
Identify the part labeled as A, B, C, and E in the given diagram of human sperm and select the correct option.
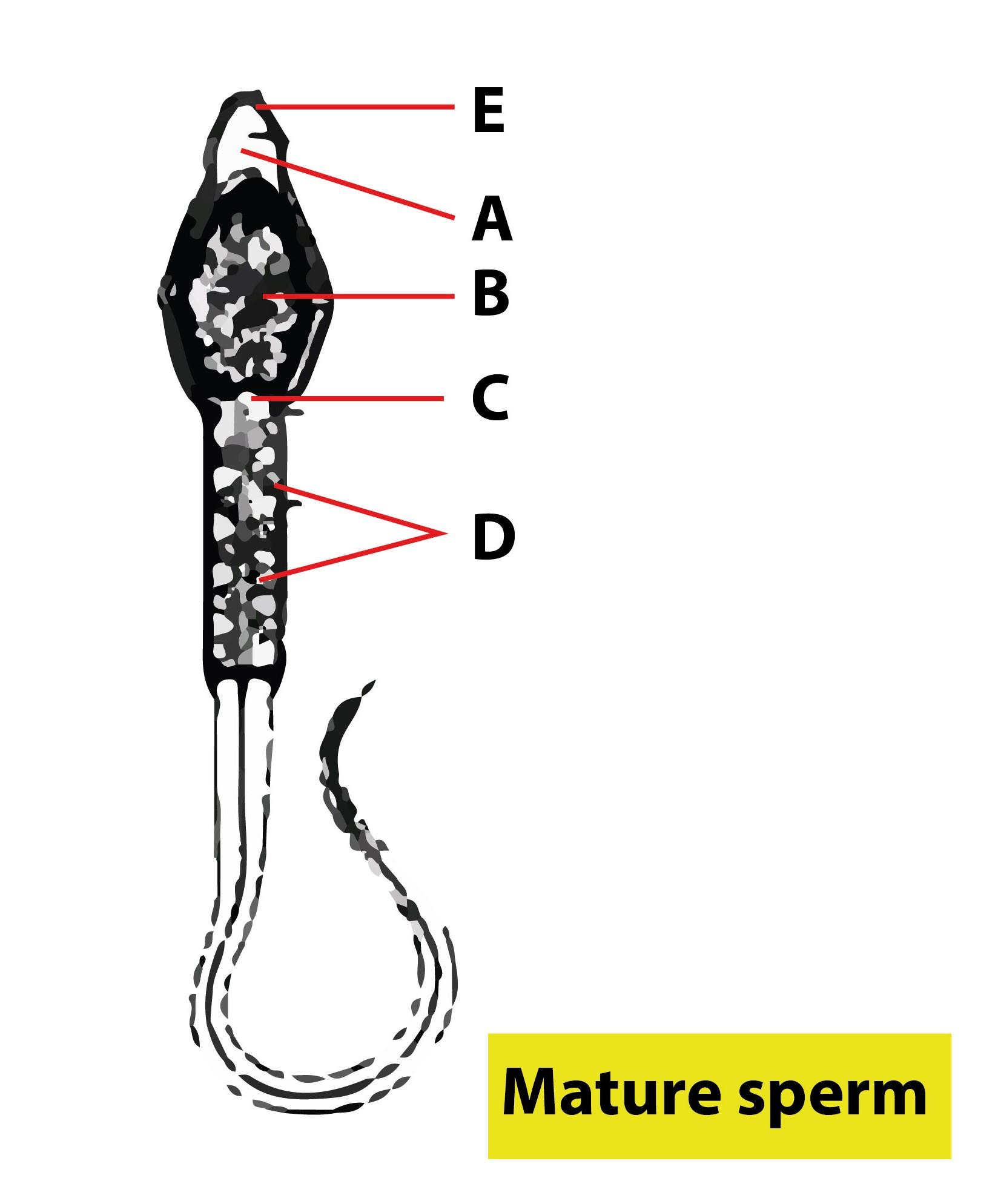
(a) A-Nucleus, B-Tail, C-Mitochondria, D-Acrosome, E-Centriole
(b) A-Acrosome, B-Nucleus, C-Centriole, D-Mitochondria, E-Plasma membrane
(c) A-Nucleus, B-Mitochondria, C-Plasma membrane, D-Centriole, E-Neck
(d) A-Acrosome, B-Centriole, C-Mitochondria, D-Plasma membrane, E-Tail

Answer
554.4k+ views
Hint: Sperm is also known as spermatozoa or male gamete. It carries the haploid genome of the father and travels all the way across the female reproductive structures to reach the ovum and fertilize it at the ampullary region of the fallopian tubes.
