
Identify the components labeled (A-D) in the given flow chart of the blood clotting process.
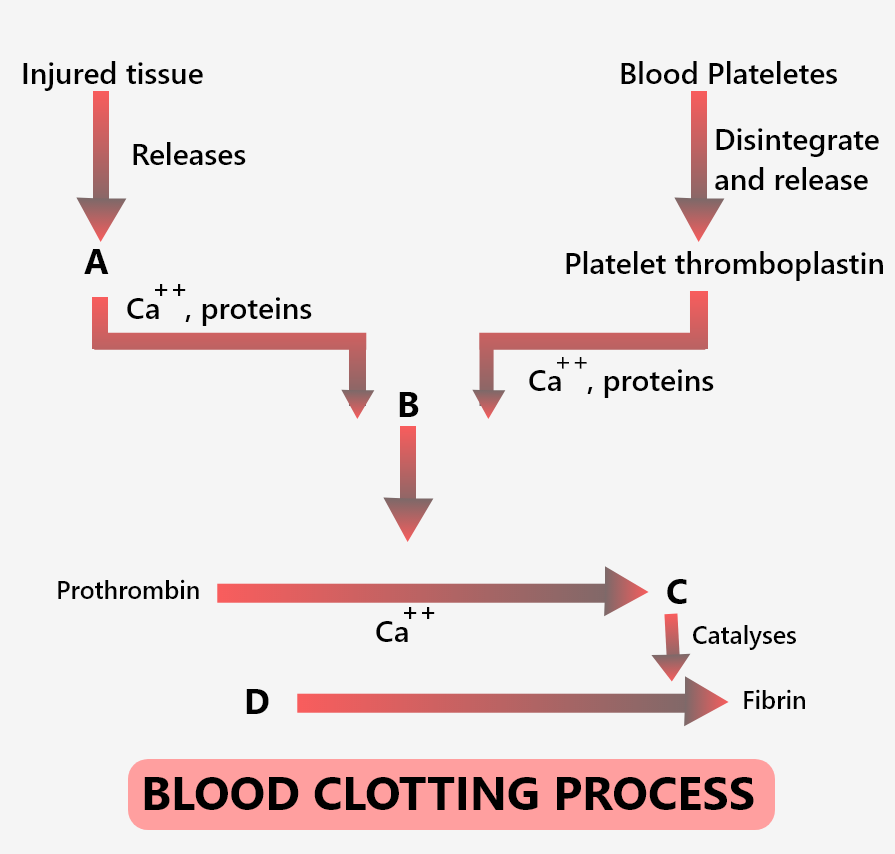
(a) A-Thromboplastin, B- Prothrombinase, C- Thrombin, D- Fibrinogen
(b) A- Fibrinogen, B- Thrombin, C - Prothrombinase, D- Thromboplastin
(c) A- Prothrombinase, B- Fibrinogen, C - Thromboplastin, D- Thrombin
(d) A- Thrombin, B- Thromboplastin, C - Fibrinogen, D- Prothrombinase

Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: The clotting of blood is a process of forming a clot with the help of platelets and proteins in your plasma in order to prevent excess loss of blood from the body. It makes the clot at the site of injury that stops the flow of blood.
Complete answer:
Given below are the major steps involved in the process of clotting of blood:
-Injury to the blood vessel (or tissues) releases thromboplastin and platelets disintegrate and release platelet thromboplastin.
-The above two in the presence of calcium ions and proteins come together to form a prothrombinase.
- Prothrombin is activated to thrombin with the help of prothrombinase and calcium ion.
- Fibrinogen is split to form fibrin by thrombin.
- A mesh is formed around the wound controlling RBC (red blood cells) by fibers present in fibrins that stop the bleeding.
- With days passing by, the clot hardens and becomes smaller in size.
- New skin cells are grown to rebuild the wounded site then plasmin enzymes are released and the clot is dissolved.
So, the correct answer is option A) ‘A-Thromboplastin, B- Prothrombinase, C- Thrombin, D- Fibrinogen’.
Note:
Different events can cause unnatural clotting and each factor may initiate clotting in a different way. There are molecules in your system that signal your body to where and when to form a clot. Certain factors such as obesity, smoking, cancer, diabetes, etc. slow the flow of blood in the veins. While healthy teenagers have increased natural ability to blood clotting and even certain medications can affect how quickly your blood clots.
Complete answer:
Given below are the major steps involved in the process of clotting of blood:
-Injury to the blood vessel (or tissues) releases thromboplastin and platelets disintegrate and release platelet thromboplastin.
-The above two in the presence of calcium ions and proteins come together to form a prothrombinase.
- Prothrombin is activated to thrombin with the help of prothrombinase and calcium ion.
- Fibrinogen is split to form fibrin by thrombin.
- A mesh is formed around the wound controlling RBC (red blood cells) by fibers present in fibrins that stop the bleeding.
- With days passing by, the clot hardens and becomes smaller in size.
- New skin cells are grown to rebuild the wounded site then plasmin enzymes are released and the clot is dissolved.
So, the correct answer is option A) ‘A-Thromboplastin, B- Prothrombinase, C- Thrombin, D- Fibrinogen’.
Note:
Different events can cause unnatural clotting and each factor may initiate clotting in a different way. There are molecules in your system that signal your body to where and when to form a clot. Certain factors such as obesity, smoking, cancer, diabetes, etc. slow the flow of blood in the veins. While healthy teenagers have increased natural ability to blood clotting and even certain medications can affect how quickly your blood clots.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




