
If the $\pi $-backbonding involves the vacant orbital of the central atom, then the bond angle gets widened due to:
(A) The increased bp/bp repulsion for the enhanced bond multiplicity
(B) The decreased of lp/bp repulsion(s)
(C) Both (a) and (b)
(D) None of the above
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: During $\pi $-backbonding, one of the bonds will gain bond multiplicity and hence there will be a bond pair - bond pair repulsion created. Widening of the bond angle occurs when there is a greater repulsion between both the bonds.
Complete Step by Step answer:
- During the $\pi$ backbonding, the lone pair is donated to the vacant $\pi$ orbital of the central atom. So, thereby the bond multiplicity increases and hence there is an increased bond pair-bond pair repulsion.
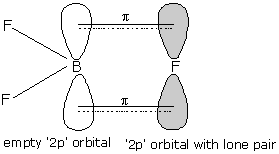
- Above given figure shows the $\pi$ backbonding in the $B{{F}_{3}}$ molecule.
- Here, backbonding is the tendency of halogen atoms to donate electron pairs to boron atoms through $p\pi -p\pi$ bonding.
- Then the electron deficiency of boron decreases and hence, Lewis acidic character also decreases.
- Here, we can see that the bond multiplicity of one of the bonds increases and hence bond pair-bond pair repulsion exists here.
- And hence, the bond angle also increases.
- The decreased bond pair - lone pair repulsion does not contribute to the increment in bond angle.
Hence, the correct answer is Option (A). The increased bp/bp repulsion for the enhanced bond multiplicity.
Additional information:
- Back bonding can be considered to be a type of resonance that is exhibited by several chemical compounds.
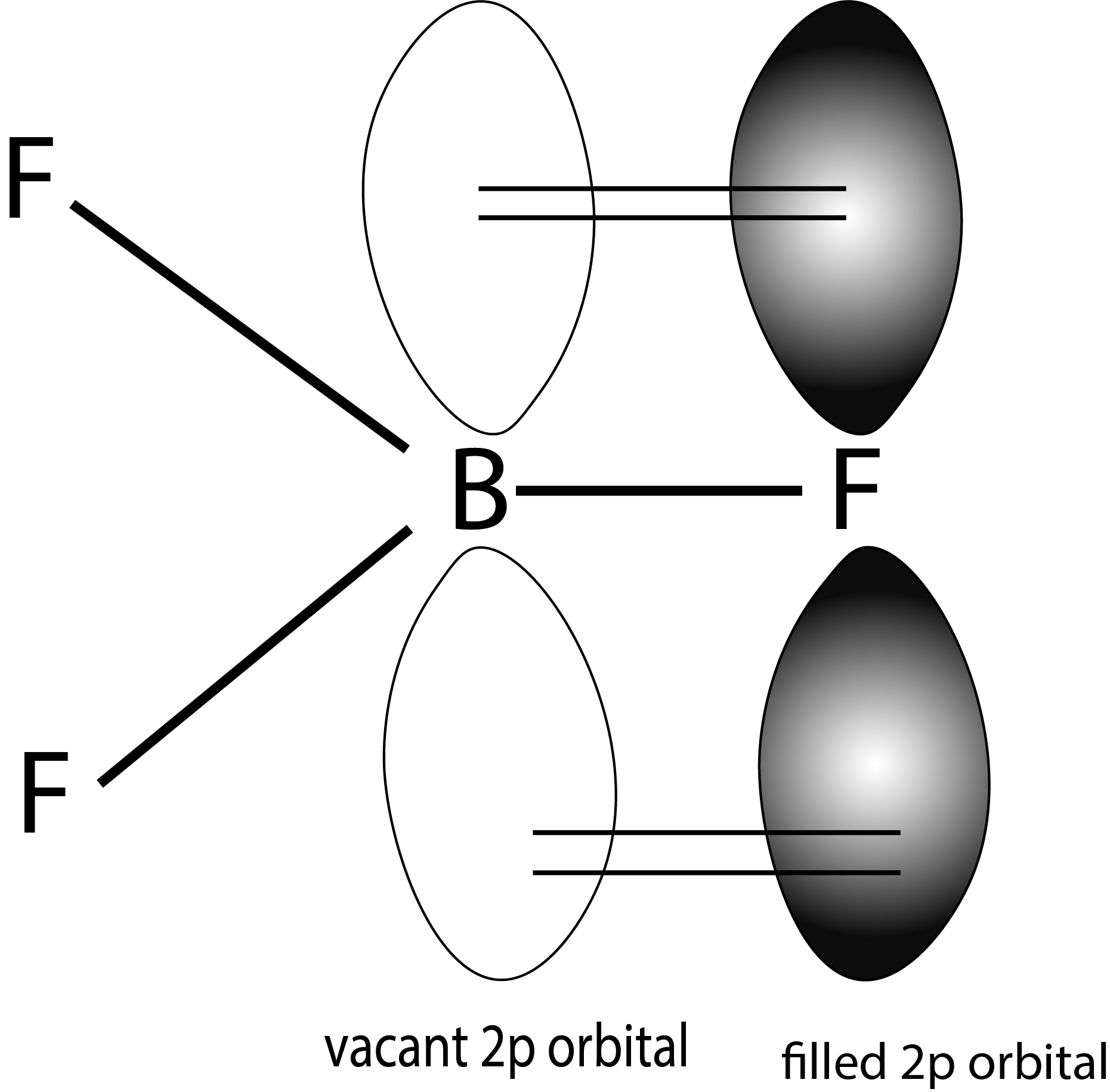

