
How do you graph $y = \cos 2x$?
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint: First find amplitude, period, phase shift, and vertical shift for given periodic function. Select a few points to graph. Find the point at $x = 0$, $x = \dfrac{\pi }{4}$, $x = \dfrac{\pi }{2}$, $x = \dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}$, $x = \pi $. List the points in a table. Then graph the trigonometric function using the amplitude, period, phase shift, vertical shift and the points.
Formula used:
Period: The period goes from one peak to the next (or from any point to the next matching point).
Amplitude: The amplitude is the height from the center line to the peak (or to the trough). Or we can measure the height from highest to lowest points and divide them by $2$.
Phase Shift: The phase shift is how far the function is shifted horizontally from the usual position.
Vertical Shift: The vertical shift is how far the function is shifted vertically from the usual position.
Complete step by step answer:
Use the form $a\cos \left( {bx - c} \right) + d$ to find the amplitude, period, phase shift, and vertical shift.
Compare the given equation $y = \cos 2x$with $a\cos \left( {bx - c} \right) + d$ and find variables $a,b,c$ and $d$.
$a = 1$, $b = 2$, $c = 0$ and $d = 0$.
Find the amplitude $\left| a \right|$.
Here, $a = 1$.
Amplitude, $\left| a \right| = 1$.
The period of the function can be calculated using $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| b \right|}}$.
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| b \right|}}$
Replace $b$ with $2$ in the formula for period.
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| 2 \right|}}$
The absolute value is the distance between a number and zero.
The distance between $0$ and $2$ is$2$.
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{2}$
Cancel the common factor of $2$.
Period: $\dfrac{{\not{2}\pi }}{{\not{2}}}$
Divide $\pi $ by $1$.
Period: $\pi $
Find the phase shift using the formula $\dfrac{c}{b}$.
The phase shift of the function can be calculated from $\dfrac{c}{b}$.
Phase Shift: $\dfrac{c}{b}$
Replace the values of $c$ and $b$ in the equation for phase shift.
Phase Shift: $\dfrac{0}{2}$
Divide $0$ by $2$.
Phase Shift: $0$
Find the vertical shift $d$.
Vertical Shift: $0$
Now we have to List the properties of the trigonometric function.
Amplitude: $1$
Period: $\pi $
Phase Shift: $0$($0$ to the right)
Vertical Shift: $0$
Also, we select a few points to graph.
Find the point at $x = 0$.
Replace the variable $x$ with $0$ in the expression.
$f\left( 0 \right) = \cos \left( {2\left( 0 \right)} \right)$
Multiply $2$ by $0$.
$f\left( 0 \right) = \cos \left( 0 \right)$
The exact value of $\cos \left( 0 \right)$ is $1$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( 0 \right) = 1$
The final answer is $1$.
Find the point at $x = \dfrac{\pi }{4}$.
Replace the variable $x$ with $\dfrac{\pi }{4}$ in the expression.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) = \cos \left( {2\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right)} \right)$
Cancel the common factor of $2$.
Factor $2$ out of $4$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) = \cos \left( {2\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{{2\left( 2 \right)}}} \right)} \right)$
Cancel the common factor.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) = \cos \left( {\not{2}\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{{2 \times \not{2}}}} \right)} \right)$
Rewrite the expression.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) = \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)$
The exact value of $\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)$ is $0$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) = 0$
The final answer is $0$.
Also, we have to find the point at $x = \dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Replace the variable $x$ with $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ in the expression.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = \cos \left( {2\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)} \right)$
Cancel the common factor of $2$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = \cos \left( {\not{2}\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{{\not{2}}}} \right)} \right)$
Rewrite the expression.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = \cos \left( \pi \right)$
Apply the reference angle by finding the angle with equivalent trigonometric values in the first quadrant.
Make the expression negative because cosine is negative in the second quadrant.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = - \cos \left( 0 \right)$
The exact value of $\cos \left( 0 \right)$ is $1$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = - 1 \times 1$
Multiply $ - 1$ by $1$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = - 1$
The final answer is $ - 1$.
Again, we have to find the point at $x = \dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}$.
Replace the variable $x$ with $\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}$ in the expression.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) = \cos \left( {2\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right)} \right)$
Cancel the common factor of $2$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) = \cos \left( {2\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{{2\left( 2 \right)}}} \right)} \right)$
Cancel the common factor.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) = \cos \left( {\not{2}\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{{2 \cdot \not{2}}}} \right)} \right)$
Rewrite the expression.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) = \cos \left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}} \right)$
Apply the reference angle by finding the angle with equivalent trigonometric values in the first quadrant.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) = - \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)$
The exact value of $\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)$ is $0$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) = 0$
The final answer is $0$.
Find the point at $x = \pi $.
Replace the variable $x$ with $\pi $ in the expression.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( \pi \right) = \cos \left( {2\left( \pi \right)} \right)$
$2\pi $ is a full rotation so replace with $0$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( \pi \right) = \cos \left( 0 \right)$
The exact value of $\cos \left( 0 \right)$ is $1$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( \pi \right) = 1$
The final answer is $1$.
