
Identify B in the given equation.
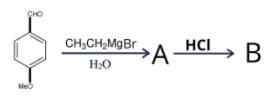
A.
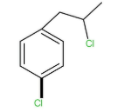
B.
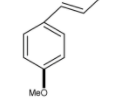
C.
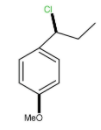
D.
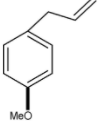





Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: In the presence of Grignard reagent, the addition of respective alkyl group in Grignard reagent and hydroxyl group occurs on the aldehyde group. And then nucleophilic substitution of the hydroxide group will occur.
Complete step by step answer:
In the above reaction the ethyl group in the Grignard reagent gets added to the aldehyde functional group. Hence the molecular formula of compound A forms will become:
\[{\text{MeO}}{{\text{C}}_6}{{\text{H}}_4}{\text{C}}({\text{OH}}){{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_5}\]
Alcohol molecule is present in the above molecule, and a strong acid is present that is \[{\text{HCl}}\]. Chloride ion acts as nucleophile because of the presence of negative charge and replaces the hydroxide group present in the molecule. The above reaction is known as the nucleophilic substitution reaction because one group substitutes the other group. The above is the type of \[{\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_1}\]. Carbocation is formed as an intermediate during the reaction. Rate of reaction will depend upon the stability of carbocation formed. More is the stability of carbocation higher is the rate of reaction. Since tertiary carbocation is more stable and hence the rate of \[{\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_1}\] reaction is maximum for tertiary alcohol whereas, the primary carbocation is least stable and hence will not easily forms. So the rate for primary alcohol is least.
Hence the correct option is C.
Note:
Grignard reagent is a very useful and important organometallic compound. Organometallic compounds are those compounds which contain carbon and metal bonds. The metal used in Grignard reagent is magnesium, hence it is called organomagnesium. It is generally written as RMgX. It was named after the scientist Victor Grignard.
Complete step by step answer:
In the above reaction the ethyl group in the Grignard reagent gets added to the aldehyde functional group. Hence the molecular formula of compound A forms will become:
\[{\text{MeO}}{{\text{C}}_6}{{\text{H}}_4}{\text{C}}({\text{OH}}){{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_5}\]
Alcohol molecule is present in the above molecule, and a strong acid is present that is \[{\text{HCl}}\]. Chloride ion acts as nucleophile because of the presence of negative charge and replaces the hydroxide group present in the molecule. The above reaction is known as the nucleophilic substitution reaction because one group substitutes the other group. The above is the type of \[{\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_1}\]. Carbocation is formed as an intermediate during the reaction. Rate of reaction will depend upon the stability of carbocation formed. More is the stability of carbocation higher is the rate of reaction. Since tertiary carbocation is more stable and hence the rate of \[{\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_1}\] reaction is maximum for tertiary alcohol whereas, the primary carbocation is least stable and hence will not easily forms. So the rate for primary alcohol is least.
Hence the correct option is C.
Note:
Grignard reagent is a very useful and important organometallic compound. Organometallic compounds are those compounds which contain carbon and metal bonds. The metal used in Grignard reagent is magnesium, hence it is called organomagnesium. It is generally written as RMgX. It was named after the scientist Victor Grignard.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 12 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




