
If the segment joining the points $ (a,b) $ , $ (c,d) $ subtends a right angle at the origin, then
(A) $ ac - bd = 0 $
(B) $ ac + bd = 0 $
(C) $ ab + cd = 0 $
(D) $ ab - cd = 0 $
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: Write the coordinate on the Cartesian plane and give them some name. Form a right angle triangle by joining those points with the origin. Then find all the sides of the triangle using distance formula. And then substitute them in the Pythagoras theorem to solve the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Observe the diagram
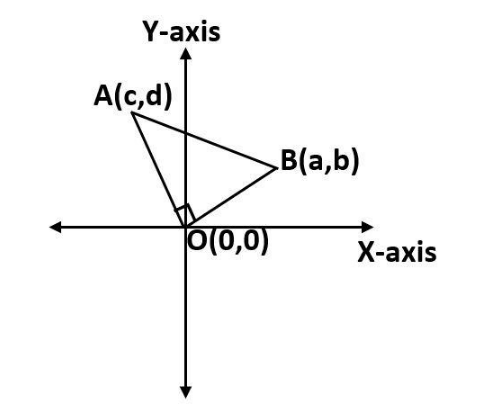
According to the question, $ (a,b),(c,d) $ subtend a right angle at the origin.
Now, observe the diagram and let us assume that A and B are the points which have the coordinates $ (c,d) $ and $ (a,b) $ respectively.
Then using distance formula, we can write
$ O{B^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} $
$ O{A^2} = {c^2} + {d^2} $
$ A{B^2} = {(a - c)^2} + {(b - d)^2} $
And by using Pythagoras theorem, we can write
$ A{B^2} = O{A^2} + O{B^2} $
By substituting the value of in the above equation, we get
$ {(a - c)^2} + {(b - d)^2} = {c^2} + {d^2} + {a^2} + {b^2} $
Now, by using the expansion formula of square, $ {(a - b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab $ , we can expand the above equation as,
$ {a^2} + {c^2} - 2ac + {b^2} + {d^2} - 2bd = {c^2} + {d^2} + {a^2} + {b^2} $
By cancelling the common terms, we get
$ - 2ac - 2bd = 0 $
By taking common terms out, we get
$ - 2(ac + bd) = 0 $
$ \Rightarrow ac + bd = 0 $
Therefore, from the above explanation, the correct answer is, option (B) $ ac + bd = 0 $
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Always draw a rough diagram. It helps to understand what approach should be taken to solve the question. Like in this question, it became easy to observe in the diagram that we can use the Pythagoras theorem as well as distance formula and then compare the two to find the answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Observe the diagram

According to the question, $ (a,b),(c,d) $ subtend a right angle at the origin.
Now, observe the diagram and let us assume that A and B are the points which have the coordinates $ (c,d) $ and $ (a,b) $ respectively.
Then using distance formula, we can write
$ O{B^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} $
$ O{A^2} = {c^2} + {d^2} $
$ A{B^2} = {(a - c)^2} + {(b - d)^2} $
And by using Pythagoras theorem, we can write
$ A{B^2} = O{A^2} + O{B^2} $
By substituting the value of in the above equation, we get
$ {(a - c)^2} + {(b - d)^2} = {c^2} + {d^2} + {a^2} + {b^2} $
Now, by using the expansion formula of square, $ {(a - b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab $ , we can expand the above equation as,
$ {a^2} + {c^2} - 2ac + {b^2} + {d^2} - 2bd = {c^2} + {d^2} + {a^2} + {b^2} $
By cancelling the common terms, we get
$ - 2ac - 2bd = 0 $
By taking common terms out, we get
$ - 2(ac + bd) = 0 $
$ \Rightarrow ac + bd = 0 $
Therefore, from the above explanation, the correct answer is, option (B) $ ac + bd = 0 $
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Always draw a rough diagram. It helps to understand what approach should be taken to solve the question. Like in this question, it became easy to observe in the diagram that we can use the Pythagoras theorem as well as distance formula and then compare the two to find the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




