
If the circumradius and inradius of a triangle be 10 and 3 respectively, then the value of a cot A + b cot B + c cot C is equal to 25.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer
611.4k+ views
Hint:First of all, draw the diagram to visualize the question. Now, write a = 2R sin A, b = 2R sin B, c = 2R sin C and also, \[\cot \theta =\dfrac{\cos \theta }{\sin \theta }\] in the given expression. Now, proceed with solving the expression and finally substitute \[4\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}=\dfrac{r}{R}\] to get the desired value.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that the circumradius and inradius of a triangle be 10 and 3 respectively, then we have to verify if a cot A + b cot B + c cot C is equal to 25 or not. Let us see what inradius and circumradius are by the diagram.
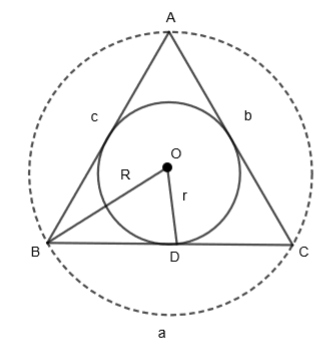
In the above figure, OB is the circumradius (R) of \[\Delta ABC\] and OD is the inradius (r) of \[\Delta ABC\]. Also, a, b and c are the sides of \[\Delta ABC\]. Here, we are given that R = OB = 10. Also, R = OB = OC = OA = 10 as all the radii are of the same length.
We are also given that r = OD = 3. Now, let us consider the expression given in the question.
E = a cot A + b cot B + c cot C
We know that \[\cot \theta =\dfrac{\cos \theta }{\sin \theta }\]. So by using this in the above equation, we get,
\[E=a\dfrac{\cos A}{\sin A}+b\dfrac{\cos B}{\sin B}+c\dfrac{\cos C}{\sin C}\]
Now, we know that, a = 2R sin A, b = 2R sin B, c = 2R sin C. By substituting them in the above equation, we get,
\[E=2R\sin A\dfrac{\cos A}{\sin A}+2R\sin B\dfrac{\cos B}{\sin B}+2R\sin C\dfrac{\cos C}{\sin C}\]
By cancelling the like terms from the above equation, we get,
\[E=2R\cos A+2R\cos B+2R\cos C\]
\[E=2R\left( \cos A+\cos B+\cos C \right)\]
Now, we know that,
\[\cos x+\cos y=2\cos \left( \dfrac{x+y}{2} \right)\cos \left( \dfrac{x-y}{2} \right)\]
Also, \[\cos x=1-2{{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{x}{2}\]. By using this in the above equation, we get,
\[E=2R\left[ 2\cos \left( \dfrac{A+B}{2} \right)\cos \left( \dfrac{A-B}{2} \right)+1-2{{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{C}{2} \right]\]
We know that for any triangle,
\[A+B+C=\pi \]
\[A+B=\pi -C\]
By using this, we get,
\[E=2R\left[ 2\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi -C}{2} \right)\cos \left( \dfrac{A-B}{2} \right)+1-2{{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{C}{2} \right]\]
We know that,
\[\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2}-\theta \right)=\sin \theta \]
So, by using this, we get,
\[E=2R\left[ 2\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\cos \left( \dfrac{A-B}{2} \right)+1-2{{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{C}{2} \right]\]
We can write the above equation as,
\[E=2R\left[ 1+2\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\left( \cos \left( \dfrac{A-B}{2} \right)-\sin \dfrac{C}{2} \right) \right]\]
By replacing C by \[\pi -\left( A+B \right)\] in the second bracket, we get,
\[E=2R\left[ 1+2\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\left( \cos \left( \dfrac{A-B}{2} \right)-\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2}-\left( \dfrac{A+B}{2} \right) \right) \right) \right]\]
We know that \[\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2}-\theta \right)=\cos \theta \]. By using this, we get,
\[E=2R\left[ 1+2\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\left( \cos \left( \dfrac{A-B}{2} \right)-\cos \left( \dfrac{A+B}{2} \right) \right) \right]\]
We know that,
\[\cos x-\cos y=-2\sin \left( \dfrac{x+y}{2} \right)\sin \left( \dfrac{x-y}{2} \right)\]
By using this, we get,
\[E=2R\left[ 1+2\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\left[ -2\sin \left( \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{A-B}{2} \right)+\left( \dfrac{A+B}{2} \right)}{2} \right)\sin \left( \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{A-B}{2} \right)-\left( \dfrac{A+B}{2} \right)}{2} \right) \right] \right]\]
\[E=2R\left[ 1+2\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\left( -2\sin \left( \dfrac{A}{2} \right)\sin \left( \dfrac{-B}{2} \right) \right) \right]\]
We know that \[\sin \left( -\theta \right)=-\sin \theta \]. By using this, we get,
\[E=2R\left[ 1+4\sin \dfrac{C}{2}.\sin \dfrac{A}{2}.\sin \dfrac{B}{2} \right]\]
Now, we know that for any triangle ABC, \[\dfrac{\text{inradius}}{\text{circumradius}}\]=$4\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}$
Or, \[\dfrac{r}{R}=4\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\]
By using this we get,
\[E=2R\left( 1+\dfrac{r}{R} \right)\]
\[E=2R+2r\]
By substituting the values of R = 10 and r = 3. We get,
\[E=2\left( 10 \right)+2\left( 3 \right)\]
\[E=20+6\]
\[E=26\]
Hence, the value of a cot A + b cos B + c cot C = 26.
