
How does an enzyme work?
Answer
555k+ views
Hint: Enzymes are the biological molecules which are always or mostly protein that catalyses or speeds up a biological reaction. Enzymes are present in the living system and they work by following the ‘lock and key model’ hypothesis.
Complete answer:
Before explaining the working of an enzyme we need to understand a few terminologies:
• Reactants: The molecules which undergo a chemical reaction are called reactants.
• Product: Reactants undergo a chemical reaction to give a product.
• Catalyst: A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without itself reacting with other substances or reactants.
• Enzyme: An enzyme is a catalyst for a biological system that speeds up any biological reaction taking place in a living system. Enzymes are proteins.
• Active site: The site at which the substrate or reactants bind to an enzyme is called an active site.

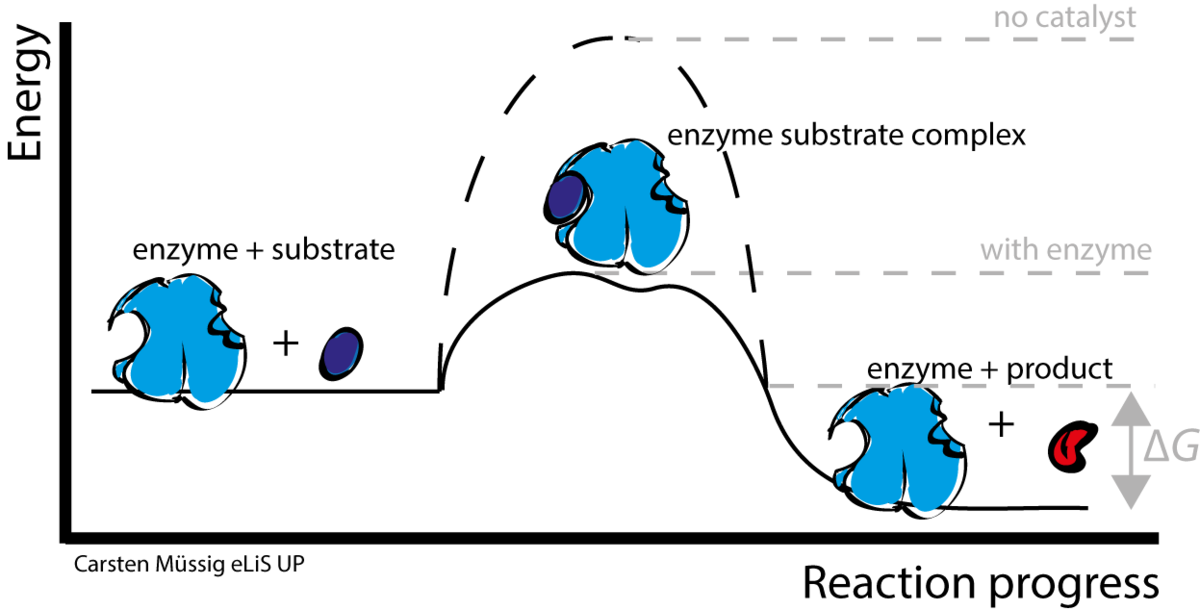
Mechanism of enzyme function:
The working of an enzyme or binding of an enzyme to a substrate is compared to the lock-and-key model or induced fit model. The enzyme binds to a particular substrate by its active site and forms an enzyme-substrate complex which further gives rise to the product. Once the product is formed the enzyme leaves the substrate and the reaction. The enzyme doesn’t directly participate in the reaction but only facilitates the reaction and once the product is formed it leaves the particular biological reaction.
Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy as well as the transition state energy of a particular reaction. Activation energy is the energy required to initiate a particular biological or biochemical reaction. The transition state is the unstable state which reactants must overcome to form products.
Once these are achieved the role of the enzyme is accomplished.
Note: As we know enzymes are proteins and building blocks for proteins are amino acids so the specificity of enzyme comes from its active site i.e. the structure and arrangement of amino acids.
The working of the enzyme depends on numerous factors –
• Temperature very high temperature denatures an enzyme.
• pH- if optimum pH is not maintained the enzyme function may lose.
Complete answer:
Before explaining the working of an enzyme we need to understand a few terminologies:
• Reactants: The molecules which undergo a chemical reaction are called reactants.
• Product: Reactants undergo a chemical reaction to give a product.
• Catalyst: A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without itself reacting with other substances or reactants.
• Enzyme: An enzyme is a catalyst for a biological system that speeds up any biological reaction taking place in a living system. Enzymes are proteins.
• Active site: The site at which the substrate or reactants bind to an enzyme is called an active site.

Mechanism of enzyme function:
The working of an enzyme or binding of an enzyme to a substrate is compared to the lock-and-key model or induced fit model. The enzyme binds to a particular substrate by its active site and forms an enzyme-substrate complex which further gives rise to the product. Once the product is formed the enzyme leaves the substrate and the reaction. The enzyme doesn’t directly participate in the reaction but only facilitates the reaction and once the product is formed it leaves the particular biological reaction.
Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy as well as the transition state energy of a particular reaction. Activation energy is the energy required to initiate a particular biological or biochemical reaction. The transition state is the unstable state which reactants must overcome to form products.
Once these are achieved the role of the enzyme is accomplished.

Note: As we know enzymes are proteins and building blocks for proteins are amino acids so the specificity of enzyme comes from its active site i.e. the structure and arrangement of amino acids.
The working of the enzyme depends on numerous factors –
• Temperature very high temperature denatures an enzyme.
• pH- if optimum pH is not maintained the enzyme function may lose.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




