
Hydrogenation of the above compound in the presence of poisoned Pd catalyst gives:
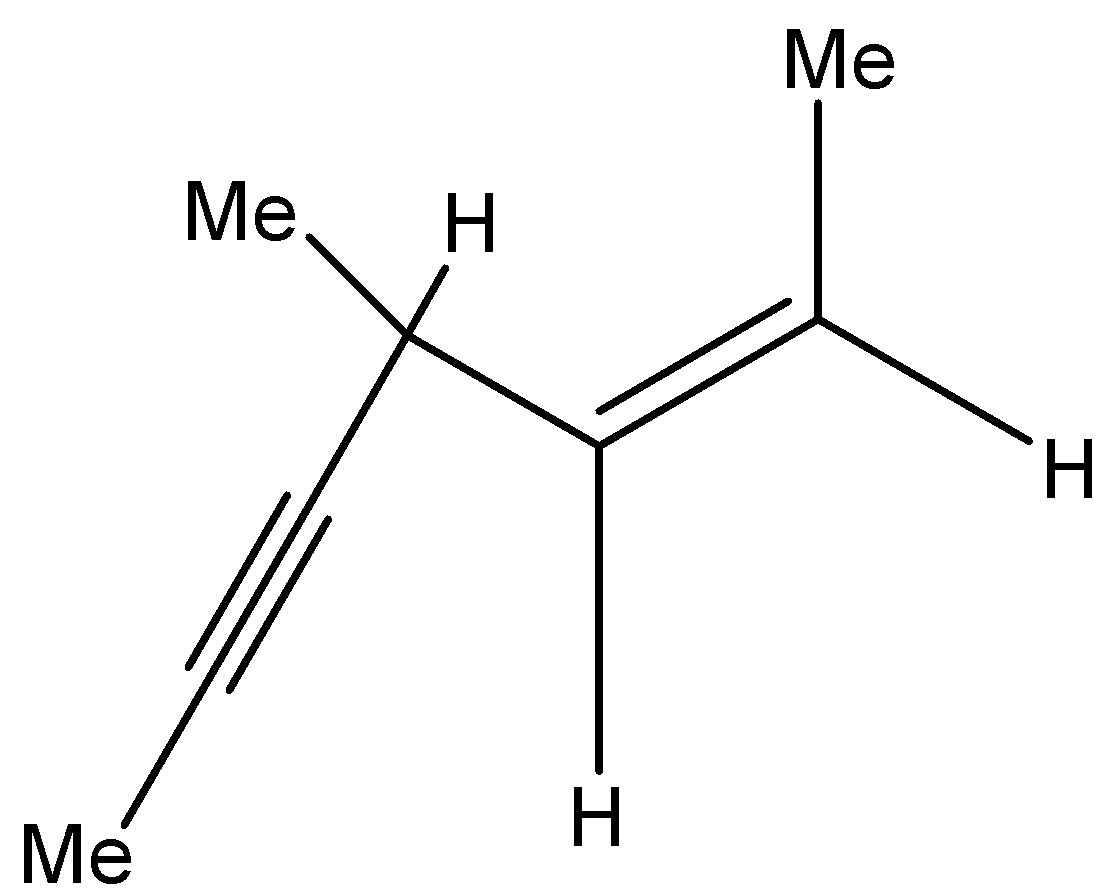
a.) – an optically active compound
b.) – an optically inactive compound
c.) – a racemic mixture
d.) – a diastereomeric mixture

Answer
524.9k+ views
Hint: In this question, we are given with the alkyne molecule that will be hydrogenated. It means that it will react in the presence of dihydrogen. Write the chemical reaction, and on the basis of the product formed we can decide the nature of the compound. It depends on the plane of symmetry.
Complete step by step solution:
Now, first we are given with the alkyne molecule. As mentioned, it undergoes hydrogenation in the presence of palladium.
So, we can say that it reacts with the dihydrogen, and if there is a poisoned palladium catalyst, then there will be presence of barium sulphate too.
Thus, we can write the chemical reaction for the given molecule, i.e.