So, given the value of the expression is false.
Note: In these types of questions, students can directly remember that for a triangle ABC, (cos A + cos B + cos C) is equal to \[1+\dfrac{r}{R}\]. This is a very useful result in the solution of the triangle and would save a lot of steps. In this question, students often make mistakes while adding angles. So, this must be avoided.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that the circumradius and inradius of a triangle be 10 and 3 respectively, then we have to verify if a cot A + b cot B + c cot C is equal to 25 or not. Let us see what inradius and circumradius are by the diagram.

In the above figure, OB is the circumradius (R) of \[\Delta ABC\] and OD is the inradius (r) of \[\Delta ABC\]. Also, a, b and c are the sides of \[\Delta ABC\]. Here, we are given that R = OB = 10. Also, R = OB = OC = OA = 10 as all the radii are of the same length.
We are also given that r = OD = 3. Now, let us consider the expression given in the question.
E = a cot A + b cot B + c cot C
We know that \[\cot \theta =\dfrac{\cos \theta }{\sin \theta }\]. So by using this in the above equation, we get,
\[E=a\dfrac{\cos A}{\sin A}+b\dfrac{\cos B}{\sin B}+c\dfrac{\cos C}{\sin C}\]
Now, we know that, a = 2R sin A, b = 2R sin B, c = 2R sin C. By substituting them in the above equation, we get,
\[E=2R\sin A\dfrac{\cos A}{\sin A}+2R\sin B\dfrac{\cos B}{\sin B}+2R\sin C\dfrac{\cos C}{\sin C}\]
By cancelling the like terms from the above equation, we get,
\[E=2R\cos A+2R\cos B+2R\cos C\]
\[E=2R\left( \cos A+\cos B+\cos C \right)\]
Now, we know that,
\[\cos x+\cos y=2\cos \left( \dfrac{x+y}{2} \right)\cos \left( \dfrac{x-y}{2} \right)\]
Also, \[\cos x=1-2{{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{x}{2}\]. By using this in the above equation, we get,
\[E=2R\left[ 2\cos \left( \dfrac{A+B}{2} \right)\cos \left( \dfrac{A-B}{2} \right)+1-2{{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{C}{2} \right]\]
We know that for any triangle,
\[A+B+C=\pi \]
\[A+B=\pi -C\]
By using this, we get,
\[E=2R\left[ 2\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi -C}{2} \right)\cos \left( \dfrac{A-B}{2} \right)+1-2{{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{C}{2} \right]\]
We know that,
\[\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2}-\theta \right)=\sin \theta \]
So, by using this, we get,
\[E=2R\left[ 2\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\cos \left( \dfrac{A-B}{2} \right)+1-2{{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{C}{2} \right]\]
We can write the above equation as,
\[E=2R\left[ 1+2\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\left( \cos \left( \dfrac{A-B}{2} \right)-\sin \dfrac{C}{2} \right) \right]\]
By replacing C by \[\pi -\left( A+B \right)\] in the second bracket, we get,
\[E=2R\left[ 1+2\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\left( \cos \left( \dfrac{A-B}{2} \right)-\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2}-\left( \dfrac{A+B}{2} \right) \right) \right) \right]\]
We know that \[\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2}-\theta \right)=\cos \theta \]. By using this, we get,
\[E=2R\left[ 1+2\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\left( \cos \left( \dfrac{A-B}{2} \right)-\cos \left( \dfrac{A+B}{2} \right) \right) \right]\]
We know that,
\[\cos x-\cos y=-2\sin \left( \dfrac{x+y}{2} \right)\sin \left( \dfrac{x-y}{2} \right)\]
By using this, we get,
\[E=2R\left[ 1+2\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\left[ -2\sin \left( \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{A-B}{2} \right)+\left( \dfrac{A+B}{2} \right)}{2} \right)\sin \left( \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{A-B}{2} \right)-\left( \dfrac{A+B}{2} \right)}{2} \right) \right] \right]\]
\[E=2R\left[ 1+2\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\left( -2\sin \left( \dfrac{A}{2} \right)\sin \left( \dfrac{-B}{2} \right) \right) \right]\]
We know that \[\sin \left( -\theta \right)=-\sin \theta \]. By using this, we get,
\[E=2R\left[ 1+4\sin \dfrac{C}{2}.\sin \dfrac{A}{2}.\sin \dfrac{B}{2} \right]\]
Now, we know that for any triangle ABC, \[\dfrac{\text{inradius}}{\text{circumradius}}\]=$4\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}$
Or, \[\dfrac{r}{R}=4\sin \dfrac{A}{2}\sin \dfrac{B}{2}\sin \dfrac{C}{2}\]
By using this we get,
\[E=2R\left( 1+\dfrac{r}{R} \right)\]
\[E=2R+2r\]
By substituting the values of R = 10 and r = 3. We get,
\[E=2\left( 10 \right)+2\left( 3 \right)\]
\[E=20+6\]
\[E=26\]
Hence, the value of a cot A + b cos B + c cot C = 26.
So, given the value of the expression is false.
Note: In these types of questions, students can directly remember that for a triangle ABC, (cos A + cos B + cos C) is equal to \[1+\dfrac{r}{R}\]. This is a very useful result in the solution of the triangle and would save a lot of steps. In this question, students often make mistakes while adding angles. So, this must be avoided.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