List the points in a table.
The trigonometric function can be graphed using the amplitude, period, phase shift, vertical shift and the points.
Amplitude: $1$
Period: $\pi $
Phase Shift: $0$($0$ to the right)
Vertical Shift: $0$
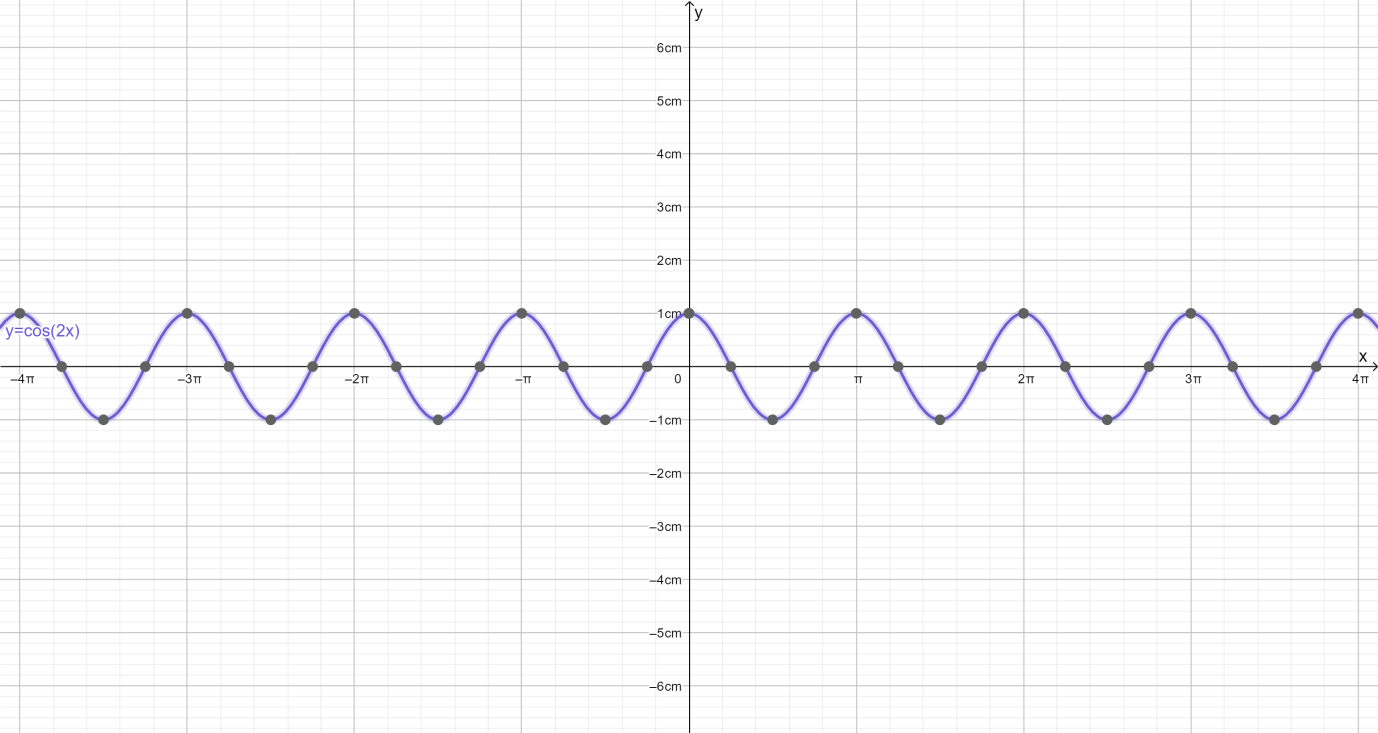
Note: $\cos 2x$ and $2\cos x$ are entirely different terms.
$2\cos x$ is twice the cosine of angle $x$. It lies between $ - 2$ and $2$.
$\cos 2x$ is the cosine of angle $2x$. It is two times the angle $x$. The value of $\cos 2x$ is between $ - 1$ and $1$.
Formula used:
Period: The period goes from one peak to the next (or from any point to the next matching point).
Amplitude: The amplitude is the height from the center line to the peak (or to the trough). Or we can measure the height from highest to lowest points and divide them by $2$.
Phase Shift: The phase shift is how far the function is shifted horizontally from the usual position.
Vertical Shift: The vertical shift is how far the function is shifted vertically from the usual position.
Complete step by step answer:
Use the form $a\cos \left( {bx - c} \right) + d$ to find the amplitude, period, phase shift, and vertical shift.
Compare the given equation $y = \cos 2x$with $a\cos \left( {bx - c} \right) + d$ and find variables $a,b,c$ and $d$.
$a = 1$, $b = 2$, $c = 0$ and $d = 0$.
Find the amplitude $\left| a \right|$.
Here, $a = 1$.
Amplitude, $\left| a \right| = 1$.