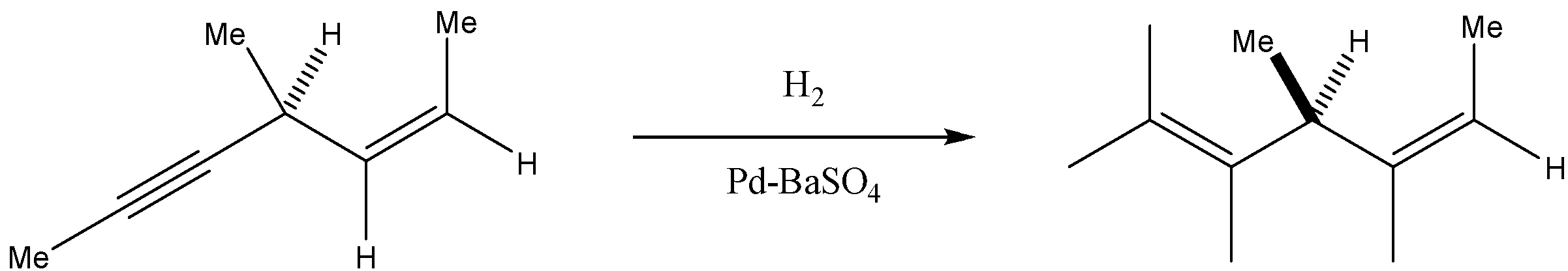
Here, we can see that the hydrogenation of alkyne molecules leads to the formation of alkene molecules.
Now, if we talk about the nature of the product, then we see it has a plane of symmetry.
In the options, racemic mixture, and diastereomeric mixture is incorrect, as the product formed is only one.
Now, if the molecule has a plane of symmetry, then it is considered to be an optically inactive compound.
In the last we can conclude that the hydrogenation of the above compound in the presence of a poisoned Pd catalyst gives an optically inactive compound.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note: There could be confusion in the two options, i.e. optically active compound, and optically inactive compound. The optically active compound is the compound which represents no plane of symmetry, whereas the optically inactive compound is the compound which represents the plane of symmetry.
Complete step by step solution:
Now, first we are given with the alkyne molecule. As mentioned, it undergoes hydrogenation in the presence of palladium.
So, we can say that it reacts with the dihydrogen, and if there is a poisoned palladium catalyst, then there will be presence of barium sulphate too.
Thus, we can write the chemical reaction for the given molecule, i.e.
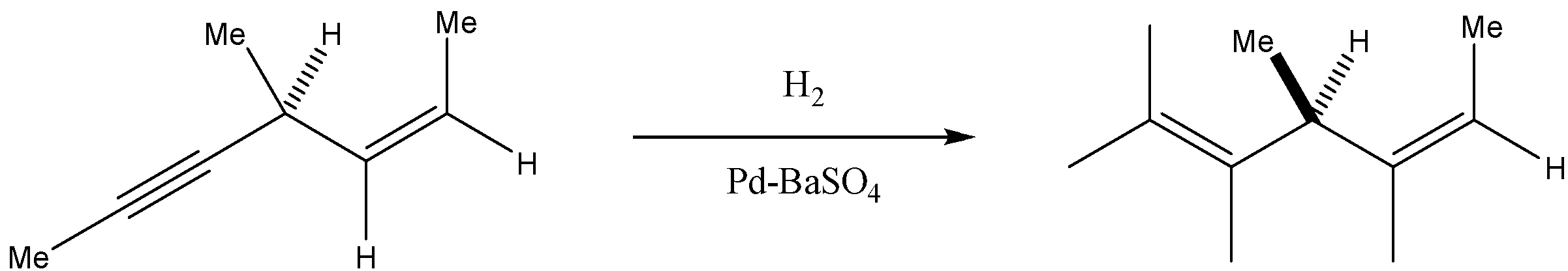
Here, we can see that the hydrogenation of alkyne molecules leads to the formation of alkene molecules.
Now, if we talk about the nature of the product, then we see it has a plane of symmetry.
In the options, racemic mixture, and diastereomeric mixture is incorrect, as the product formed is only one.
Now, if the molecule has a plane of symmetry, then it is considered to be an optically inactive compound.
In the last we can conclude that the hydrogenation of the above compound in the presence of a poisoned Pd catalyst gives an optically inactive compound.
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note: There could be confusion in the two options, i.e. optically active compound, and optically inactive compound. The optically active compound is the compound which represents no plane of symmetry, whereas the optically inactive compound is the compound which represents the plane of symmetry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




