
What happens when borax is heated strongly?
Answer
515.7k+ views
Hint: Borax is a boron compound, a mineral, and a salt of boric acid. It is also known as sodium borate, sodium tetraborate, or disodium tetraborate. Borax powder is a white powder made up of soft colourless crystals that dissolve in water. Borax is a term that refers to a group of minerals or chemical compounds that vary in their crystal water content, and it is most often used to refer to the octahydrate. Borax that is sold commercially is partly dehydrated.
Complete answer:
Borax develops a yellow green dye when applied to a blaze. Owing to the overwhelming yellow hue of sodium, borax is not used for this reason in fireworks. Boric acid is used to transform methanol fires into a translucent green hue.
In ethylene glycol, borax is very soluble, mildly soluble in diethylene glycol and methanol, and somewhat soluble in acetone. It is poorly soluble in cold water, but as the temperature rises, so does its solubility.
As borax is heated to a high temperature, it loses water and expands into a white mass, which melts to create a clear glassy solid known as borax glass or borax bead with further heating. Sodium metaborate ($NaBO_2$) is a colourless solid chemical compound containing sodium, boron, and oxygen. To emphasise the relationship between sodium and boron oxides, the formula can also be written as.$Na_2O.B_2O_3$
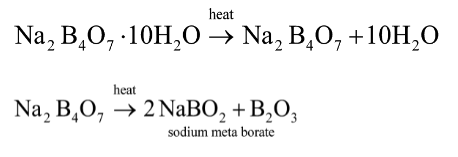
Note:
Borax was found in dry lake beds in Tibet and brought to the Arabian Peninsula by the Silk Road in the 8th century AD. As Francis Marion Smith's Pacific Coast Borax Company began marketing and popularising a wide range of applications under the 20 Mule Team Borax trademark, named for the process by which borax was initially hauled out of the California and Nevada deserts, borax became widely used.
Complete answer:
Borax develops a yellow green dye when applied to a blaze. Owing to the overwhelming yellow hue of sodium, borax is not used for this reason in fireworks. Boric acid is used to transform methanol fires into a translucent green hue.
In ethylene glycol, borax is very soluble, mildly soluble in diethylene glycol and methanol, and somewhat soluble in acetone. It is poorly soluble in cold water, but as the temperature rises, so does its solubility.
As borax is heated to a high temperature, it loses water and expands into a white mass, which melts to create a clear glassy solid known as borax glass or borax bead with further heating. Sodium metaborate ($NaBO_2$) is a colourless solid chemical compound containing sodium, boron, and oxygen. To emphasise the relationship between sodium and boron oxides, the formula can also be written as.$Na_2O.B_2O_3$
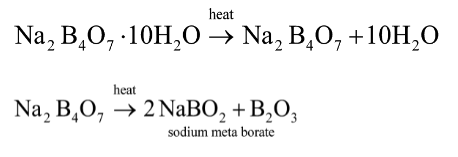
Note:
Borax was found in dry lake beds in Tibet and brought to the Arabian Peninsula by the Silk Road in the 8th century AD. As Francis Marion Smith's Pacific Coast Borax Company began marketing and popularising a wide range of applications under the 20 Mule Team Borax trademark, named for the process by which borax was initially hauled out of the California and Nevada deserts, borax became widely used.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