Complete Answer:
The structure of a sperm consists of a head, a neck, a middle piece, and a tail. The plasma membrane envelops the entire body of the sperm. The head of the sperm consists of an elongated haploid nucleus and centriole. At its anterior portion, a cap-like structure known as acrosome is present.
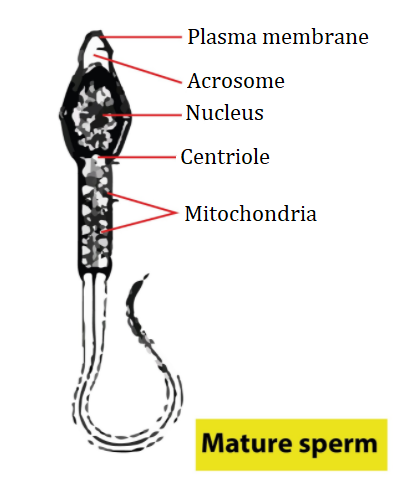
Thus, A-Acrosome: The acrosome is formed by the Golgi body during the process of spermiogenesis and it contains a number of substances in it such as acrosin enzyme, mannose, galactose, etc.
B- Nucleus: Contains the genetic information of the father and it is present inside the head of the sperm.
C- Centriole: Necessary for the division of the zygote which is formed after the fertilization of ovum and sperm.
D- Mitochondria: The mitochondria are present inside the middle piece of the sperm that produce the energy required for the motility of the sperm. The mitochondria also play a role in apoptosis which is also known as cell death.
E- Plasma membrane: It forms a protective covering around the sperm.
So, the correct option is ‘(b) A-Acrosome, B-Nucleus, C-Centriole, D-Mitochondria, E-Plasma membrane’.
Note:
- A human male ejaculates an average of 200-300 million sperms out of which $60\%$ need to be of normal shape and size and $40\%$ need to show vigorous motility for normal fertilization.
- The process by which sperms are formed is known as spermatogenesis.
Complete Answer:
The structure of a sperm consists of a head, a neck, a middle piece, and a tail. The plasma membrane envelops the entire body of the sperm. The head of the sperm consists of an elongated haploid nucleus and centriole. At its anterior portion, a cap-like structure known as acrosome is present.

Thus, A-Acrosome: The acrosome is formed by the Golgi body during the process of spermiogenesis and it contains a number of substances in it such as acrosin enzyme, mannose, galactose, etc.
B- Nucleus: Contains the genetic information of the father and it is present inside the head of the sperm.
C- Centriole: Necessary for the division of the zygote which is formed after the fertilization of ovum and sperm.
D- Mitochondria: The mitochondria are present inside the middle piece of the sperm that produce the energy required for the motility of the sperm. The mitochondria also play a role in apoptosis which is also known as cell death.
E- Plasma membrane: It forms a protective covering around the sperm.
So, the correct option is ‘(b) A-Acrosome, B-Nucleus, C-Centriole, D-Mitochondria, E-Plasma membrane’.
Note:
- A human male ejaculates an average of 200-300 million sperms out of which $60\%$ need to be of normal shape and size and $40\%$ need to show vigorous motility for normal fertilization.
- The process by which sperms are formed is known as spermatogenesis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




