
How is soil formed?
Answer
591k+ views
Hint:
The soil covers mainly 2 layers of earth’s profile and they are mainly topsoil and subsoil. Soil formation is slow but a continuous process which consists of gradual breakdown of rocks through the process of weathering.
Complete answer:
Soil is one of the thinnest layers of material covering earth’s surface and it is formed due to weathering of rocks. Weathering is generally of three types: physical, chemical or biological.
PHYSICAL WEATHERING: - It is breakdown of rocks due to mechanical actions. Which consists of temperature change, abrasion (rocks collide with each other to form soil) or frost which lead to breakdown of the rocks.
CHEMICAL WEATHERING: - It is breakdown of rocks due to change in rock’s chemical makeup. This process happens when minerals present within the rocks react with water, air, or any other chemical components present in the atmosphere.
BIOLOGICAL WEATHERING: - It is the breakdown of rocks by living organisms. When animals dig in the rocks and provide water and air within them, plant roots begin to grow in those cracks, which eventually lead the rocks to split.
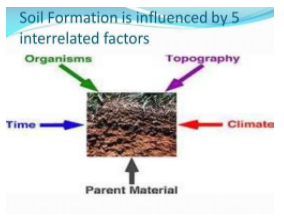
Soil is a mixture of certain mineral particles like organic materials, air, water and some of the living organisms. It is a slow but constant process. Plants get their nutrients mainly from soil and animals, birds and humans feed on those plants. Material can be accumulated through the water, wind and gravity which mainly contribute to the process of soil formation. The process of soil formation can take up to five to ten thousand years.
Note:
Soil is a valuable resource for our planet and it needs to be managed or it can be destroyed easily. If we get to know about soil management and try to manage it properly, then we can avoid the distribution of our environments, essential building blocks and natural habitat of many living organisms.
The soil covers mainly 2 layers of earth’s profile and they are mainly topsoil and subsoil. Soil formation is slow but a continuous process which consists of gradual breakdown of rocks through the process of weathering.
Complete answer:
Soil is one of the thinnest layers of material covering earth’s surface and it is formed due to weathering of rocks. Weathering is generally of three types: physical, chemical or biological.
PHYSICAL WEATHERING: - It is breakdown of rocks due to mechanical actions. Which consists of temperature change, abrasion (rocks collide with each other to form soil) or frost which lead to breakdown of the rocks.
CHEMICAL WEATHERING: - It is breakdown of rocks due to change in rock’s chemical makeup. This process happens when minerals present within the rocks react with water, air, or any other chemical components present in the atmosphere.
BIOLOGICAL WEATHERING: - It is the breakdown of rocks by living organisms. When animals dig in the rocks and provide water and air within them, plant roots begin to grow in those cracks, which eventually lead the rocks to split.
Soil is a mixture of certain mineral particles like organic materials, air, water and some of the living organisms. It is a slow but constant process. Plants get their nutrients mainly from soil and animals, birds and humans feed on those plants. Material can be accumulated through the water, wind and gravity which mainly contribute to the process of soil formation. The process of soil formation can take up to five to ten thousand years.

Note:
Soil is a valuable resource for our planet and it needs to be managed or it can be destroyed easily. If we get to know about soil management and try to manage it properly, then we can avoid the distribution of our environments, essential building blocks and natural habitat of many living organisms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




