by resonance.
The acylium ion goes on to execute an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring. The aromaticity of the ring is temporarily lost as a complex is formed.
The intermediate complex is now deprotonated, restoring the aromaticity to the ring. This proton attaches itself to a chloride ion (from the complexed Lewis acid), forming $ HCl $ . The $ AlC{l_3} $ catalyst is now regenerated.
The regenerated catalyst can now attack the carbonyl oxygen. Therefore, the ketone product must be liberated by adding water to the products formed in the previous step.
Step 3: In this step we will Follow the above listed mechanism to solve the question:
When Benzene is treated with ethanoyl chloride in the presence of an Aluminium Chloride catalyst then as a product which we obtain a ketonic group get attached to the benzene ring which is named as Phenylethanone and $ HCl $ gas is evolved out.
Hence, the final product which we get from the reaction is Phenylethanone.
Note :
Friedel–Crafts alkylation has been hypothesized to be reversible. In a retro-Friedel–Crafts reaction of Friedel–Crafts dealkylation, alkyl groups are removed in the presence of protons or other Lewis acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




