
(i) State Ohm’s law.
(ii) Diagrammatically show how you will connect a key, a battery, a voltmeter, an ammeter, an unknown resistance and a rheostat so that it can be used to verify the law.
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint:Recall the statement for Ohm’s law. Also give the mathematical expression for Ohm’s law in terms of potential difference across the current carrying conductor, electric current flowing in the current carrying conductor and the resistance offered by the current carrying conductor to the electric current through it. Then construct a circuit diagram using a key, a battery, a voltmeter, an ammeter, an unknown resistance and a rheostat to verify Ohm’s law.
Complete step by step answer:
(i) Ohm’s law states that the potential difference across the two ends of a current carrying conductor is directly proportional to the electric current flowing through the current carrying conductor provided that the temperature and the physical properties of the current carrying conductor are kept constant.
\[V \propto I\]
\[ \Rightarrow V = IR\]
Here, is the potential difference across the ends of the conductor, is the electric current flowing through the conductor and is the constant of proportionality known as resistance of the conductor.
(ii) The circuit diagram to verify Ohm’s law is as follows:
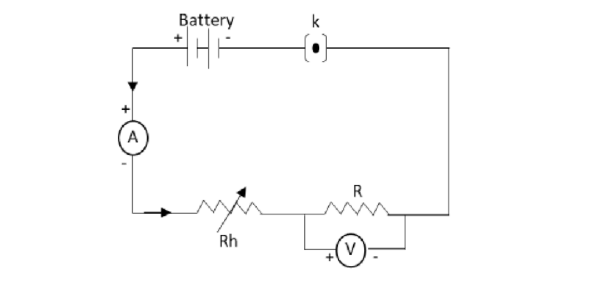
In the above circuit diagram, k is the key, R is the resistance, A is the ammeter, V is the voltmeter and Rh is the rheostat.
The supply of electric current from the battery is passed through the current carrying wire in which an ammeter is connected in series to measure the electric current flowing through the wire. The rheostat is used to adjust the resistance and a voltmeter which measures the potential difference between the ends of the current carrying wire is connected in parallel with the resistor of resistance R.
This circuit is used to verify Ohm’s law.
Note:While constructing the circuit diagram to verify Ohm’s law, the students should keep in mind that the voltmeter is always connected in parallel with the resistor in order to measure the same potential difference and an ammeter is always connected in series so that it can measure the same current which is flowing in the whole circuit because the resistance of the ammeter is very low.
Complete step by step answer:
(i) Ohm’s law states that the potential difference across the two ends of a current carrying conductor is directly proportional to the electric current flowing through the current carrying conductor provided that the temperature and the physical properties of the current carrying conductor are kept constant.
\[V \propto I\]
\[ \Rightarrow V = IR\]
Here, is the potential difference across the ends of the conductor, is the electric current flowing through the conductor and is the constant of proportionality known as resistance of the conductor.
(ii) The circuit diagram to verify Ohm’s law is as follows:

In the above circuit diagram, k is the key, R is the resistance, A is the ammeter, V is the voltmeter and Rh is the rheostat.
The supply of electric current from the battery is passed through the current carrying wire in which an ammeter is connected in series to measure the electric current flowing through the wire. The rheostat is used to adjust the resistance and a voltmeter which measures the potential difference between the ends of the current carrying wire is connected in parallel with the resistor of resistance R.
This circuit is used to verify Ohm’s law.
Note:While constructing the circuit diagram to verify Ohm’s law, the students should keep in mind that the voltmeter is always connected in parallel with the resistor in order to measure the same potential difference and an ammeter is always connected in series so that it can measure the same current which is flowing in the whole circuit because the resistance of the ammeter is very low.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




