
What is the hybridization of carbenes?
(a) $s{{p}^{2}}$
(b) $s{{p}^{3}}$
(c) $sp$
(d) $s{{p}^{3}}d$
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: Carbenes are those compounds in the carbon consists of total six electrons in its valence and the remaining two electrons are present as unpaired electrons and in singlet carbenes, one s and two p orbitals of the same shell of an atom mix to form three equivalent orbital and in triplet carbenes, one s and one p orbital of the atom mix to form two new equivalent orbitals. Now you can easily identify its hybridization.
Complete answer:
First of all ,let’s discuss what carbenes are. Carbenes are the neutral divalent species in which a carbon is covalently bonded to two atoms and has got two non-bonding orbitals having two electrons between them.
In simple words, we can say that the carbenes contain a neutral carbon atom having six electrons in the valence shell out of which two are unshared.
Carbenes are highly reactive species having a very short life period.
The carbenes exist in two distinct states;
1. Singlet carbenes: These are the carbenes in which unshared electrons are paired(i.e. they are present in one orbitals).
2.Triplet carbenes: These are the carbenes in which unshared electrons are not paired(i.e. they are present in different orbitals).
Example: methylene carbene can have either of the following two structures depending upon its mode of formation.
Triplet carbenes present biradicals i.e. divalent free radicals.
In singlet carbenes, the central carbon atom is in a state of $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridization. One of the three $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals, two are used in forming two single bonds with the monovalent atoms or groups attached to carbon. The third $s{{p}^{2}}$ orbital contains the unshared pair of electrons while the unhybridized p-orbital is empty. The structure of singlet carbenes is as;
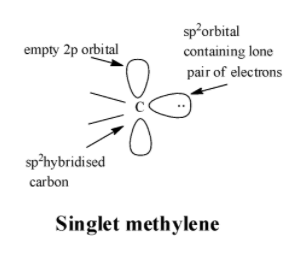
In triplet carbenes, the central carbon atom is in a state of $sp$ hybridization. The two $sp$ hybrid orbitals are used in forming single bonds with the two monovalent atoms or groups attached to carbon. The two unhybridized p-orbitals contain one unshared electron each. The structure of triplet carbenes is as;
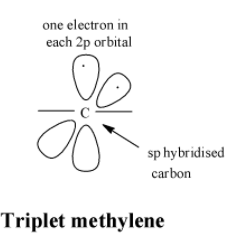
So, thus the hybridization of singlet carbenes is $s{{p}^{2}}$ and that of the triplet carbenes is $sp$.
Hence, option (a) and (c) both are correct.
Note:
The triplet carbenes are lower in energy and therefore, more stable than singlet carbenes because in triplet carbenes the electrons occupy different orbitals and the electron repulsion is much less than that in case of singlet carbenes where the repulsions are more due to the presence of electrons in the same orbitals.
Complete answer:
First of all ,let’s discuss what carbenes are. Carbenes are the neutral divalent species in which a carbon is covalently bonded to two atoms and has got two non-bonding orbitals having two electrons between them.
In simple words, we can say that the carbenes contain a neutral carbon atom having six electrons in the valence shell out of which two are unshared.
Carbenes are highly reactive species having a very short life period.
The carbenes exist in two distinct states;
1. Singlet carbenes: These are the carbenes in which unshared electrons are paired(i.e. they are present in one orbitals).
2.Triplet carbenes: These are the carbenes in which unshared electrons are not paired(i.e. they are present in different orbitals).
Example: methylene carbene can have either of the following two structures depending upon its mode of formation.
Triplet carbenes present biradicals i.e. divalent free radicals.
In singlet carbenes, the central carbon atom is in a state of $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridization. One of the three $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals, two are used in forming two single bonds with the monovalent atoms or groups attached to carbon. The third $s{{p}^{2}}$ orbital contains the unshared pair of electrons while the unhybridized p-orbital is empty. The structure of singlet carbenes is as;

In triplet carbenes, the central carbon atom is in a state of $sp$ hybridization. The two $sp$ hybrid orbitals are used in forming single bonds with the two monovalent atoms or groups attached to carbon. The two unhybridized p-orbitals contain one unshared electron each. The structure of triplet carbenes is as;

So, thus the hybridization of singlet carbenes is $s{{p}^{2}}$ and that of the triplet carbenes is $sp$.
Hence, option (a) and (c) both are correct.
Note:
The triplet carbenes are lower in energy and therefore, more stable than singlet carbenes because in triplet carbenes the electrons occupy different orbitals and the electron repulsion is much less than that in case of singlet carbenes where the repulsions are more due to the presence of electrons in the same orbitals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




