
Identify the animal in the following diagram. How can this be evidence regarding evolution?

Answer
508.8k+ views
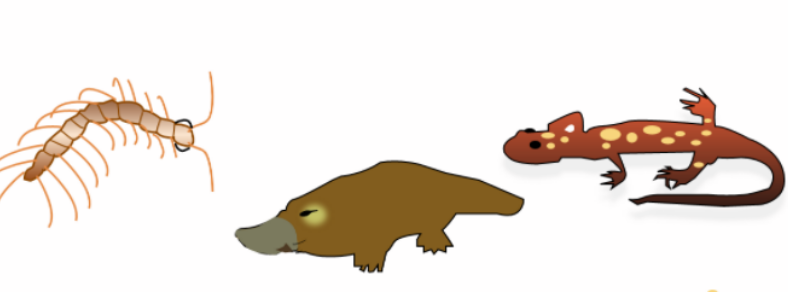
Hint: The first diagram is a predatory belonging to arthropods, the second one is a semi-aquatic egg-laying mammal and the last one belongs to a group of amphibians typically characterized by a lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults.
Complete answer
The unfolding of the process of different types of organism formation tells us about organic evolution.
1. Centipede- They belong to Myriapoda and their fossil records extend back to 430 million years ago. The modification of the first pair of legs into venomous forceps is unique in the animal world, resulting in venom-producing cells from the transformation of related subepidermal gland units into an adaptation to a new terrestrial predatory niche. It is one of the most ancient known terrestrial venomous organisms.
2. Duck-billed Platypus- has a link with both reptiles and mammals. Platypus was one of the earliest offshoots of mammals. At least 166 million years ago monotremes (which includes the platypus) are thought to have split from other mammals. This means that the platypus genes carry information on the evolutionary timeline leading from reptiles to mammals so we understand what genes were present in the ancestral reptiles and how mammals evolved their particular traits.
3. Salamander- Ancestral salamanders had a basic tetrapod body form and had a complex aquatic-to-terrestrial life cycle. In the embryonic development of all vertebrates (fishes to mammals) the gill lifts and notochord appears but the notochord is replaced by the vertebral column in all vertebrates.

Note:
Tetrapods are four-limbed animals which include amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Humans and even snakes are tetrapods even though one walks on two legs and the other has no legs to walk because they descend from the tetrapod ancestor.
Complete answer
The unfolding of the process of different types of organism formation tells us about organic evolution.
1. Centipede- They belong to Myriapoda and their fossil records extend back to 430 million years ago. The modification of the first pair of legs into venomous forceps is unique in the animal world, resulting in venom-producing cells from the transformation of related subepidermal gland units into an adaptation to a new terrestrial predatory niche. It is one of the most ancient known terrestrial venomous organisms.
2. Duck-billed Platypus- has a link with both reptiles and mammals. Platypus was one of the earliest offshoots of mammals. At least 166 million years ago monotremes (which includes the platypus) are thought to have split from other mammals. This means that the platypus genes carry information on the evolutionary timeline leading from reptiles to mammals so we understand what genes were present in the ancestral reptiles and how mammals evolved their particular traits.
3. Salamander- Ancestral salamanders had a basic tetrapod body form and had a complex aquatic-to-terrestrial life cycle. In the embryonic development of all vertebrates (fishes to mammals) the gill lifts and notochord appears but the notochord is replaced by the vertebral column in all vertebrates.

Note:
Tetrapods are four-limbed animals which include amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Humans and even snakes are tetrapods even though one walks on two legs and the other has no legs to walk because they descend from the tetrapod ancestor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




