
Hydra reproduces by budding. This is an example of
A. Asexual reproduction
B. Sexual reproduction
C. Regeneration
D. Parthenocarpy
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in which, due to cell division at one specific location, a new organism emerges from an outgrowth or bud. The small bulb-like projection that comes out of the Hydra cell is called a bud. Since reproduction is asexual, the newly formed organism is a clone and the genetically identical to the parent organism except for mutations.
Complete answer:
Asexual reproduction is a form of reproduction that does not require the fusion of gametes. It requires only one parent. The offspring, which originates from asexual reproduction, is identical to the parent plant. The reproduction is differentiated into four types except for binary fission, such as spores, vegetative propagation, budding, and fragmentation.
Budding is a process in which a species reproduces by the production of small outgrowths from its cell. This outgrowth is referred to as a bud. New cells are formed from these buds.
The mechanism of budding in Hydra is given below:
● The nucleus divides.
● From the parent plant, an outgrowth grows which is known as bud.
● The bud receives the copy of the nucleus from the parent plant.
● The bud develops and gets mature. It then separates from the parent after taking a nucleus and small amount of cytoplasm.
● The bud grows into a well-developed Hydra.
The diagram of budding in Hydra is given below:
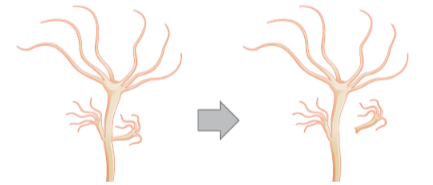
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Asexual and sexual reproduction are two different types of processes. Sexual reproduction requires male and female gametes for their fusion. The pollen grain comprises the male gamete while the ovule comprises the female gamete. Pollination is the method of transferring pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of another flower. The offspring is genetically different from the parent plants. On the contrary, in asexual reproduction, the new plant is obtained without the production of seeds or spores. The new plant is genetically identical to the parent.
Complete answer:
Asexual reproduction is a form of reproduction that does not require the fusion of gametes. It requires only one parent. The offspring, which originates from asexual reproduction, is identical to the parent plant. The reproduction is differentiated into four types except for binary fission, such as spores, vegetative propagation, budding, and fragmentation.
Budding is a process in which a species reproduces by the production of small outgrowths from its cell. This outgrowth is referred to as a bud. New cells are formed from these buds.
The mechanism of budding in Hydra is given below:
● The nucleus divides.
● From the parent plant, an outgrowth grows which is known as bud.
● The bud receives the copy of the nucleus from the parent plant.
● The bud develops and gets mature. It then separates from the parent after taking a nucleus and small amount of cytoplasm.
● The bud grows into a well-developed Hydra.
The diagram of budding in Hydra is given below:

Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Asexual and sexual reproduction are two different types of processes. Sexual reproduction requires male and female gametes for their fusion. The pollen grain comprises the male gamete while the ovule comprises the female gamete. Pollination is the method of transferring pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of another flower. The offspring is genetically different from the parent plants. On the contrary, in asexual reproduction, the new plant is obtained without the production of seeds or spores. The new plant is genetically identical to the parent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




