
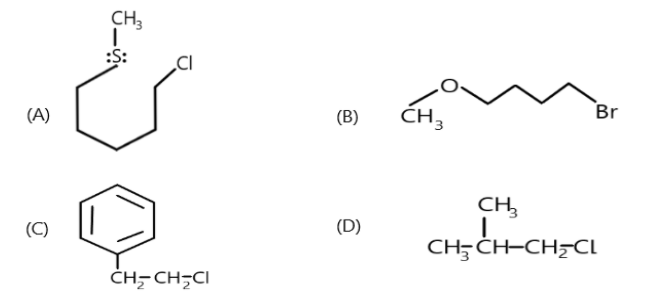
Identify the compound which may give NGP reaction:

Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: NGP is basically a neighbouring group participation reaction which is applied when a leaving group is removed by the help of the electrons pairs present on the neighbouring group or element in the same compound.
Complete step by step solution:
As we all know that in simple language we can say that NGP is basically a neighbouring group participation reaction which is applied when a leaving a group is removed by the help of the electrons pairs present on the neighbouring group or element in the same compound. It can easily take place where a five-membered or six-membered transition state is forming.
So in the given compounds, the first compound contains a lone pair of electrons on the sulphur which can abstract the hydrogen from the β-carbon adjacent to chlorine attached carbon which will result in the removal of chlorine from the compound. A six-membered transition state will be formed which is a highly stable transition state. Hence, this compound will give an NGP reaction.
In the second compound we can see that oxygen is present which contains the lone pair of electrons which will abstract the hydrogen from the β-carbon and a five- membered ring will be formed and a pi-bond will be formed and elimination of bromine will take place. Hence this compound will give an NGP reaction.
In the third compound, the chlorine will not be able to abstract the hydrogen, so the benzene ring will pass on its electron to the β-carbon which will help in removal of chlorine and a positive charge will be acquired on the benzene ring. A three membered ring attached with benzene will be formed. Now to remove the positive charge, the nucleophile can either eliminate or substitute and hence the compound will give NGP reaction.
In the last compound the leaving group is only chlorine and there is also no pi bond as well as no nucleophile so removal of chlorine will not take place. Hence this compound will not show NGP reaction.
Therefore the correct options are (A), (B) and (C).
Note: When NGP reactions take place the reaction rate normally increases which disturbs the stereochemistry of the reaction. The pi-orbitals present in an alkene can stabilise the transition state by delocalizing the positive charge of the carbocation.
Complete step by step solution:
As we all know that in simple language we can say that NGP is basically a neighbouring group participation reaction which is applied when a leaving a group is removed by the help of the electrons pairs present on the neighbouring group or element in the same compound. It can easily take place where a five-membered or six-membered transition state is forming.
So in the given compounds, the first compound contains a lone pair of electrons on the sulphur which can abstract the hydrogen from the β-carbon adjacent to chlorine attached carbon which will result in the removal of chlorine from the compound. A six-membered transition state will be formed which is a highly stable transition state. Hence, this compound will give an NGP reaction.
In the second compound we can see that oxygen is present which contains the lone pair of electrons which will abstract the hydrogen from the β-carbon and a five- membered ring will be formed and a pi-bond will be formed and elimination of bromine will take place. Hence this compound will give an NGP reaction.
In the third compound, the chlorine will not be able to abstract the hydrogen, so the benzene ring will pass on its electron to the β-carbon which will help in removal of chlorine and a positive charge will be acquired on the benzene ring. A three membered ring attached with benzene will be formed. Now to remove the positive charge, the nucleophile can either eliminate or substitute and hence the compound will give NGP reaction.
In the last compound the leaving group is only chlorine and there is also no pi bond as well as no nucleophile so removal of chlorine will not take place. Hence this compound will not show NGP reaction.
Therefore the correct options are (A), (B) and (C).
Note: When NGP reactions take place the reaction rate normally increases which disturbs the stereochemistry of the reaction. The pi-orbitals present in an alkene can stabilise the transition state by delocalizing the positive charge of the carbocation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