The period of the function can be calculated using $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| b \right|}}$.
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| b \right|}}$
Replace $b$ with $2$ in the formula for period.
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{{\left| 2 \right|}}$
The absolute value is the distance between a number and zero.
The distance between $0$ and $2$ is$2$.
Period: $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{2}$
Cancel the common factor of $2$.
Period: $\dfrac{{\not{2}\pi }}{{\not{2}}}$
Divide $\pi $ by $1$.
Period: $\pi $
Find the phase shift using the formula $\dfrac{c}{b}$.
The phase shift of the function can be calculated from $\dfrac{c}{b}$.
Phase Shift: $\dfrac{c}{b}$
Replace the values of $c$ and $b$ in the equation for phase shift.
Phase Shift: $\dfrac{0}{2}$
Divide $0$ by $2$.
Phase Shift: $0$
Find the vertical shift $d$.
Vertical Shift: $0$
Now we have to List the properties of the trigonometric function.
Amplitude: $1$
Period: $\pi $
Phase Shift: $0$($0$ to the right)
Vertical Shift: $0$
Also, we select a few points to graph.
Find the point at $x = 0$.
Replace the variable $x$ with $0$ in the expression.
$f\left( 0 \right) = \cos \left( {2\left( 0 \right)} \right)$
Multiply $2$ by $0$.
$f\left( 0 \right) = \cos \left( 0 \right)$
The exact value of $\cos \left( 0 \right)$ is $1$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( 0 \right) = 1$
The final answer is $1$.
Find the point at $x = \dfrac{\pi }{4}$.
Replace the variable $x$ with $\dfrac{\pi }{4}$ in the expression.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) = \cos \left( {2\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right)} \right)$
Cancel the common factor of $2$.
Factor $2$ out of $4$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) = \cos \left( {2\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{{2\left( 2 \right)}}} \right)} \right)$
Cancel the common factor.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) = \cos \left( {\not{2}\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{{2 \times \not{2}}}} \right)} \right)$
Rewrite the expression.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) = \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)$
The exact value of $\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)$ is $0$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) = 0$
The final answer is $0$.
Also, we have to find the point at $x = \dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Replace the variable $x$ with $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ in the expression.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = \cos \left( {2\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)} \right)$
Cancel the common factor of $2$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = \cos \left( {\not{2}\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{{\not{2}}}} \right)} \right)$
Rewrite the expression.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = \cos \left( \pi \right)$
Apply the reference angle by finding the angle with equivalent trigonometric values in the first quadrant.
Make the expression negative because cosine is negative in the second quadrant.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = - \cos \left( 0 \right)$
The exact value of $\cos \left( 0 \right)$ is $1$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = - 1 \times 1$
Multiply $ - 1$ by $1$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) = - 1$
The final answer is $ - 1$.
Again, we have to find the point at $x = \dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}$.
Replace the variable $x$ with $\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}$ in the expression.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) = \cos \left( {2\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right)} \right)$
Cancel the common factor of $2$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) = \cos \left( {2\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{{2\left( 2 \right)}}} \right)} \right)$
Cancel the common factor.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) = \cos \left( {\not{2}\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{{2 \cdot \not{2}}}} \right)} \right)$
Rewrite the expression.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) = \cos \left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}} \right)$
Apply the reference angle by finding the angle with equivalent trigonometric values in the first quadrant.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) = - \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)$
The exact value of $\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)$ is $0$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( {\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}} \right) = 0$
The final answer is $0$.
Find the point at $x = \pi $.
Replace the variable $x$ with $\pi $ in the expression.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( \pi \right) = \cos \left( {2\left( \pi \right)} \right)$
$2\pi $ is a full rotation so replace with $0$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( \pi \right) = \cos \left( 0 \right)$
The exact value of $\cos \left( 0 \right)$ is $1$.
$ \Rightarrow f\left( \pi \right) = 1$
The final answer is $1$.
List the points in a table.
| $x$ | $f\left( x \right)$ |
| $0$ | $1$ |
| $\dfrac{\pi }{4}$ | $0$ |
| $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ | $ - 1$ |
| $\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}$ | $0$ |
| $\pi $ | $1$ |
The trigonometric function can be graphed using the amplitude, period, phase shift, vertical shift and the points.
Amplitude: $1$
Period: $\pi $
Phase Shift: $0$($0$ to the right)
Vertical Shift: $0$
| $x$ | $f\left( x \right)$ |
| $0$ | $1$ |
| $\dfrac{\pi }{4}$ | $0$ |
| $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ | $ - 1$ |
| $\dfrac{{3\pi }}{4}$ | $0$ |
| $\pi $ | $1$ |

Note: $\cos 2x$ and $2\cos x$ are entirely different terms.
$2\cos x$ is twice the cosine of angle $x$. It lies between $ - 2$ and $2$.
$\cos 2x$ is the cosine of angle $2x$. It is two times the angle $x$. The value of $\cos 2x$ is between $ - 1$ and $1$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




