
How do you identify the vertical and horizontal translations of sine and cosine from a graph and an equation?
Answer
537k+ views
Hint: For the function \[y = f\left( x \right)\], the vertical translation is described by the equation \[y = f\left( x \right) + a\] and horizontal translation is described by the equation \[y = f\left( {x - a} \right)\]. the vertical translation is described by the equation \[y = f\left( x \right) + a\] such that if \[a\] is greater than zero then the shift in the graph is upward from the original and if \[a\] is less than zero then the shift in the graph is downward from the original. the horizontal translation is described by the equation \[y = f\left( {x - a} \right)\] such that if \[a\] is greater than zero then the shift in the graph is toward right from the original and if \[a\] is less than zero then the shift in the graph is toward left from the original.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider the sine function as \[y = \sin x\] and the cosine function as \[y = \cos x\].
It is known that for a function \[y = f\left( x \right)\], the vertical translation is described by the equation \[y = f\left( x \right) + a\] such that if \[a\] is greater than zero then the shift in the graph is upward from the original and if \[a\] is less than zero then the shift in the graph is downward from the original.
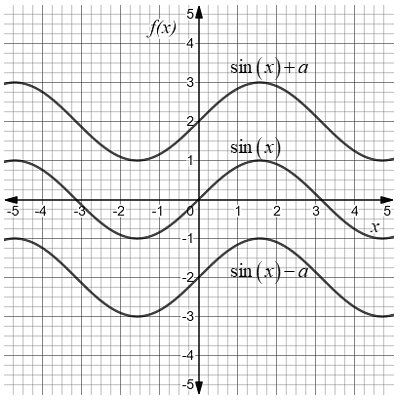
Therefore vertical translation of a sine function is written as \[y = \sin x + a\] and the vertical translation of a cosine function is written as \[y = \cos x + a\]. Where \[a\] cannot be zero.
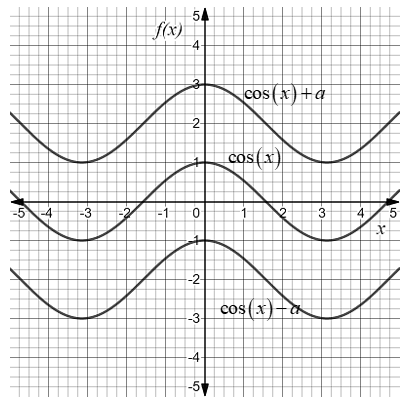
Thus, if we are able to write the sin function in the form \[y = \sin x + a\] and the cosine function in the form \[y = \cos x + a\] where in both cases \[a \ne 0\] then it represents vertical translation in both trigonometric functions from the original.
In the graph, if sine functions or cosine functions wave is not symmetric to \[x\]-axis then there is a vertical shift in the graph from the original.
It is known that for a function \[y = f\left( x \right)\], the horizontal translation is described by the equation \[y = f\left( {x - a} \right)\] such that if \[a\] is greater than zero then the shift in the graph is toward right from the original and if \[a\] is less than zero then the shift in the graph is toward left from the original.
Therefore horizontal translation of a sine function is written as \[y = \sin \left( {x - a} \right)\] and the horizontal translation of a cosine function is written as \[y = \cos \left( {x - a} \right)\]. Where \[a\] cannot be zero.
Thus, if we are able to write the sin function in the form \[y = \sin \left( {x - a} \right)\] and the cosine function in the form \[y = \cos \left( {x - a} \right)\] where in both cases \[a \ne 0\] then it represents horizontal translation in both trigonometric functions from the original.
In the graph, if sine functions or cosine functions wave is not symmetric to \[y\]-axis then there is a horizontal shift in the graph from the original.
Note: For horizontal shift, the function is \[y = f\left( {x - a} \right)\] and for vertical shift, the function is \[y = f\left( x \right) + a\] if the original function is \[y = f\left( x \right)\]. The horizontal translation of a sine function is written as \[y = \sin \left( {x - a} \right)\] and the horizontal translation of a cosine function is written as \[y = \cos \left( {x - a} \right)\]. Where \[a\] cannot be zero. The vertical translation of a sine function is written as \[y = \sin x + a\] and the vertical translation of a cosine function is written as \[y = \cos x + a\]. Where \[a\] cannot be zero.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider the sine function as \[y = \sin x\] and the cosine function as \[y = \cos x\].
It is known that for a function \[y = f\left( x \right)\], the vertical translation is described by the equation \[y = f\left( x \right) + a\] such that if \[a\] is greater than zero then the shift in the graph is upward from the original and if \[a\] is less than zero then the shift in the graph is downward from the original.

Therefore vertical translation of a sine function is written as \[y = \sin x + a\] and the vertical translation of a cosine function is written as \[y = \cos x + a\]. Where \[a\] cannot be zero.

Thus, if we are able to write the sin function in the form \[y = \sin x + a\] and the cosine function in the form \[y = \cos x + a\] where in both cases \[a \ne 0\] then it represents vertical translation in both trigonometric functions from the original.
In the graph, if sine functions or cosine functions wave is not symmetric to \[x\]-axis then there is a vertical shift in the graph from the original.
It is known that for a function \[y = f\left( x \right)\], the horizontal translation is described by the equation \[y = f\left( {x - a} \right)\] such that if \[a\] is greater than zero then the shift in the graph is toward right from the original and if \[a\] is less than zero then the shift in the graph is toward left from the original.
Therefore horizontal translation of a sine function is written as \[y = \sin \left( {x - a} \right)\] and the horizontal translation of a cosine function is written as \[y = \cos \left( {x - a} \right)\]. Where \[a\] cannot be zero.
Thus, if we are able to write the sin function in the form \[y = \sin \left( {x - a} \right)\] and the cosine function in the form \[y = \cos \left( {x - a} \right)\] where in both cases \[a \ne 0\] then it represents horizontal translation in both trigonometric functions from the original.
In the graph, if sine functions or cosine functions wave is not symmetric to \[y\]-axis then there is a horizontal shift in the graph from the original.
Note: For horizontal shift, the function is \[y = f\left( {x - a} \right)\] and for vertical shift, the function is \[y = f\left( x \right) + a\] if the original function is \[y = f\left( x \right)\]. The horizontal translation of a sine function is written as \[y = \sin \left( {x - a} \right)\] and the horizontal translation of a cosine function is written as \[y = \cos \left( {x - a} \right)\]. Where \[a\] cannot be zero. The vertical translation of a sine function is written as \[y = \sin x + a\] and the vertical translation of a cosine function is written as \[y = \cos x + a\]. Where \[a\] cannot be zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




