
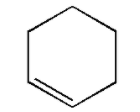
If enthalpy of hydrogenation of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\left( {\text{l}} \right)$ into ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}\left( {\text{l}} \right)$ is $ - 205{\text{ kJ}}$ and resonance energy of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\left( {\text{l}} \right)$ is $ - 152{\text{ kJ/mol}}$ then enthalpy of hydrogenation of the given figure is:
[Assume: $\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{vap}}}}$ of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\left( {\text{l}} \right)$, ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}\left( {\text{l}} \right)$, ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}\left( {\text{l}} \right)$ are all equal]
A. $ + 535.5{\text{ kJ/mol}}$
B. $ - 238{\text{ kJ/mol}}$
C. $ - 357{\text{ kJ/mol}}$
D. $ - 119{\text{ kJ/mol}}$

Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint: We know that benzene $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\left( {\text{l}} \right)} \right)$ contains three double bonds. To break these three bonds and convert benzene $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\left( {\text{l}} \right)} \right)$ to cyclohexane $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}\left( {\text{l}} \right)} \right)$ three molecules of hydrogen $\left( {{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$ will be required. To calculate the enthalpy of hydrogenation of the given compound we must add resonance energy to the total enthalpy of the reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given that the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\left( {\text{l}} \right)} \right)$ is $ - 205{\text{ kJ}}$ and the resonance energy of benzene as $ - 152{\text{ kJ/mol}}$.
To calculate the actual enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene if there is no resonance we add the enthalpy of hydrogenation and the resonance energy. Thus,
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}} = \Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}} + {\text{Resonance energy}}$
Where $\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}}$ is the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene,
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}}$ is the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene.
Substitute $ - 205{\text{ kJ}}$ for the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene, $ - 152{\text{ kJ/mol}}$ for the resonance energy of benzene and solve for the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene. Thus,
\[\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}} = \left( { - 205{\text{ kJ/mol}}} \right) + \left( { - 152{\text{ kJ/mol}}} \right)\]
\[\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}} = - 357{\text{ kJ/mol}}\]
Thus, the actual enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is \[ - 357{\text{ kJ/mol}}\].
The hydrogenation reaction of benzene is as follows:
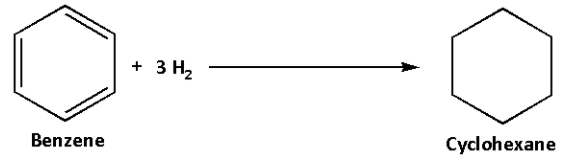
In this reaction, three bonds break and three hydrogen molecules are required.
In the given figure i.e. cyclohexene there is only one double bond. Thus, only one molecule of hydrogen will be required for the breaking of the bond.
Thus, enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene will be,
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}} = \dfrac{{\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}}}}{3}$
Where $\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}}$ is the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene,
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}}$ is the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene.
Substitute \[ - 357{\text{ kJ/mol}}\] for the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene. Thus,
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}} = \dfrac{{ - 357{\text{ kJ/mol}}}}{3}$
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}} = - 119{\text{ kJ/mol}}$
Thus, the enthalpy of hydrogenation of the given figure is $ - 119{\text{ kJ/mol}}$.
Thus, the correct option is (D) $ - 119{\text{ kJ/mol}}$.
Note:
Do not forget to consider the signs of enthalpy of hydrogenation and the resonance energy in the calculation. To break one pi-bond one molecule of hydrogen is required.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given that the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene $\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\left( {\text{l}} \right)} \right)$ is $ - 205{\text{ kJ}}$ and the resonance energy of benzene as $ - 152{\text{ kJ/mol}}$.
To calculate the actual enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene if there is no resonance we add the enthalpy of hydrogenation and the resonance energy. Thus,
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}} = \Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}} + {\text{Resonance energy}}$
Where $\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}}$ is the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene,
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}}$ is the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene.
Substitute $ - 205{\text{ kJ}}$ for the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene, $ - 152{\text{ kJ/mol}}$ for the resonance energy of benzene and solve for the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene. Thus,
\[\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}} = \left( { - 205{\text{ kJ/mol}}} \right) + \left( { - 152{\text{ kJ/mol}}} \right)\]
\[\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}} = - 357{\text{ kJ/mol}}\]
Thus, the actual enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is \[ - 357{\text{ kJ/mol}}\].
The hydrogenation reaction of benzene is as follows:

In this reaction, three bonds break and three hydrogen molecules are required.
In the given figure i.e. cyclohexene there is only one double bond. Thus, only one molecule of hydrogen will be required for the breaking of the bond.
Thus, enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene will be,
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}} = \dfrac{{\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}}}}{3}$
Where $\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}}$ is the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene,
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{benzene}}}}$ is the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene.
Substitute \[ - 357{\text{ kJ/mol}}\] for the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene. Thus,
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}} = \dfrac{{ - 357{\text{ kJ/mol}}}}{3}$
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{{\text{cyclohexene}}}} = - 119{\text{ kJ/mol}}$
Thus, the enthalpy of hydrogenation of the given figure is $ - 119{\text{ kJ/mol}}$.
Thus, the correct option is (D) $ - 119{\text{ kJ/mol}}$.
Note:
Do not forget to consider the signs of enthalpy of hydrogenation and the resonance energy in the calculation. To break one pi-bond one molecule of hydrogen is required.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




