
How is sin calculated?
Answer
545.1k+ views
Hint: In a right triangle, sin of an angle is the length of the side opposite to it divided by the length of the hypotenuse of the angle. i.e.
\[\sin (angle)=\dfrac{length \;of \;opposite \;side}{length \;of\; hypotenuse}\]
Complete step by step solution:
Consider a right angled triangle ABC such that
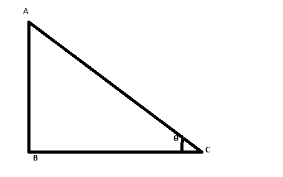
The sine of angle \[\theta \] is given as
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{AB}{AC}\]
Here, as we can see in the figure , the side AB is called the perpendicular of the triangle and the side BC as the base whereas the side AC is called the hypotenuse of the triangle.
Therefore, we can write that
\[\begin{align}
& AB=P \\
& BC=B \\
& AC=H \\
\end{align}\]
Such that
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{P}{H}\]
Formula used: An angle which forms the part of a right angled triangle, it is very easy to determine the sine function of that angle. The formula used to determine sine of an angle is
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{P}{H}\]
Where, \[P\] is the perpendicular of the triangle and \[H\] is the hypotenuse of the triangle.
Additional information: The other trigonometric functions of the angle can be defined similarly; for example, the cosine of the angle is the ratio between the adjacent side and the hypotenuse, while the tangent gives the ratio between the opposite and adjacent sides
So, the correct answer is “ \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{P}{H}\] ”.
Note: It is very important to carefully recognize the three sides of the triangle. Confusing base with perpendicular can convert sine to cosine or vice versa. Similarly, taking the longest side only as the hypotenuse is very important. The value of \[\sin \theta \] lies in the range between the values \[\left[ -1,+1 \right] \] so if you get any value that is less than \[-1\] or more than \[+1\] denotes a calculation mistake.
\[\sin (angle)=\dfrac{length \;of \;opposite \;side}{length \;of\; hypotenuse}\]
Complete step by step solution:
Consider a right angled triangle ABC such that

The sine of angle \[\theta \] is given as
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{AB}{AC}\]
Here, as we can see in the figure , the side AB is called the perpendicular of the triangle and the side BC as the base whereas the side AC is called the hypotenuse of the triangle.
Therefore, we can write that
\[\begin{align}
& AB=P \\
& BC=B \\
& AC=H \\
\end{align}\]
Such that
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{P}{H}\]
Formula used: An angle which forms the part of a right angled triangle, it is very easy to determine the sine function of that angle. The formula used to determine sine of an angle is
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{P}{H}\]
Where, \[P\] is the perpendicular of the triangle and \[H\] is the hypotenuse of the triangle.
Additional information: The other trigonometric functions of the angle can be defined similarly; for example, the cosine of the angle is the ratio between the adjacent side and the hypotenuse, while the tangent gives the ratio between the opposite and adjacent sides
So, the correct answer is “ \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{P}{H}\] ”.
Note: It is very important to carefully recognize the three sides of the triangle. Confusing base with perpendicular can convert sine to cosine or vice versa. Similarly, taking the longest side only as the hypotenuse is very important. The value of \[\sin \theta \] lies in the range between the values \[\left[ -1,+1 \right] \] so if you get any value that is less than \[-1\] or more than \[+1\] denotes a calculation mistake.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




