
Identify the floral diagram
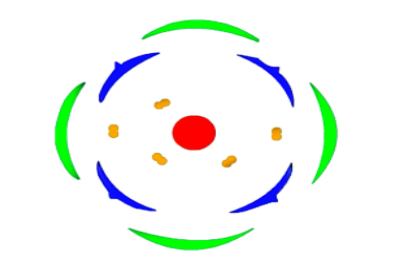
(a)Floral diagram of a family Brassicaceae
(b)Floral diagram of a family Solanaceae
(c)Floral diagram of a family Euphorbiaceae
(d)Floral diagram of a family Liliaceae

Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: species belonging to the present family are mostly annual, biennial, or perennial herbaceous plants, some are dwarf shrubs or shrubs, and really few vines. Although generally terrestrial, a couple of species like water awlwort live submerged in freshwater. they'll have a taproot or a sometimes woody caudex which will have few or many branches, some have thin or tuberous rhizomes, or rarely develop runners.
Complete answer:
The diagram is demonstrating sepals and petals as 4 free and is organized in valvate aestivation and in a cross structure. Hence, the given diagram contains a cruciform corolla. The androecium is 6 in number and is arranged in two whorls as 4 within the inner whorl and a couple of in an outer whorl. The central ovary shown is bilocular.
Flowers of Solanaceae are pentamerous i.e. sepals, petals and stamens are present within the set of 5.
In flowers of the Euphorbiaceae family, sometimes corolla is absent, and sometimes sepals, petals are present during a set of 5.
Blossoms of the Liliaceae are made out of 6 tepals (sepals and petals are indistinct), 6 stamens during a solitary whorl, and a trilocular ovary.
Flowers of Cruciferae show cruciform corolla, 6 stamens in two whorls (4+2), and a unilocular ovary which becomes bilocular thanks to the septum.
Additional information:
Blossoms could likewise be arranged in racemes, panicles, or corymbs, with pedicels here and there inside the axil of a bract, and few species have blossoms that sit exclusively on bloom stems that spring from the axils of rosette leaves. The orientation of the pedicels when fruits are ripe varies hooked on the species. The flowers are bisexual, star symmetrical (zygomorphic in Iberis and Teesdalia), and therefore the ovary positioned above the opposite floral parts.
So, the correct answer is ‘Floral diagram of a family Brassicaceae’.
Note: There's one superior pistil that consists of two carpels that will either sit directly above the bottom of the stamens or on a stalk. It initially consists of just one cavity but during its further development, a skinny wall grows that divides the cavity, both placentas, and separates the 2 valves (a so-called false septum). Rarely, there's just one cavity without a septum. The 2–600 ovules are usually along the side margin of the carpels, or rarely at the highest. Fruits are capsules that open with two valves, usually towards the highest.
Complete answer:
The diagram is demonstrating sepals and petals as 4 free and is organized in valvate aestivation and in a cross structure. Hence, the given diagram contains a cruciform corolla. The androecium is 6 in number and is arranged in two whorls as 4 within the inner whorl and a couple of in an outer whorl. The central ovary shown is bilocular.
Flowers of Solanaceae are pentamerous i.e. sepals, petals and stamens are present within the set of 5.
In flowers of the Euphorbiaceae family, sometimes corolla is absent, and sometimes sepals, petals are present during a set of 5.
Blossoms of the Liliaceae are made out of 6 tepals (sepals and petals are indistinct), 6 stamens during a solitary whorl, and a trilocular ovary.
Flowers of Cruciferae show cruciform corolla, 6 stamens in two whorls (4+2), and a unilocular ovary which becomes bilocular thanks to the septum.
Additional information:
Blossoms could likewise be arranged in racemes, panicles, or corymbs, with pedicels here and there inside the axil of a bract, and few species have blossoms that sit exclusively on bloom stems that spring from the axils of rosette leaves. The orientation of the pedicels when fruits are ripe varies hooked on the species. The flowers are bisexual, star symmetrical (zygomorphic in Iberis and Teesdalia), and therefore the ovary positioned above the opposite floral parts.
So, the correct answer is ‘Floral diagram of a family Brassicaceae’.
Note: There's one superior pistil that consists of two carpels that will either sit directly above the bottom of the stamens or on a stalk. It initially consists of just one cavity but during its further development, a skinny wall grows that divides the cavity, both placentas, and separates the 2 valves (a so-called false septum). Rarely, there's just one cavity without a septum. The 2–600 ovules are usually along the side margin of the carpels, or rarely at the highest. Fruits are capsules that open with two valves, usually towards the highest.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




