
If a man of weight $W$ is standing in a lift moving upward with an acceleration a, then apparent weight of the man will be:
A. $W\left( {1 + \dfrac{a}{g}} \right)$
B. $W$
C. $W\left( {1 - \dfrac{a}{g}} \right)$
D. $W\left( {1 - \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{{{g^2}}}} \right)$
Answer
495.3k+ views
Hint: This is the question of Newton’s laws of motion. The pseudo force acts on the person due to motion in a non-inertial frame (Lift). So, the solution is given by conversion of non-inertial frame to inertial frame with the help of pseudo force.
Complete answer:
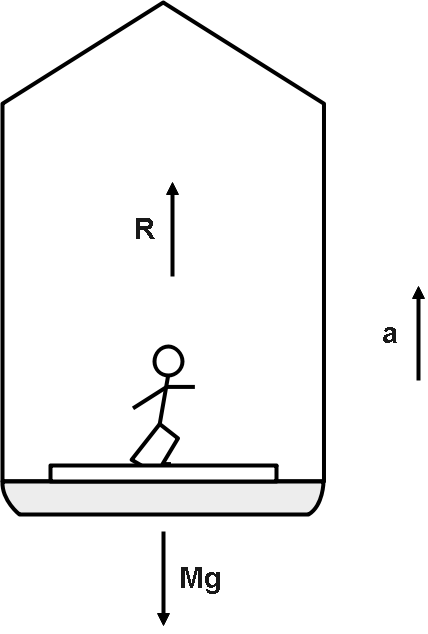
As we know that when lift moves upward or downward, it accelerates or de-accelerates. Which denotes that the lift behaves as a non-inertial frame. So, if we want to observe the phenomena inside the lift, we should convert this non-inertial frame to an inertial frame. Because we can apply Newton’s laws of motion only for inertial frames of reference.
To convert a non-inertial frame to an inertial frame, we use pseudo force on the person.
Apparent weight is the virtual weight of man that makes the sense of heaviness or weightlessness during the motion of lift.
From the figure we can say that as lift is accelerated upwards, we can say that,
Applying Newton's law of motion,
Here, $R$ is the pseudo force acting upwards or Apparent weight.
$
R - mg = ma \\
\Rightarrow R = mg + ma \\
\Rightarrow R = mg\left( {1 + \dfrac{{ma}}{{mg}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow R = mg\left( {1 + \dfrac{a}{g}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow R = W\left( {1 + \dfrac{a}{g}} \right) \\
$
As, $mg = W$
So, apparent weight of the man is $W\left( {1 + \dfrac{a}{g}} \right)$
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
Sometimes we don’t remember that the lift constructs a non-inertial frame and applies Newton’s laws to the question, which will end up wrong in this condition. So, always make sure that the given frame is inertial.
Complete answer:

As we know that when lift moves upward or downward, it accelerates or de-accelerates. Which denotes that the lift behaves as a non-inertial frame. So, if we want to observe the phenomena inside the lift, we should convert this non-inertial frame to an inertial frame. Because we can apply Newton’s laws of motion only for inertial frames of reference.
To convert a non-inertial frame to an inertial frame, we use pseudo force on the person.
Apparent weight is the virtual weight of man that makes the sense of heaviness or weightlessness during the motion of lift.
From the figure we can say that as lift is accelerated upwards, we can say that,
Applying Newton's law of motion,
Here, $R$ is the pseudo force acting upwards or Apparent weight.
$
R - mg = ma \\
\Rightarrow R = mg + ma \\
\Rightarrow R = mg\left( {1 + \dfrac{{ma}}{{mg}}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow R = mg\left( {1 + \dfrac{a}{g}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow R = W\left( {1 + \dfrac{a}{g}} \right) \\
$
As, $mg = W$
So, apparent weight of the man is $W\left( {1 + \dfrac{a}{g}} \right)$
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
Sometimes we don’t remember that the lift constructs a non-inertial frame and applies Newton’s laws to the question, which will end up wrong in this condition. So, always make sure that the given frame is inertial.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




