
Identify the structures indicated by the labels (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv). Select the correct option.
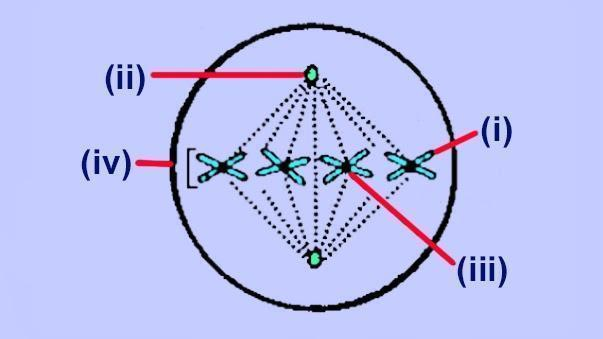
(a) (i)-Chromatid, (ii)-Centriole, (iii)-Centromere, (iv)-Chromosome
(b) (i)-Chromosome, (ii)-Centriole, (iii)-Centromere, (iv)-Chromatid
(c) (i)-Chromatid, (ii)-Centromere, (iii)-Centriole, (iv)-Chromosome
(d) (i)-Chromosome, (ii)-Centromere, (iii)-Centriole, (iv)-Chromatid

Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: In the metaphase stage of the cell cycle, the sister chromatids which are joined at their centres by the centromere, are pulled apart by centrosomes with the help of spindle fibres. The two centrosomes are present as one each on the two opposite poles of the cell.
Complete Answer:
The given picture is of the metaphase stage in cell division. The two sister chromatids (i) which form a chromosome (iv) are joined together by the centromeres i.e. (iii). They are pulled apart from the centre by centrioles i.e. (ii) which are present one on each pole of the cell.
Additional information:
Cells divide for many different reasons such as healing of a wound or simply for growth of the organism. Cell division is of two types: mitosis or equational division and meiosis a reductional division. Both types have four common stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Mitosis is called an equational division due to the reason that the number of chromosomes remains the same in the daughter cells formed. However, in meiosis, the number of chromosomes reduces to half. In order to achieve this, it has two divisions: meiosis 1 in which the chromosome number is halved and meiosis 2 which is similar to mitosis.
So, the correct answer is (i)-Chromatid, (ii)-Centriole, (iii)-Centromere, (iv)-Chromosome.
Note:
Spindle fibres which arise from centrosomes are of two types: kinetochore spindle fibres and non-kinetochore spindle fibres. Kinetochore spindle fibres attach to centromeres and push themselves towards the centrosome. Non-kinetochore fibres do not attach to any chromosomes but to each other only and push against each other. Hence the balance between this pushing and pulling forces drag the chromatids towards the centrosome.
Complete Answer:
The given picture is of the metaphase stage in cell division. The two sister chromatids (i) which form a chromosome (iv) are joined together by the centromeres i.e. (iii). They are pulled apart from the centre by centrioles i.e. (ii) which are present one on each pole of the cell.
Additional information:
Cells divide for many different reasons such as healing of a wound or simply for growth of the organism. Cell division is of two types: mitosis or equational division and meiosis a reductional division. Both types have four common stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Mitosis is called an equational division due to the reason that the number of chromosomes remains the same in the daughter cells formed. However, in meiosis, the number of chromosomes reduces to half. In order to achieve this, it has two divisions: meiosis 1 in which the chromosome number is halved and meiosis 2 which is similar to mitosis.
So, the correct answer is (i)-Chromatid, (ii)-Centriole, (iii)-Centromere, (iv)-Chromosome.
Note:
Spindle fibres which arise from centrosomes are of two types: kinetochore spindle fibres and non-kinetochore spindle fibres. Kinetochore spindle fibres attach to centromeres and push themselves towards the centrosome. Non-kinetochore fibres do not attach to any chromosomes but to each other only and push against each other. Hence the balance between this pushing and pulling forces drag the chromatids towards the centrosome.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