- Above given is the representation of resonance structures of $BF_3$, due to backbonding.
- Back bonding also leads to increased stability to the chemical compounds.
- It also affects the overall dipole moment of the molecule and its hybridization.
- $\pi$ backbonding also known as back donation, is a type of back bonding in which the electrons move from the atomic orbital of a given atom into the ${{\pi }^{*}}$ anti-bonding orbital on a ligand ,which is a pi-acceptor.
- $\pi$ backbonding can be most commonly seen in organometallic chemistry, where transition elements form coordinate covalent bonds with polyatomic ligands .
Note: Increased lone pair-lone pair or bond pair-bond pair repulsion leads to the widening of the bond angle but decrement among these won’t make a widening of bond angle.
Complete Step by Step answer:
- During the $\pi$ backbonding, the lone pair is donated to the vacant $\pi$ orbital of the central atom. So, thereby the bond multiplicity increases and hence there is an increased bond pair-bond pair repulsion.

- Above given figure shows the $\pi$ backbonding in the $B{{F}_{3}}$ molecule.
- Here, backbonding is the tendency of halogen atoms to donate electron pairs to boron atoms through $p\pi -p\pi$ bonding.
- Then the electron deficiency of boron decreases and hence, Lewis acidic character also decreases.
- Here, we can see that the bond multiplicity of one of the bonds increases and hence bond pair-bond pair repulsion exists here.
- And hence, the bond angle also increases.
- The decreased bond pair - lone pair repulsion does not contribute to the increment in bond angle.
Hence, the correct answer is Option (A). The increased bp/bp repulsion for the enhanced bond multiplicity.
Additional information:
- Back bonding can be considered to be a type of resonance that is exhibited by several chemical compounds.


- Above given is the representation of resonance structures of $BF_3$, due to backbonding.
- Back bonding also leads to increased stability to the chemical compounds.
- It also affects the overall dipole moment of the molecule and its hybridization.
- $\pi$ backbonding also known as back donation, is a type of back bonding in which the electrons move from the atomic orbital of a given atom into the ${{\pi }^{*}}$ anti-bonding orbital on a ligand ,which is a pi-acceptor.
- $\pi$ backbonding can be most commonly seen in organometallic chemistry, where transition elements form coordinate covalent bonds with polyatomic ligands .
Note: Increased lone pair-lone pair or bond pair-bond pair repulsion leads to the widening of the bond angle but decrement among these won’t make a widening of bond angle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




