
How do you solve $2{{x}^{2}}-x-6=0$?
Answer
550.8k+ views
Hint: In this problem we need to solve the given quadratic equation i.e., we need to calculate the values of $x$ where the given equation is satisfied. For solving a quadratic equation, we have several methods. But in the problem, we are going to use the quadratic formula which is given by $x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$. For this we need to compare the given equation with the standard quadratic equation $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$ and write the values of $a$, $b$, $c$. Now we will substitute those values in the formula $x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$ and simplify the obtained equation to get the required result.
Complete step by step solution:
Given equation $2{{x}^{2}}-x-6=0$.
Comparing the above quadratic equation with standard quadratic equation $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$, then we will get the values of $a$, $b$, $c$ as
$a=2$, $b=-1$, $c=-6$.
We have the quadratic formula for the solution as
$x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$
Substituting the values of $a$, $b$, $c$ in the above equation, then we will get
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-\left( -1 \right)\pm \sqrt{{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 2 \right)\left( -6 \right)}}{2\left( 2 \right)}$
We know that when we multiplied a negative sign with the negative sign, then we will get a positive sign. Applying the above rule and simplifying the above equation, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1\pm \sqrt{1+48}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1\pm \sqrt{49}}{4} \\
\end{align}$
In the above equation we have the value $\sqrt{49}$. We need to simplify this value to get the simplified result. We can write $49=7\times 7={{7}^{2}}$, then the value of $\sqrt{49}$ will be $\sqrt{49}=\sqrt{{{7}^{2}}}=7$. Substituting this value in the above equation, then we will get
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1\pm 7}{4}$
Calculating each value individually, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1+7}{4}\text{ or }\dfrac{1-7}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{8}{4}\text{ or }\dfrac{-6}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow x=2\text{ or }-\dfrac{3}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the solution of the given quadratic equation $2{{x}^{2}}-x-6=0$ are $x=2,-\dfrac{3}{2}$.
Note: We can also see the graph of the above given equation to observe the roots of the equation. When we plot the graph of the given equation $2{{x}^{2}}-x-6=0$ it looks like below graph
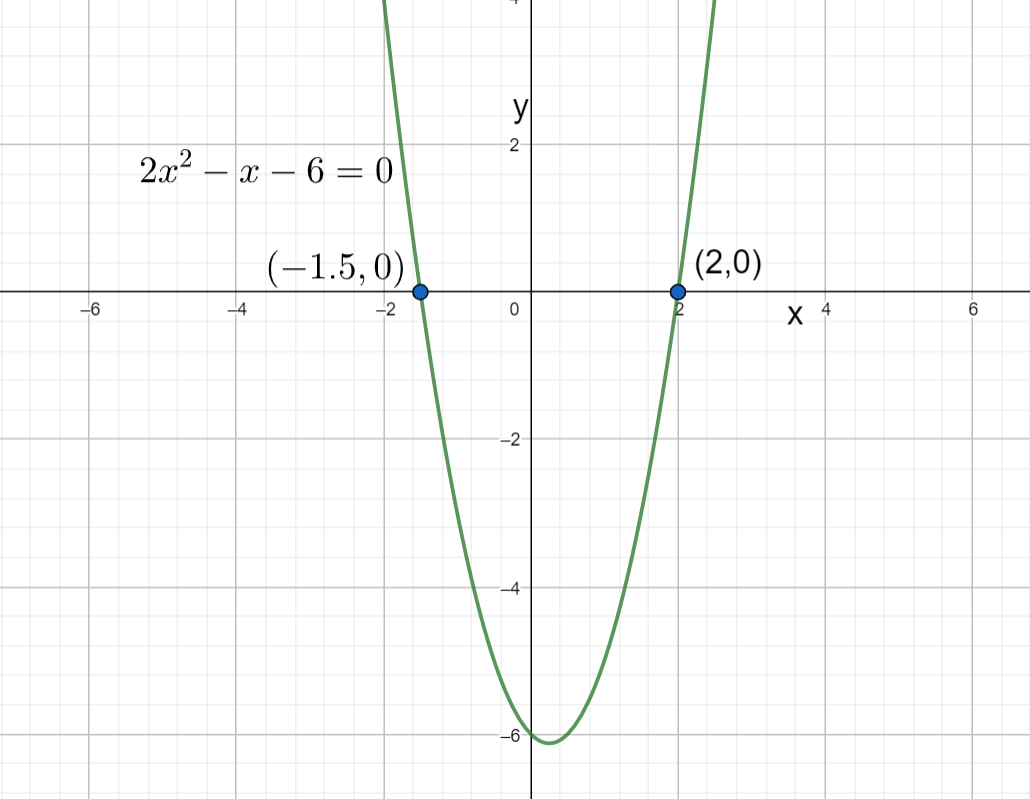
From the above graph also, we can say that the roots of the given equation $2{{x}^{2}}-x-6=0$ are $x=2,-\dfrac{3}{2}$.
Complete step by step solution:
Given equation $2{{x}^{2}}-x-6=0$.
Comparing the above quadratic equation with standard quadratic equation $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$, then we will get the values of $a$, $b$, $c$ as
$a=2$, $b=-1$, $c=-6$.
We have the quadratic formula for the solution as
$x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$
Substituting the values of $a$, $b$, $c$ in the above equation, then we will get
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-\left( -1 \right)\pm \sqrt{{{\left( -1 \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 2 \right)\left( -6 \right)}}{2\left( 2 \right)}$
We know that when we multiplied a negative sign with the negative sign, then we will get a positive sign. Applying the above rule and simplifying the above equation, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1\pm \sqrt{1+48}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1\pm \sqrt{49}}{4} \\
\end{align}$
In the above equation we have the value $\sqrt{49}$. We need to simplify this value to get the simplified result. We can write $49=7\times 7={{7}^{2}}$, then the value of $\sqrt{49}$ will be $\sqrt{49}=\sqrt{{{7}^{2}}}=7$. Substituting this value in the above equation, then we will get
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1\pm 7}{4}$
Calculating each value individually, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1+7}{4}\text{ or }\dfrac{1-7}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{8}{4}\text{ or }\dfrac{-6}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow x=2\text{ or }-\dfrac{3}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the solution of the given quadratic equation $2{{x}^{2}}-x-6=0$ are $x=2,-\dfrac{3}{2}$.
Note: We can also see the graph of the above given equation to observe the roots of the equation. When we plot the graph of the given equation $2{{x}^{2}}-x-6=0$ it looks like below graph

From the above graph also, we can say that the roots of the given equation $2{{x}^{2}}-x-6=0$ are $x=2,-\dfrac{3}{2}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




