
If the radius of the incircle of a triangle with its sides 5k, 6k, 5k is 6, then k is equal to?
$
(a){\text{ 3}} \\
(b){\text{ 4}} \\
(c){\text{ 5}} \\
(d){\text{ 6}} \\
$
Answer
613.5k+ views
Hint: In this question use the concept that the perpendicular bisector of A, B and C (see figure) of an in circle always passing through the center of the circle. Use the radius given to determine the sides of the triangle. Then formulation of the area of the triangle will help getting the value of k.
Complete step-by-step answer:
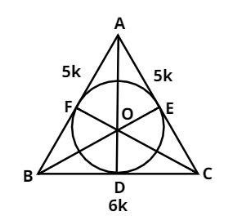
In the circle of a triangle ABC having center O is shown above.
The perpendicular bisector of A, B and C of an in circle always passes through the center of the circle as shown in figure.
$ \Rightarrow BD = \dfrac{{6k}}{2} = 3k$
And OD = OE = OF = 6cm (given).
Now as we know that the area (A) of the triangle is half multiplied by base (b) time’s height (h).
$ \Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times h$ Square units.
So in triangle ABD apply Pythagoras theorem we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {AB} \right)^2} = {\left( {BD} \right)^2} + {\left( {AD} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {5k} \right)^2} = {\left( {3k} \right)^2} + {\left( {AD} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {5k} \right)^2} - {\left( {3k} \right)^2} = {\left( {AD} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {AD} \right)^2} = 25{k^2} - 9{k^2} = 16{k^2} = {\left( {4k} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow AD = 4k$
So the area of the triangle ABC is
$ \Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {BC} \right)\left( {AD} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {6k} \right)\left( {4k} \right) = 12{k^2}$ $cm^2$.
Now the area (A1) of triangle BOC is
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {BC} \right)\left( {OD} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {6k} \right)\left( 6 \right) = 18k$ $cm^2$.
Now the area (A2) of triangle AOB is
$ \Rightarrow {A_2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {AB} \right)\left( {OF} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {5k} \right)\left( 6 \right) = 15k$ $cm^2$.
Now the area (A3) of triangle AOC is
$ \Rightarrow {A_3} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {AC} \right)\left( {OE} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {5k} \right)\left( 6 \right) = 15k$ $cm^2$.
Now area (A) = area (A1 + A2 + A3)
$ \Rightarrow 12{k^2} = 18k + 15k + 15k$
$ \Rightarrow 12{k^2} = 48k$
$ \Rightarrow k = \dfrac{{48}}{{12}} = 4$
So this is the required answer.
Hence option (B) is correct.
Note: An incircle is a circle inscribed in a triangle or other figure such that it touches each side but not actually crosses it. There are certain other properties of incircle to a triangle that helps solving problems of this kind, some of them are, the distance from the incenter to each side are equal to the inscribed circle’s radius, the segment from the incenter to each vertex bisects each angle.
Complete step-by-step answer:

In the circle of a triangle ABC having center O is shown above.
The perpendicular bisector of A, B and C of an in circle always passes through the center of the circle as shown in figure.
$ \Rightarrow BD = \dfrac{{6k}}{2} = 3k$
And OD = OE = OF = 6cm (given).
Now as we know that the area (A) of the triangle is half multiplied by base (b) time’s height (h).
$ \Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times h$ Square units.
So in triangle ABD apply Pythagoras theorem we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {AB} \right)^2} = {\left( {BD} \right)^2} + {\left( {AD} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {5k} \right)^2} = {\left( {3k} \right)^2} + {\left( {AD} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {5k} \right)^2} - {\left( {3k} \right)^2} = {\left( {AD} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {AD} \right)^2} = 25{k^2} - 9{k^2} = 16{k^2} = {\left( {4k} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow AD = 4k$
So the area of the triangle ABC is
$ \Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {BC} \right)\left( {AD} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {6k} \right)\left( {4k} \right) = 12{k^2}$ $cm^2$.
Now the area (A1) of triangle BOC is
$ \Rightarrow {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {BC} \right)\left( {OD} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {6k} \right)\left( 6 \right) = 18k$ $cm^2$.
Now the area (A2) of triangle AOB is
$ \Rightarrow {A_2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {AB} \right)\left( {OF} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {5k} \right)\left( 6 \right) = 15k$ $cm^2$.
Now the area (A3) of triangle AOC is
$ \Rightarrow {A_3} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {AC} \right)\left( {OE} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {5k} \right)\left( 6 \right) = 15k$ $cm^2$.
Now area (A) = area (A1 + A2 + A3)
$ \Rightarrow 12{k^2} = 18k + 15k + 15k$
$ \Rightarrow 12{k^2} = 48k$
$ \Rightarrow k = \dfrac{{48}}{{12}} = 4$
So this is the required answer.
Hence option (B) is correct.
Note: An incircle is a circle inscribed in a triangle or other figure such that it touches each side but not actually crosses it. There are certain other properties of incircle to a triangle that helps solving problems of this kind, some of them are, the distance from the incenter to each side are equal to the inscribed circle’s radius, the segment from the incenter to each vertex bisects each angle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




