
Human eye is sensitive to light of wavelength__________.
(a) 80-280nm
(b) 280-380nm
(c) 380-760nm
(d) 760-880nm
Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: The human eye is sensitive to the wavelength range of the visible spectrum. The visible light is detected by photoreceptor cells known as cones and rods. Cones are associated with daylight vision and color vision while the rods are associated with vision under the low light.
Complete answer:
The human eye is sensitive to light of wavelength 380-760 nm. It is the wavelength range of the visible spectrum. The human eye is a sense organ that receives visual images, which are then sent to the brain for understanding the view.
Outline of the eye:
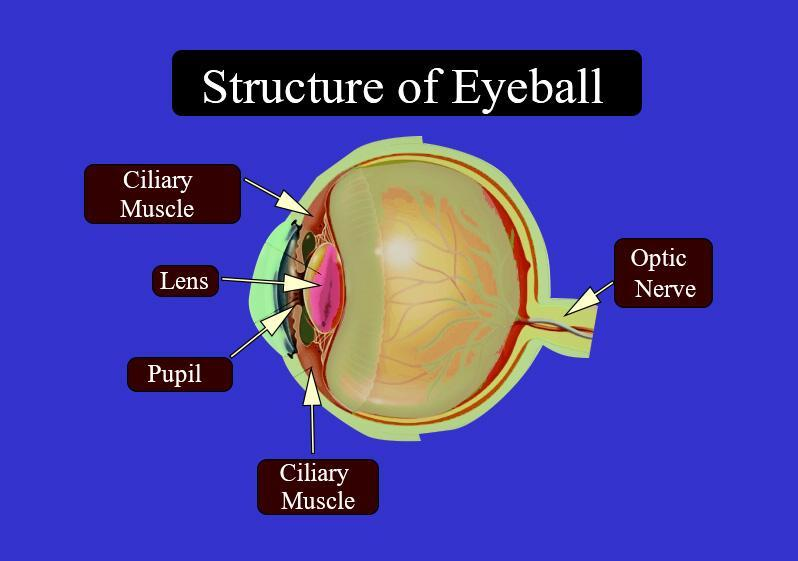
The cornea: It is a transparent structure present at the very front of the eye. It helps to focus the incoming light. A clear fluid called the aqueous humor is present between the cornea and the iris.
Iris: Behind the cornea, there is a colored, ring-shaped membrane known as the iris. It has a round customizable opening called the pupil, which controls the measure of light entering the eye.
Lens: It is situated behind the pupil and a colorless, transparent structure.
Ciliary muscles: It not only surrounds the lens but also holds it. It plays an important role in vision. On relaxation of the muscles, they pull and flatten the lens, allowing the eye to see objects far away. The ciliary muscle must contract to thicken the lens and to see closer objects.
So, the correct answer is, ’380-760nm.’
Note: Nearsightedness (can see near but not far objects) and farsightedness (can see far but not near objects) are two very common and very different types of vision defects. Both defects are due to refractive error abnormalities of the eye that affect its ability to focus light on the retina.
Complete answer:
The human eye is sensitive to light of wavelength 380-760 nm. It is the wavelength range of the visible spectrum. The human eye is a sense organ that receives visual images, which are then sent to the brain for understanding the view.
Outline of the eye:
The cornea: It is a transparent structure present at the very front of the eye. It helps to focus the incoming light. A clear fluid called the aqueous humor is present between the cornea and the iris.
Iris: Behind the cornea, there is a colored, ring-shaped membrane known as the iris. It has a round customizable opening called the pupil, which controls the measure of light entering the eye.
Lens: It is situated behind the pupil and a colorless, transparent structure.
Ciliary muscles: It not only surrounds the lens but also holds it. It plays an important role in vision. On relaxation of the muscles, they pull and flatten the lens, allowing the eye to see objects far away. The ciliary muscle must contract to thicken the lens and to see closer objects.

So, the correct answer is, ’380-760nm.’
Note: Nearsightedness (can see near but not far objects) and farsightedness (can see far but not near objects) are two very common and very different types of vision defects. Both defects are due to refractive error abnormalities of the eye that affect its ability to focus light on the retina.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




