
How did DNA evolve?
Answer
508.2k+ views
Hint: Nucleic acids are the organic materials present in all organisms in the form of DNA or RNA which are formed by the combination of nitrogenous bases, sugar molecules and also the phosphate groups which are linked by different bonds in a series of sequences. The DNA structure explains the basic genetic makeup of not only our body but the genetic makeup of nearly all life on earth.
Complete answer:
As we all know scientists James Watson and Francis Crick discovered DNA and also won a Nobel Prize in the year for their discovery of the structure of DNA. The story of DNA’s discovery began when DNA was first identified by the famous Swiss chemist named Johann Friedrich Miescher during his research on white blood cells. During his experiments to study more about the composition of the WBC’s, he noticed that these DNA molecules would dissolve in the alkali solution and when acid was added, this molecule got separated.
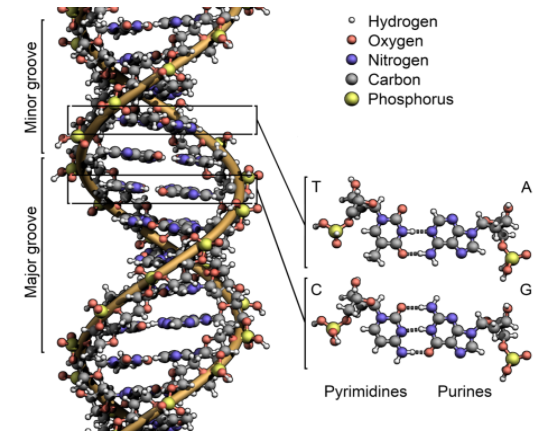
From his observations, he drew the conclusion that this DNA molecule had different properties and is different from other protein molecules. Hence, he called this substance ‘nuclein’ as it was obtained from the cell nucleus. After this conclusion, for many years, scientists continued to believe that the hereditary material was proteins. A German biochemist, Albrecht Kossel identified nuclein as nucleic acid and named it deoxyribonucleic acid also called the DNA.
Note: One of the major features of DNA is the production of proteins. These proteins are important because they provide a definite structure to bones and other tissues, bringing about transportation of materials throughout the body such as iron, cause movement of materials from one to another cell would act as hormones thereby regulating the functions of the body, enzymatic role in chemical reactions and also acts as antibodies fighting against diseases hence proteins are considered as important cells of the body.
Complete answer:
As we all know scientists James Watson and Francis Crick discovered DNA and also won a Nobel Prize in the year for their discovery of the structure of DNA. The story of DNA’s discovery began when DNA was first identified by the famous Swiss chemist named Johann Friedrich Miescher during his research on white blood cells. During his experiments to study more about the composition of the WBC’s, he noticed that these DNA molecules would dissolve in the alkali solution and when acid was added, this molecule got separated.

From his observations, he drew the conclusion that this DNA molecule had different properties and is different from other protein molecules. Hence, he called this substance ‘nuclein’ as it was obtained from the cell nucleus. After this conclusion, for many years, scientists continued to believe that the hereditary material was proteins. A German biochemist, Albrecht Kossel identified nuclein as nucleic acid and named it deoxyribonucleic acid also called the DNA.
Note: One of the major features of DNA is the production of proteins. These proteins are important because they provide a definite structure to bones and other tissues, bringing about transportation of materials throughout the body such as iron, cause movement of materials from one to another cell would act as hormones thereby regulating the functions of the body, enzymatic role in chemical reactions and also acts as antibodies fighting against diseases hence proteins are considered as important cells of the body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




