
How do you draw VSEPR diagrams?
Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint: VSEPR theory tells us to know about the geometry of the molecule and to draw VSEPR diagrams , you should know about its postulates and then, you can easily draw them. Now answer the statement.
Complete step by step answer:
First of let’s discuss the VSEPR theory. VSEPR stands for the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory. This theory states that the shapes of the molecules can be determined by the number of electron pairs in the valence shell of the central atoms.
The main postulates of this theory are as;
1. The geometry of the molecule depends upon the number of the valence electron pairs around the central atom.
2. Electron pairs tend to repel one another because their electron clouds are negatively charged. As a result, the electron pairs try to stay as far apart as possible to acquire a state of minimum energy or maximum stability.
3. Repulsion between the lone pair and lone pair of electrons is different than that between the bond pairs or one lone pair and one bond pair. The repulsive interactions decrease in the order as;
$lp-lp>lp-bp>bp-bp$
4. Repulsive forces decrease sharply with increasing angle between the electron pairs, they are strong at ${{90}^{\circ }}$, much worker at ${{120}^{\circ }}$ and much weaker at ${{180}^{\circ }}$.
Now with the help of these postulates awe can, draw the VSEPR diagrams as;
Consider the VSEPR diagram of ammonia
In ammonia, nitrogen is the central metal atom which consists of five valence electrons in its outermost valence shell and the hydrogen atoms are present around the central nitrogen atoms each consisting of one electron in its valence shell.
So, out of five, three valence electrons present in the nitrogen will form bonds with the three hydrogen atoms each of which consists of one electron and thus, results in the formation of the three N-H bonds.
Now, the two electrons left behind present on the nitrogen atom exist in the form of a lone pair of electrons.
So, thus the geometry of ammonia should be tetrahedral with bond angle as ${{109.5}^{\circ }}$ but since the lone pair-bond pair repulsions is more than the bond-bond repulsions, so the bond angle is reduced to ${{107}^{\circ }}$ and its geometry is also regarded as pyramidal. The structure of ammonia is as;
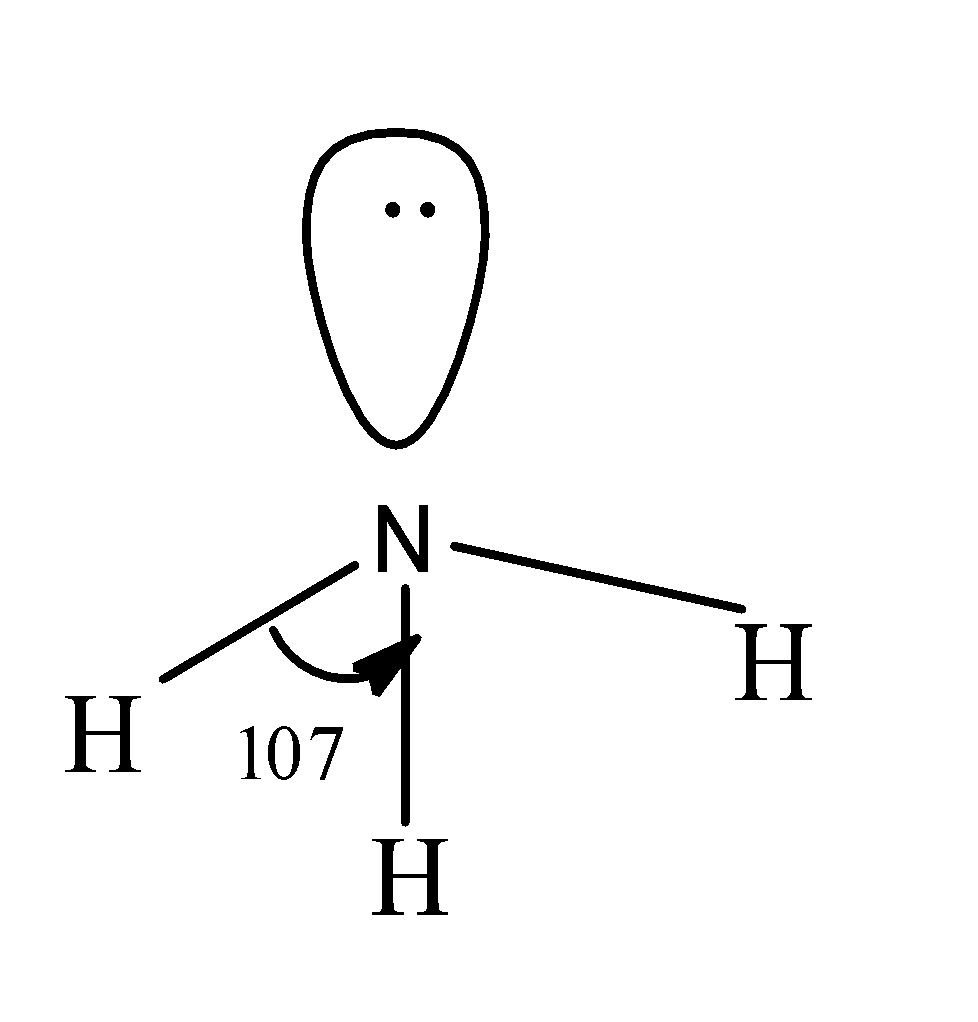
Hence, in this way we can draw the VSEPR diagrams.
Note: The molecules in which the central atom is surrounded only by similar bonded electron pairs will have regular geometries while those in which the central metal atom is surrounded by bond pairs as well as lone pairs will have regular geometries.
Complete step by step answer:
First of let’s discuss the VSEPR theory. VSEPR stands for the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory. This theory states that the shapes of the molecules can be determined by the number of electron pairs in the valence shell of the central atoms.
The main postulates of this theory are as;
1. The geometry of the molecule depends upon the number of the valence electron pairs around the central atom.
2. Electron pairs tend to repel one another because their electron clouds are negatively charged. As a result, the electron pairs try to stay as far apart as possible to acquire a state of minimum energy or maximum stability.
3. Repulsion between the lone pair and lone pair of electrons is different than that between the bond pairs or one lone pair and one bond pair. The repulsive interactions decrease in the order as;
$lp-lp>lp-bp>bp-bp$
4. Repulsive forces decrease sharply with increasing angle between the electron pairs, they are strong at ${{90}^{\circ }}$, much worker at ${{120}^{\circ }}$ and much weaker at ${{180}^{\circ }}$.
Now with the help of these postulates awe can, draw the VSEPR diagrams as;
Consider the VSEPR diagram of ammonia
In ammonia, nitrogen is the central metal atom which consists of five valence electrons in its outermost valence shell and the hydrogen atoms are present around the central nitrogen atoms each consisting of one electron in its valence shell.
So, out of five, three valence electrons present in the nitrogen will form bonds with the three hydrogen atoms each of which consists of one electron and thus, results in the formation of the three N-H bonds.
Now, the two electrons left behind present on the nitrogen atom exist in the form of a lone pair of electrons.
So, thus the geometry of ammonia should be tetrahedral with bond angle as ${{109.5}^{\circ }}$ but since the lone pair-bond pair repulsions is more than the bond-bond repulsions, so the bond angle is reduced to ${{107}^{\circ }}$ and its geometry is also regarded as pyramidal. The structure of ammonia is as;

Hence, in this way we can draw the VSEPR diagrams.
Note: The molecules in which the central atom is surrounded only by similar bonded electron pairs will have regular geometries while those in which the central metal atom is surrounded by bond pairs as well as lone pairs will have regular geometries.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a labelled diagram of the human heart and label class 11 biology CBSE

What is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p class 11 chemistry CBSE




