
If a metal has a bcc structure, then why is its coordination number is 8?
A.Each atom touches four atoms in the layer above it, four in the layer below it and none in its own layer.
B.Ten atom touches four atoms in the layer above it, four in the layer below it and one in its own layer.
C.One atom touches four atoms in the layer above it, four in the layer below them and none of their own layer.
D.Each atom touches eight atoms in the layer above it, eight in the layer below it and none in its own layer.
Answer
522.9k+ views
Hint: In a crystal structure system, the point sets and the corresponding space sets define the lattice system. Coordination number is determined by the share of nearest neighbouring atoms or ions covering the atom or ion.
Complete answer:
To understand and simplify this question, first we need to go through the lattice system.
Basically, there are \[14\] ‘Bravais lattice structures’, and these are grouped into \[7\]main categories or crystal lattices. These \[7\] groups are – cubic, rhombohedral, triclinic, orthorhombic, monoclinic, tetragonal, and hexagonal.
A BCC or Body centered cubic structure is a unit cell having a total of \[2\] atoms – eight-eighths from the corner and one at the centre. As we know that atom at the corner of the cell is surrounded by eight neighbouring atoms, so its share to the unit cell is \[\defrac{1}{8}\] . And since there are 8 corners in the unit cell, this gives us a complete \[1\] atom.
Like, \[8(corners) \times \dfrac{1}{8} + 1(at{\text{ the centre of the cell) = 2 atoms }}\]
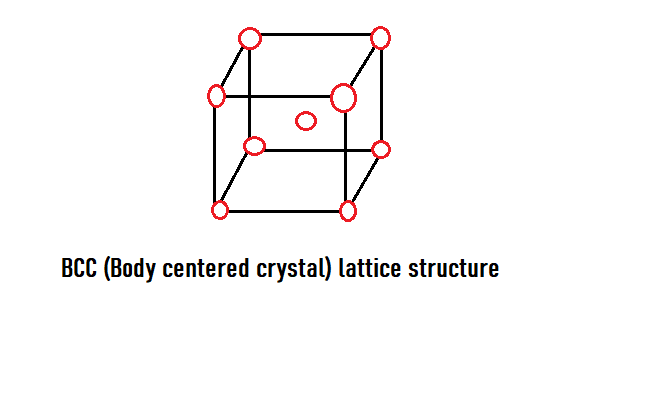
So, now we understand the structure of the bcc unit cell, this will help us find the coordination number easily.
Now we know that the central atom of the bcc unit cell is touched by the atoms of the \[8\] corners.
Thus, the coordination number of the bcc crystal structure is\[8\].
Note:
When we talk about the packing efficiency of the unit cell, it is \[68\% \]in the case of body centered cubic structure. So packing efficiency is the ratio of the space occupied by the spherical atoms to the total volume of the solid.
Complete answer:
To understand and simplify this question, first we need to go through the lattice system.
Basically, there are \[14\] ‘Bravais lattice structures’, and these are grouped into \[7\]main categories or crystal lattices. These \[7\] groups are – cubic, rhombohedral, triclinic, orthorhombic, monoclinic, tetragonal, and hexagonal.
A BCC or Body centered cubic structure is a unit cell having a total of \[2\] atoms – eight-eighths from the corner and one at the centre. As we know that atom at the corner of the cell is surrounded by eight neighbouring atoms, so its share to the unit cell is \[\defrac{1}{8}\] . And since there are 8 corners in the unit cell, this gives us a complete \[1\] atom.
Like, \[8(corners) \times \dfrac{1}{8} + 1(at{\text{ the centre of the cell) = 2 atoms }}\]

So, now we understand the structure of the bcc unit cell, this will help us find the coordination number easily.
Now we know that the central atom of the bcc unit cell is touched by the atoms of the \[8\] corners.
Thus, the coordination number of the bcc crystal structure is\[8\].
Note:
When we talk about the packing efficiency of the unit cell, it is \[68\% \]in the case of body centered cubic structure. So packing efficiency is the ratio of the space occupied by the spherical atoms to the total volume of the solid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




